Disk on chip, Figure 10-13, M9110eh cpu board annotated – Teledyne 9110EH - Nitrogen Oxides Analyzer User Manual
Page 191
Model 9110EH Instruction Manual Theory of Operation
access (DMA) devices over data busses of either 8-bit or 16-bit bandwidth. The CPU
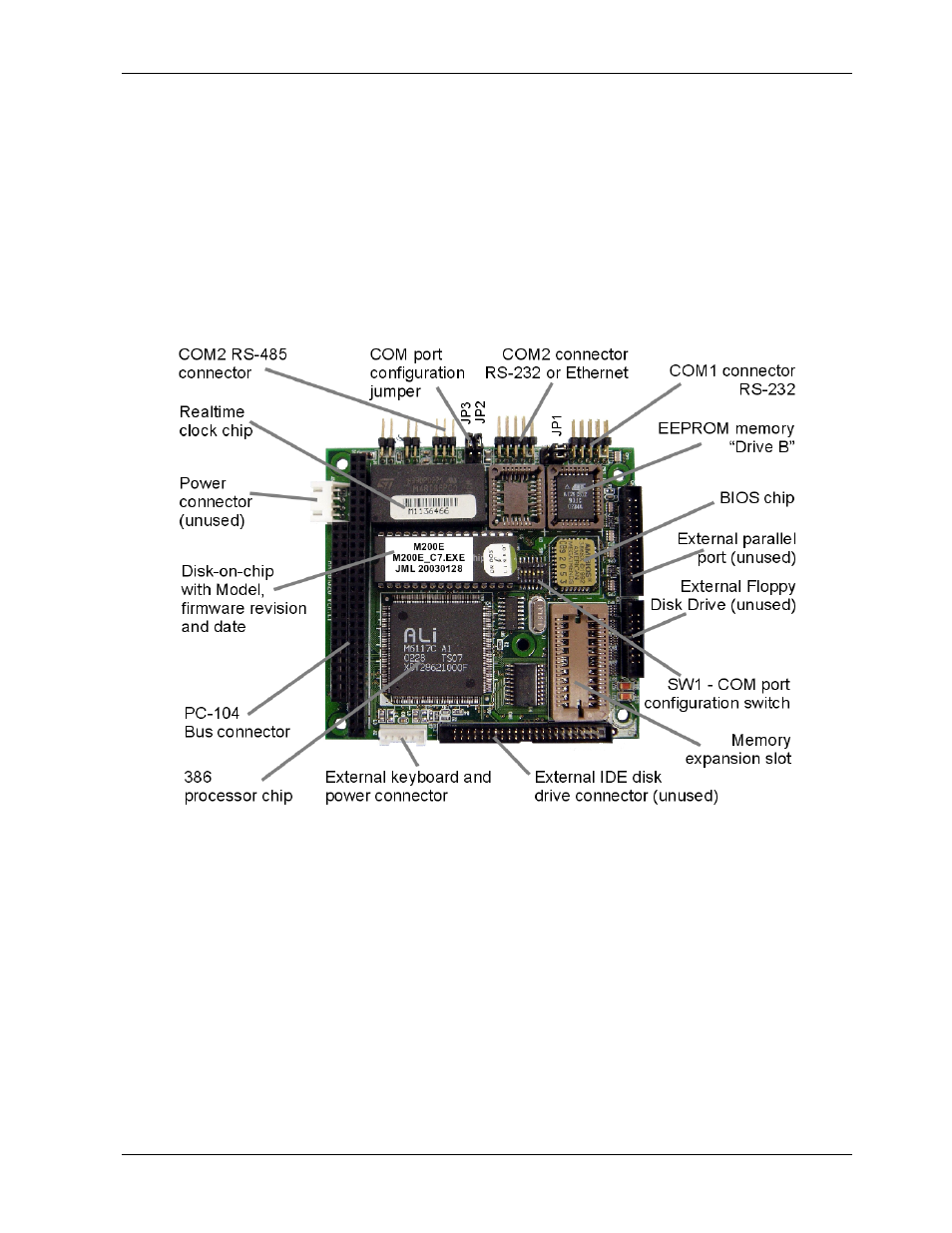
supports both RS-232 and RS-485 serial protocols. Figure 10-13 shows the CPU board.
• The CPU communicates with the user and the outside world in a variety of ways:
• Through the analyzer’s keyboard and vacuum fluorescence display over a clocked,
digital, serial I/O bus using the I
2
C protocol (read I-square-C bus)
• RS-232 and/or RS-485 serial ports (one of which can be connected to an Ethernet
converter)
• Various analog voltage and current outputs
• Several digital I/O channels
Figure 10-13: Model 9110EH CPU Board Annotated
Finally, the CPU issues commands (also over the I2C bus) to a series of relays and switches
located on a separate printed circuit assembly, the relay board (located in the right rear of
the chassis on its own mounting bracket) to control the function of heaters and valves. The
CPU includes two types of non-volatile data storage, one disk-on-chip and one or two flash
chips.
10.3.1.1. Disk On Chip
Technically, the disk-on-chip is an EEPROM, but appears to the CPU as, behaves as, and
performs the same functions in the system as an 8 mb disk drive, internally labeled as DOS
drive C:\. It is used to store the computer’s operating system files, the T-API firmware and
peripheral files, and the operational data generated by the analyzer’s internal data
acquisition system (iDAS - Sections 10.4.5 and 6.11).
M9110EH Rev 0
177
