Relay board, Motherboard, A/d functions – Teledyne 9110EH - Nitrogen Oxides Analyzer User Manual
Page 226: Analog output voltages, Table 11-5, Relay board control devices
Troubleshooting & Repair Model 9110EH Instruction Manual
11.5.8. Relay Board
The relay board circuit can most easily be checked by observing the condition of its status
LEDs as described in Section 11.1.4.3, and the associated output when toggled on and off
through the SIGNAL I/O function in the DIAG menu, see Section 11.1.3.
If the front panel display responds to key presses and D1 on the relay board is not flashing,
then either the wiring between the keyboard and the relay board is bad, or the relay board
itself is bad.
If D1 on the Relay board is flashing and the status indicator for the output in question
(heater, valve, etc.) does not toggle properly using the Signal I/O function, then the
associated device (valve or heater) or its control device (valve driver, heater relay) is
malfunctioning. Several of the control devices are in sockets and can easily be replaced.
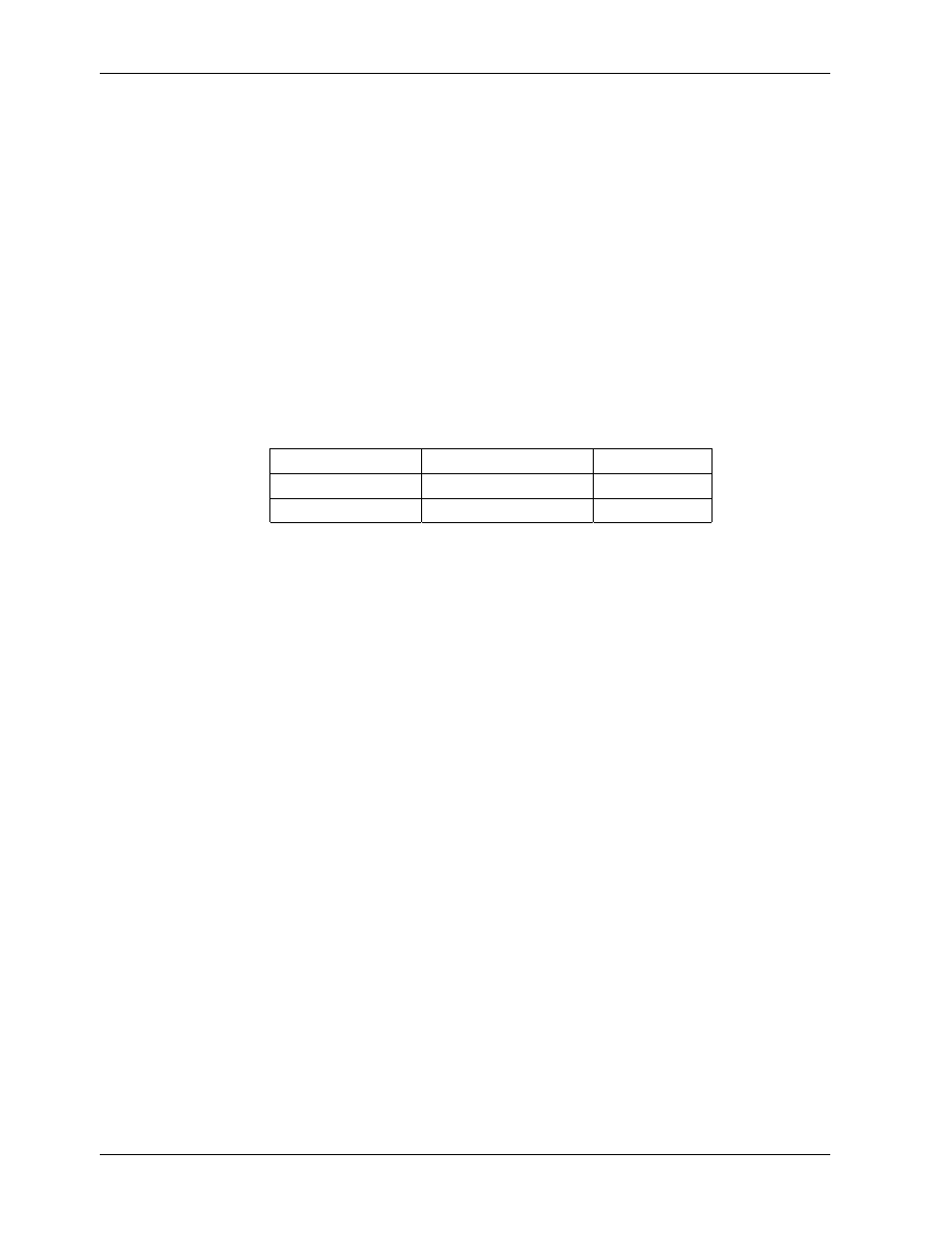
The table below lists the control device associated with a particular function:
Table 11-5: Relay Board Control Devices
Function Control
Device
Socketed
All valves
U5
Yes
All heaters
K1-K5
Yes
11.5.9. Motherboard
11.5.9.1. A/D functions
A basic check of the analog to digital (A/D) converter operation on the motherboard is to
use the Signal I/O function under the DIAG menu. Check the following two A/D reference
voltages and input signals that can be easily measured with a voltmeter.
• Using the Signal I/O function (Section 11.1.3 and Appendix D), view the value of
REF_4096_MV and REF_GND. If both are within 3 mV of their nominal values
(4096 and 0) and are stable to within ±0.5 mV, the basic A/D converter is function-
ing properly. If these values fluctuate largely or are off by more than 3 mV, one or
more of the analog circuits may be overloaded or the motherboard may be faulty.
• Choose one parameter in the Signal I/O function such as SAMPLE_PRESSURE (see
previous section on how to measure it). Compare its actual voltage with the voltage
displayed through the SIGNAL I/O function. If the wiring is intact but there is a
difference of more than ±10 mV between the measured and displayed voltage, the
motherboard may be faulty.
11.5.9.2. Analog Output Voltages
To verify that the analog outputs are working properly, connect a voltmeter to the output in
question and perform an analog output step test as described in Section 6.7.2.
For each of the steps, taking into account any offset that may have been programmed into
the channel (Section 6.7.3), the output should be within 1% of the nominal value listed in
the table below except for the 0% step, which should be within 2-3 mV. If one or more of
the steps is outside of this range, a failure of one or both D/A converters and their
associated circuitry on the motherboard is likely.
212 M9110EH Rev 0
