Rockwell Automation 1783-WAPxxx Stratix 5100 Wireless Access Point User Manual User Manual
Page 306
306
Rockwell Automation Publication 1783-UM006A-EN-P - May 2014
Chapter 9
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol
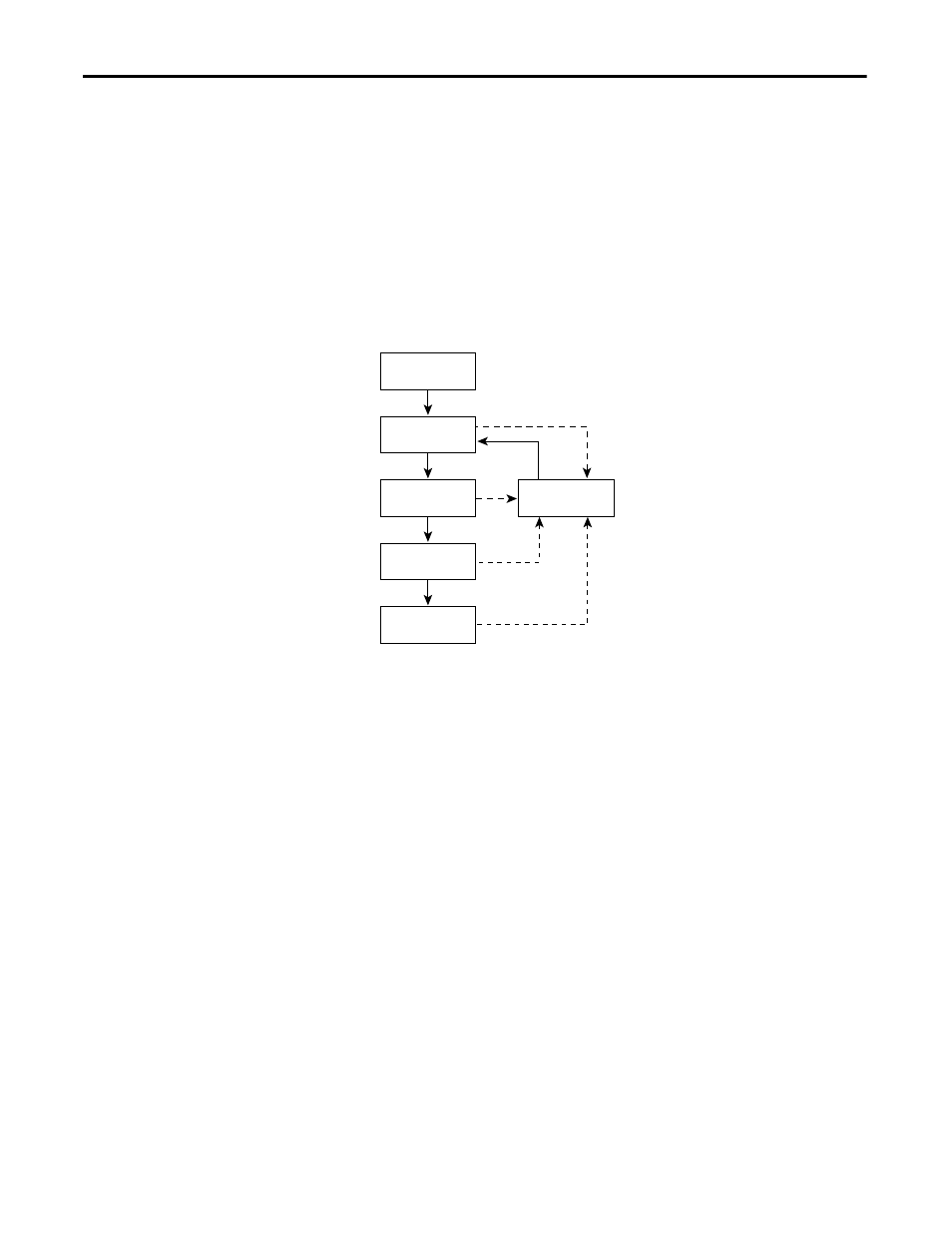
An interface moves through these states:
• From initialization to blocking
• From blocking to listening or to disabled
• From listening to learning or to disabled
• From learning to forwarding or to disabled
• From forwarding to disabled
This figure illustrates how an interface moves through the states.
Figure 90 - Spanning-tree Interface States
When you enable STP on the access point, the Ethernet and radio interfaces go
through the blocking state and the transitory states of listening and learning.
Spanning tree stabilizes each interface at the forwarding or blocking state.
When the spanning-tree algorithm places a Layer 2 interface in the forwarding
state, this process occurs:
1. The interface is in the listening state while spanning tree waits for protocol
information to transition the interface to the blocking state.
2. While spanning tree waits the forward-delay timer to expire, it moves the
interface to the learning state and resets the forward-delay timer.
3. In the learning state, the interface continues to block frame forwarding as
the access point learns end-station location information for the forwarding
database.
4. When the forward-delay timer expires, spanning tree moves the interface
to the forwarding state, where both learning and frame forwarding are
enabled.
Power-on
initialization
Blocking
state
43569
Listening
state
Disabled
state
Learning
state
Forwarding
state
