Tension control – Grass Valley Kayenne XL Package v.7.0.4 User Manual
Page 72
70
Kayenne XL Package — User Manual
Section 2 — Concepts
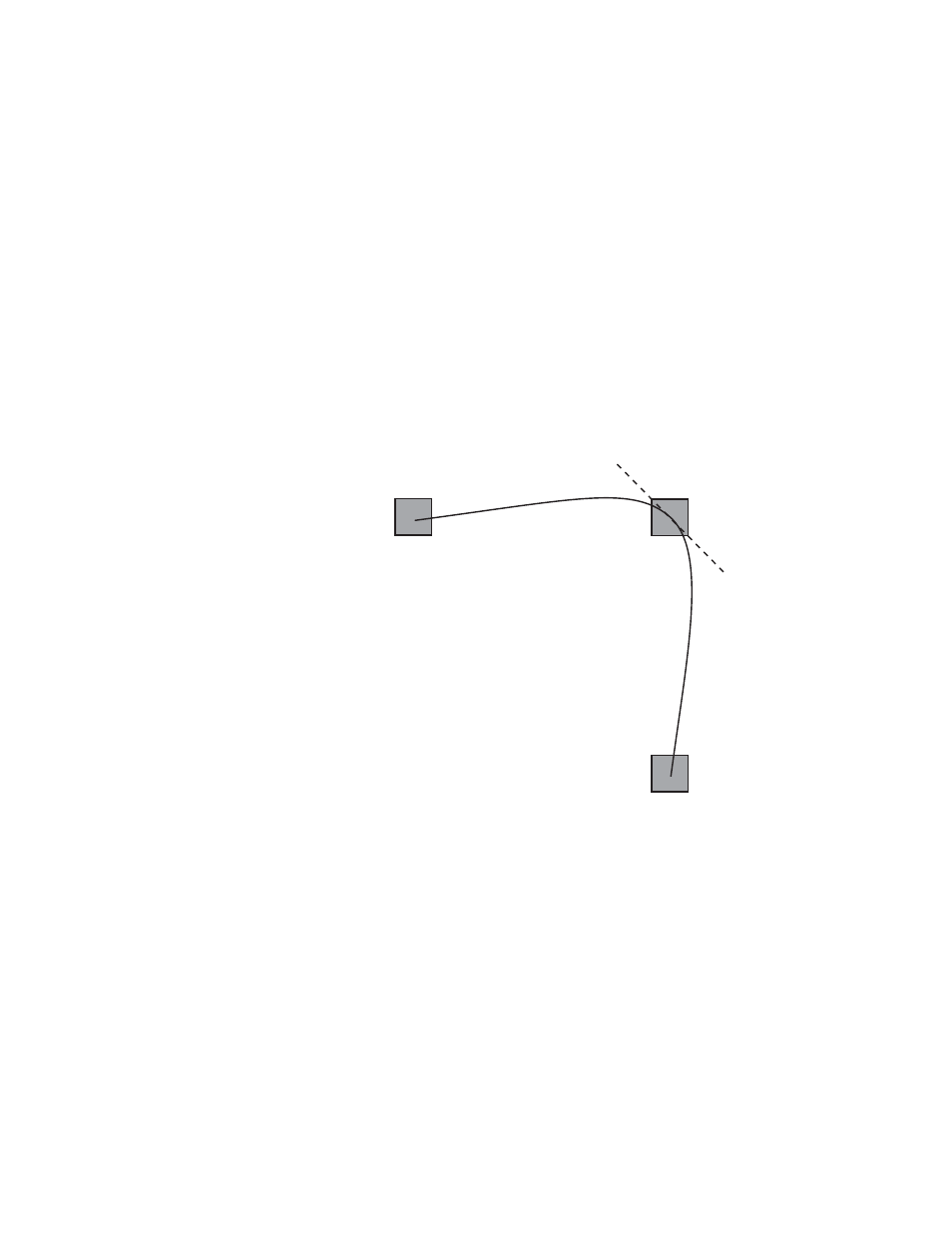
Tension Control
In the example below, the keyframes comprise a right angle, so the TENSION
control operates on a 45° line drawn through the keyframe. This line is
referred to as the Tension Vector and is parallel to a line drawn between
adjacent keyframes (
).
The TENSION soft knob controls the length of the tension vector. The length
of the tension vector is inversely proportional to its parameter value. For
example, at a Tension setting of 0 (zero), this imaginary line extends an
equal distance into and out of the keyframe, and the path through the
middle keyframe is curved. The unmodified KF2 is said to have a correc-
tion value of 0.0.
Figure 36. Tension Control Setting Zero
In the example below, the TENSION control is increased to 1.0, so that the
Tension vector is shortened to non-existence through KF2 (
). The
path enters and leaves the middle keyframe in a straight line as it takes on
an S-Linear motion; decelerating as it enters the middle keyframe and
accelerating as it leaves.
Tension = 0.0
KF1
KF2
KF3
Tension
Vector
0721_06_47_r0
