Figure 3-18 – Intel IA-32 User Manual
Page 112
3-32 Vol. 3A
PROTECTED-MODE MEMORY MANAGEMENT
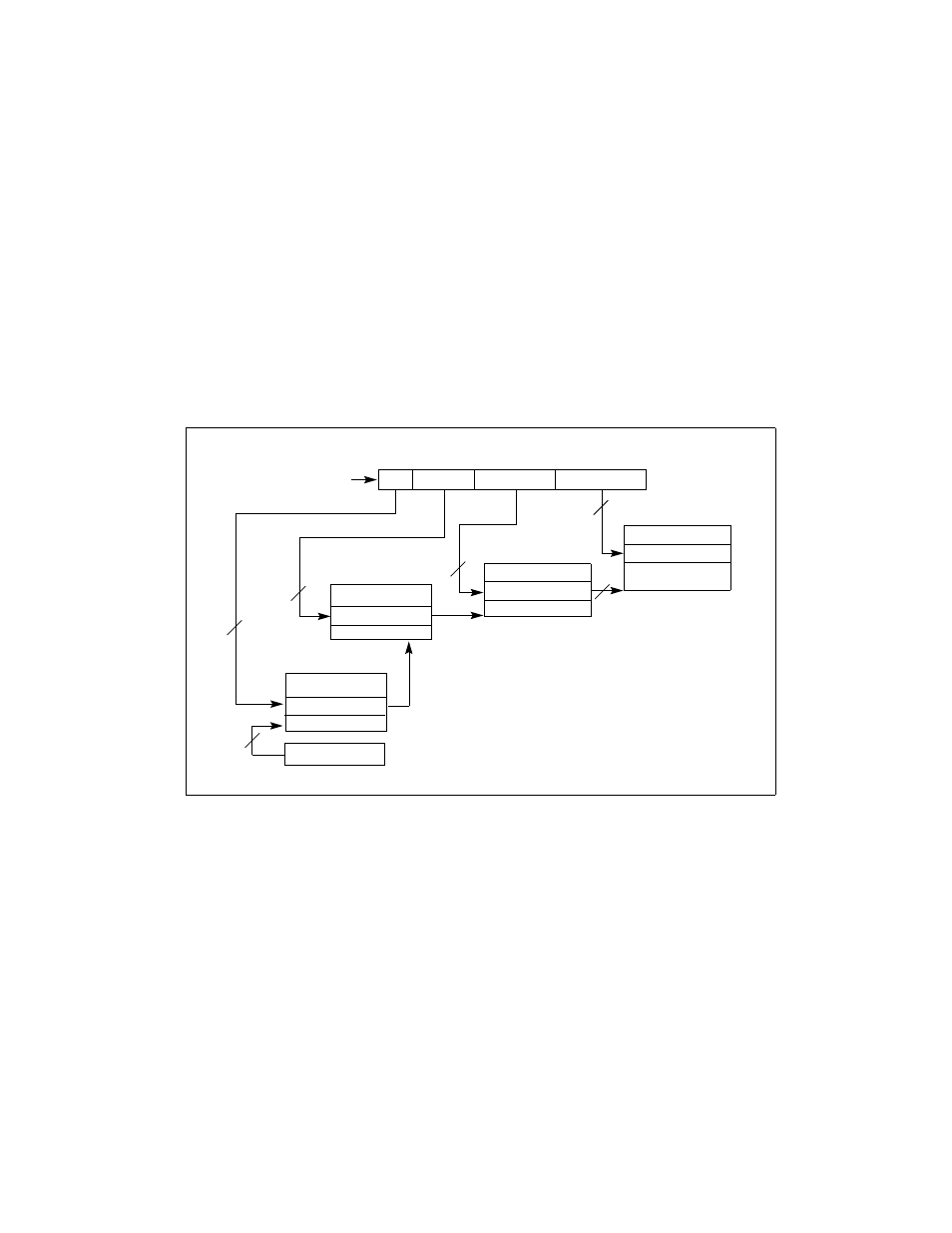
To select the various table entries, the linear address is divided into three sections:
•
Page-directory-pointer-table entry—Bits 30 and 31 provide an offset to one of the 4 entries
in the page-directory-pointer table. The selected entry provides the base physical address
of a page directory.
•
Page-directory entry—Bits 21 through 29 provide an offset to an entry in the selected page
directory. The selected entry provides the base physical address of a page table.
•
Page-table entry—Bits 12 through 20 provide an offset to an entry in the selected page
table. This entry provides the base physical address of a page in physical memory.
•
Page offset—Bits 0 through 11 provide an offset to a physical address in the page.
3.8.3
Linear Address Translation With PAE Enabled (2-MByte
Pages)
Figure 3-19 shows how a page-directory-pointer table and page directories can be used to map
linear addresses to 2-MByte pages when the PAE paging mechanism enabled. This paging
method can be used to map up to 2048 pages (4 page-directory-pointer-table entries times 512
page-directory entries) into a 4-GByte linear address space.
When PAE is enabled, the 2-MByte page size is selected by setting the page size (PS) flag in a
page-directory entry (see Figure 3-14). (As shown in Table 3-3, the PSE flag in control register
Figure 3-18. Linear Address Translation With PAE Enabled (4-KByte Pages)
0
Directory
Table
Offset
Page Directory
Directory Entry
Page Table
Page-Table Entry
4-KByte Page
Physical Address
31
20
11
12
21
Linear Address
Page-Directory-
Dir. Pointer Entry
CR3 (PDPTR)
30 29
Pointer Table
Directory Pointer
4 PDPTE
∗ 512 PDE ∗ 512 PTE = 2
20
Pages
2
9
32*
12
9
*32 bits aligned onto a 32-byte boundary
24
