Grass Valley Kayenne K-Frame v.7.0 User Manual
Page 220
220
KAYENNE K-FRAME — User Manual
Section 6 — Device Control
number of inputs available to a button on a GV Switcher system bus
(
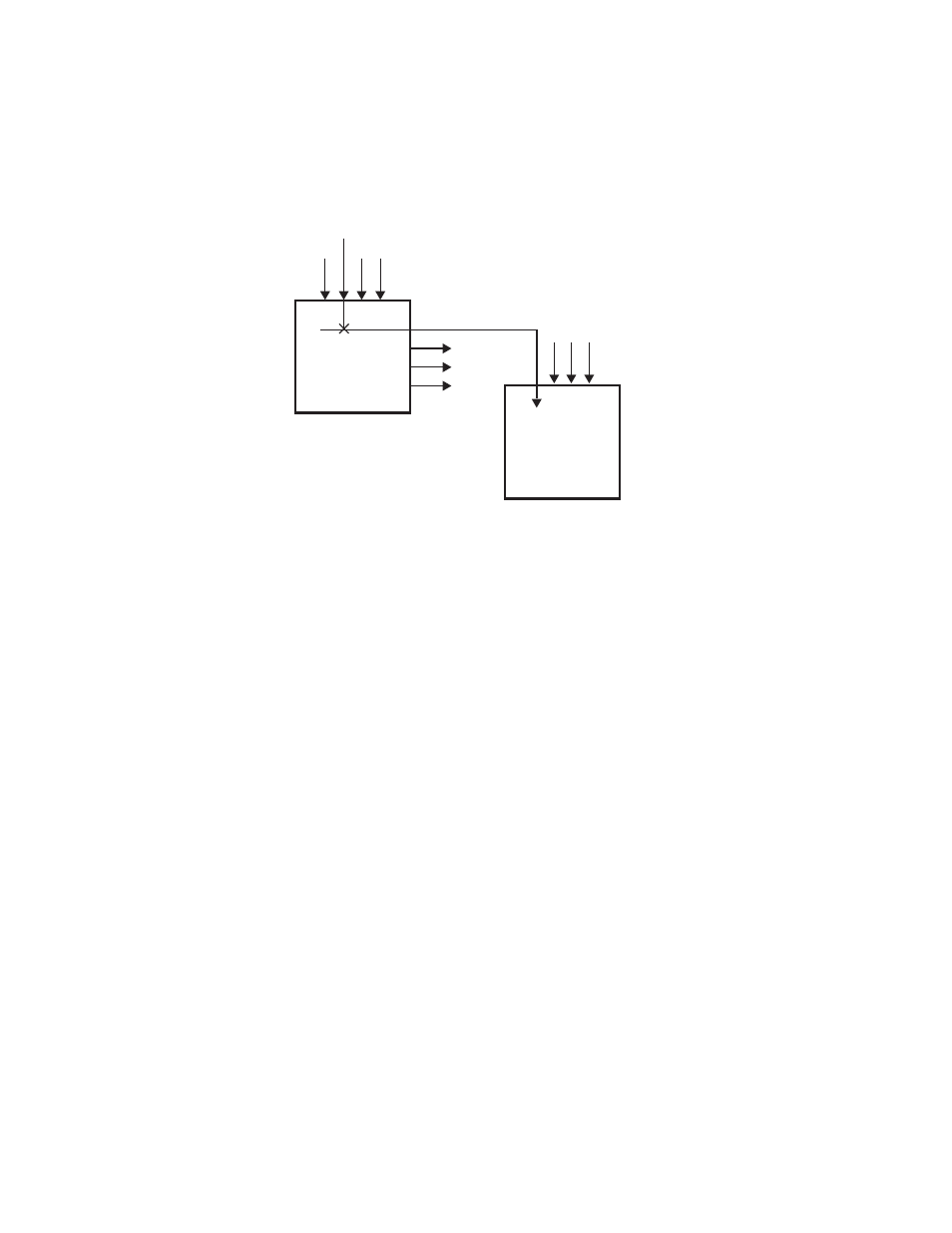
Figure 121. Router Source, Router Destination, and Routed GV Switcher Source
Router signal switching is non-deterministic, as compared to source selec-
tions performed on a production switcher. For this reason, it is better to
choose the desired router source in advance, then switch it on-air using
switcher controls, rather than select a different router source while it is on-
air.
An external router can be configured into levels, to allow the switching of
multiple signals simultaneously. For example, video signals can be orga-
nized on one level, and key signals on another. By specifying both levels
when giving a router take command, both the video and key signals of a
source will be routed to their destinations.
Note
GV Switcher system router take commands are only applied to all router
levels.The external routing system’s destinations must be configured with all
router levels selected.
Router control panels can also protect router destinations from being
changed by other control panels. A protected router destination cannot be
changed by a different control panel, but may be changed by the panel that
set the protection. Protections help prevent inappropriate router source
changes. The GV Switcher system can be considered a type of router
control panel, and so the GV Switcher system can protect router destina-
tions. GV Switcher system router protect commands are applied to all
router levels.
The names of router sources appear on the GV Switcher system source
name displays. These names originate from the router system, and their
text cannot be changed from the GV Switcher system. If a routed source has
no connection to the router, an
X
appears in place of the router source name.
Router
Inputs
Router
Outputs
Router
Source
Router
Destination
8623267_16_
r1
External Router
Switcher
Inputs
Routed
Switcher
Source
Switcher System
