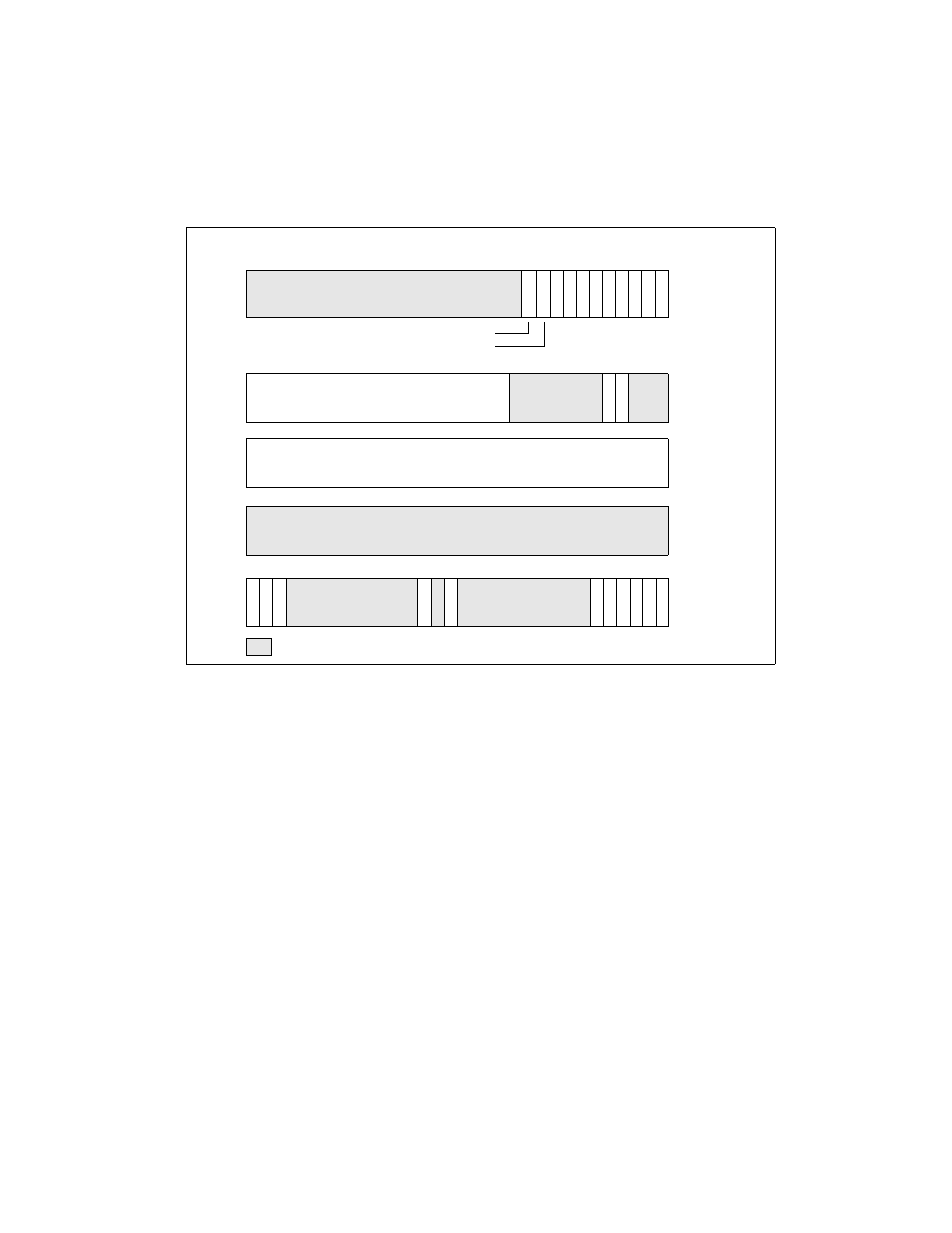
System architecture overview, Figure 2-6. control registers – Intel IA-32 User Manual
Page 66
2-18 Vol. 3A
SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE OVERVIEW
When loading a control register, reserved bits should always be set to the values previously read.
The flags in control registers are:
PG
Paging (bit 31 of CR0) — Enables paging when set; disables paging when clear.
When paging is disabled, all linear addresses are treated as physical addresses. The PG
flag has no effect if the PE flag (bit 0 of register CR0) is not also set; setting the PG
flag when the PE flag is clear causes a general-protection exception (#GP). See also:
Section 3.6, “Paging (Virtual Memory) Overview.”
On IA-32 processors that support Intel
®
EM64T, enabling and disabling IA-32e mode
operation also requires modifying CR0.PG.
CD
Cache Disable (bit 30 of CR0) — When the CD and NW flags are clear, caching of
memory locations for the whole of physical memory in the processor’s internal (and
external) caches is enabled. When the CD flag is set, caching is restricted as described
in Table 10-5. To prevent the processor from accessing and updating its caches, the CD
flag must be set and the caches must be invalidated so that no cache hits can occur.
See also: Section 10.5.3, “Preventing Caching,” and Section 10.5, “Cache Control.”
Figure 2-6. Control Registers
CR1
W
P
A
M
Page-Directory Base
V
M
E
P
S
E
T
S
D
D
E
P
V
I
P
G
E
M
C
E
P
A
E
P
C
E
N
W
P
G
C
D
P
W
T
P
C
D
Page-Fault Linear Address
P
E
E
M
M
P
T
S
N
E
E
T
CR2
CR0
CR4
Reserved
CR3
Reserved (set to 0)
31
29
30
28
19 18 17 16 15
6 5 4 3 2 1 0
31(63)
0
31(63)
0
31(63)
12 11
5 4 3 2
0
31(63)
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
(PDBR)
10
OSFXSR
OSXMMEXCPT
