Chemiluminescence detection, The photo multiplier tube, Figure 10-2 – Teledyne 9110EH - Nitrogen Oxides Analyzer User Manual
Page 175: Conversion principle, Cat o m xno ymo xno
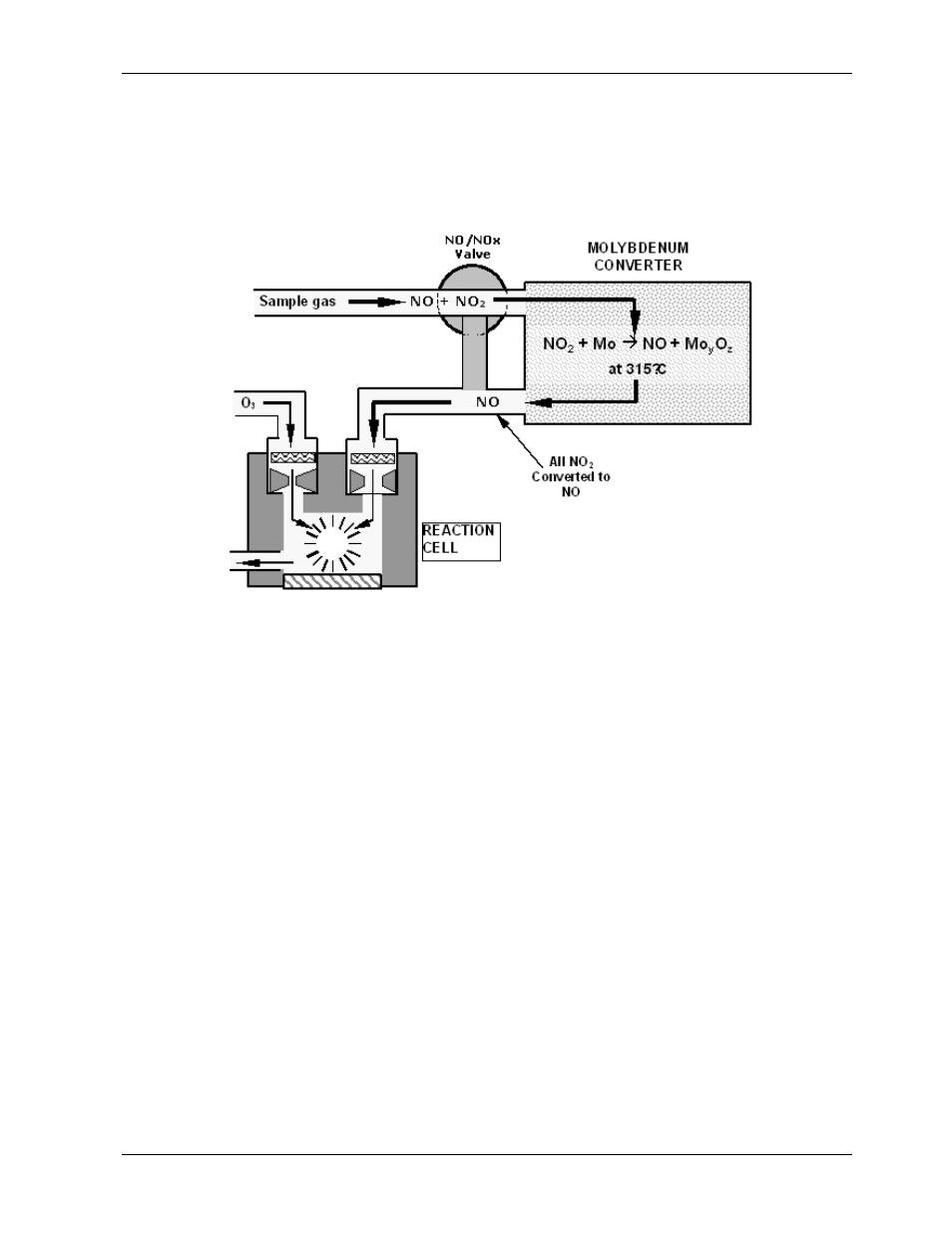
Model 9110EH Instruction Manual Theory of Operation
Eq 10-4
)
315
(
2
C
at
O
M
xNO
yMo
xNO
z
y
°
+
→
+
Once the NO
2
in the sample gas has been converted to NO, it is routed to the reaction cell
where it undergoes the chemiluminescence reaction described in Equations 10-1 and 10-2.
Figure 10-2: NO
2
Conversion Principle
By converting the NO
2
in the sample gas into NO, the analyzer can measure the total NO
X
(NO+NO
2
) content of the sample gas. By switching the NO
2
converter in and out of the
sample gas stream every 6 - 10 seconds, the M9110EH analyzer is able to quasi-continuously
measure both the NO and the total NO
X
content.
The NO
2
concentration, finally, is not measured but calculated by simply subtracting the
known NO content of the sample gas from the known NO
X
content.
10.1.3. Chemiluminescence Detection
10.1.3.1. The Photo Multiplier Tube
The M9110EH uses a photo-multiplier tube (PMT) to detect the amount of light created by the
NO and O
3
reaction in the reaction cell.
A PMT is typically a vacuum tube containing a variety of specially designed electrodes.
Photons enter the PMT and strike a negatively charged photo cathode causing it to emit
electrons. These electrons are accelerated by an applied high voltage and multiply through
a sequence of such acceleration steps (dynodes) until a useable current signal is generated.
This current increases or decreases with the amount of detected light (Section 10.3.2.2 for
more details), is converted to a voltage and amplified by the preamplifier board and then
reported to the motherboard’s analog inputs.
M9110EH Rev 0
161
