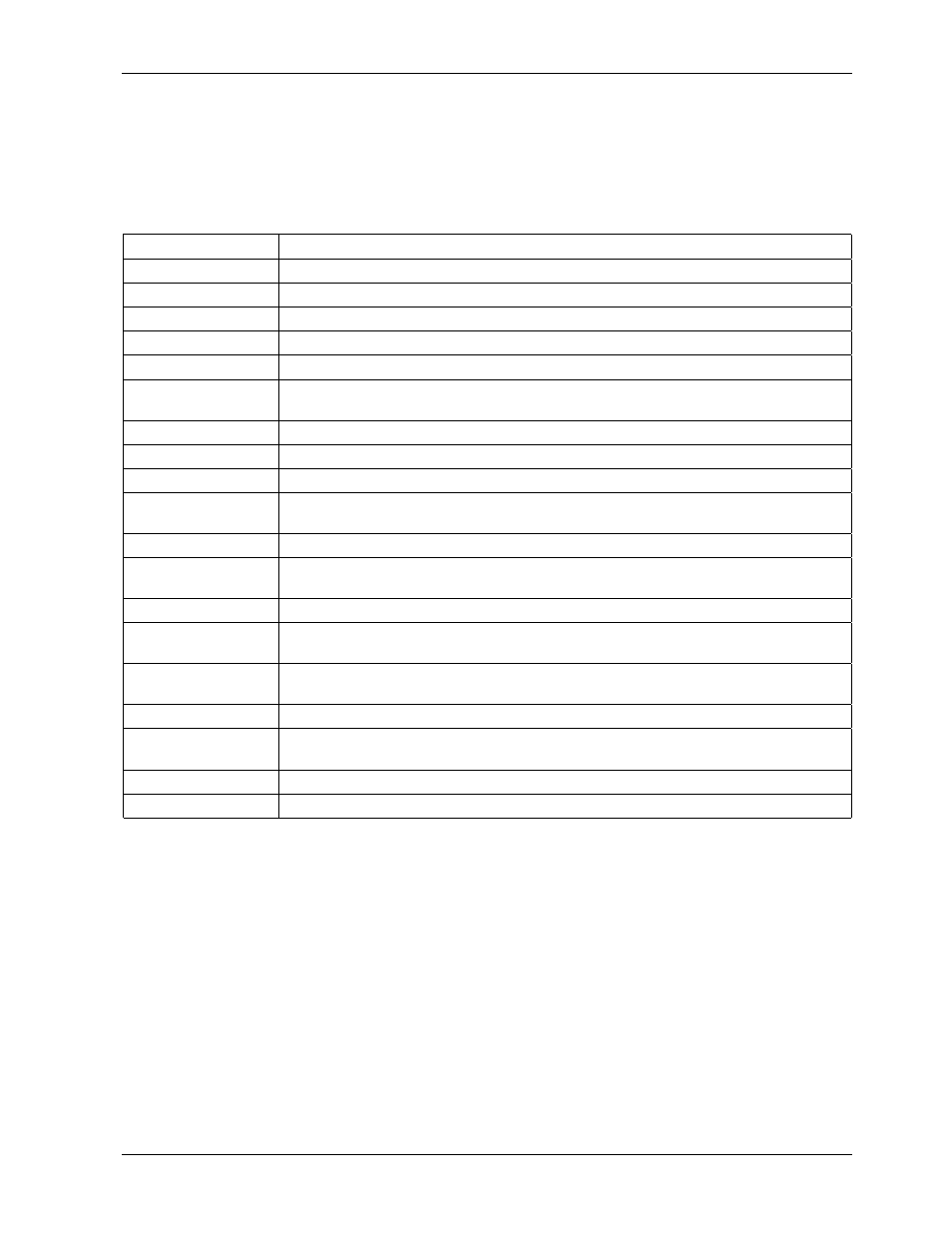
Using the diagnostic signal i/o function, Table 11-1 – Teledyne 9110EH - Nitrogen Oxides Analyzer User Manual
Page 209
Model 9110EH Instruction Manual Troubleshooting & Repair
measurements recorded on the factory data sheet may also indicate a failure or a
maintenance item. A problem report worksheet has been provided in Appendix C
to assist in recording the value of these test functions. The following
table contains some of the more common causes for these values to be out of range.
Table 11-1: Test Functions - Possible Causes for Out-Of-Range Values
Test Function
Indicated Failure(s)
NOx STB
Unstable concentrations; leaks
SAMPLE Fl
Leaks; clogged critical flow orifice
OZONE FL
Leaks; clogged critical flow orifice
PMT
Calibration off; HVPS problem; no flow (leaks)
NORM PMT
AutoZero too high
AZERO
Leaks; malfunctioning NONOx or AutoZero valve; O
3
air filter cartridge
exhausted
HVPS
HVPS broken; calibration off; preamp board circuit problems
RCELL TEMP
Malfunctioning heater; relay board communication (I
2
C bus); relay burnt out
BOX TEMP
Environment out of temperature operating range; broken thermistor
PMT TEMP
TEC cooling circuit broken; relay board communication (I
2
C bus); 12 V power
supply
IZS TEMP (option)
Malfunctioning heater; relay board communication (I
2
C bus); relay burnt out
MOLY TEMP
Malfunctioning heater; disconnected or broken thermocouple; relay board
communication (I
2
Z bus); relay burnt out; incorrect AC voltage configuration
RCEL (pressure)
Leak; malfunctioning valve; malfunctioning pump; clogged flow orifices
SAMP (pressure)
Leak; malfunctioning valve; malfunctioning pump; clogged flow orifices;
sample inlet overpressure;
NOX SLOPE
HVPS out of range; low-level (hardware) calibration needs adjustment; span
gas concentration incorrect; leaks
NOX OFF
Incorrect span gas concentration; low-level calibration off
NO SLOPE
HVPS out of range; low-level calibration off; span gas concentration incorrect;
leaks
NO OFFS
Incorrect span gas concentration; low-level calibration off
Time of Day
Internal clock drifting; move across time zones; daylight savings time?
11.1.3. Using the Diagnostic Signal I/O Function
The signal I/O parameters found under the diagnostics (DIAG) menu combined with a
thorough understanding of the instrument’s theory of operation (Chapter 10) are useful for
troubleshooting in three ways:
• The technician can view the raw, unprocessed signal level of the analyzer’s critical
inputs and outputs.
• All of the components and functions that are normally under instrument control can
be manually changed.
• Analog and digital output signals can be manually controlled.
This allows to systematically observe the effect of these functions on the operation of the
analyzer. Figure 11-2 shows an example of how to use the signal I/O menu to view the raw
M9110EH Rev 0
195
