3 comm test, Comm test -15 – Campbell Scientific LoggerNet Datalogger Support Software User Manual
Page 205
Section 6. Network Status and Resolving Communication Problems
The following settings are used to save the logs to disk as well as to control the
number and size of the log files.
To Disk – Selecting this check box enables saving the associated logs to files
on the server computer hard disk.
File Count – This setting determines the number of log files to be saved to
disk for this type of log. The server will store up to the number specified
before overwriting the oldest log.
File Size – This setting determines how big the log file is allowed to grow
before being saved to an archived file. The $ sign identifies the active file.
Once a file reaches the specified File Size, it is saved to disk with a sequential
number beginning with 0 (e.g. tran0.log, tran1.log, tran2.log…).
All of the log files in your log file directory can be deleted by selecting
File |
Delete All Log Files from the LogTool menu. All of the log files can be zipped
by selecting
File | Zip All Log Files. (When working with a Campbell
Scientific applications engineer to resolve a problem, you may be asked to use
these options in order to delete the current log files, reproduce the problem,
then zip the new log files and send them to the applications engineer for
analysis.)
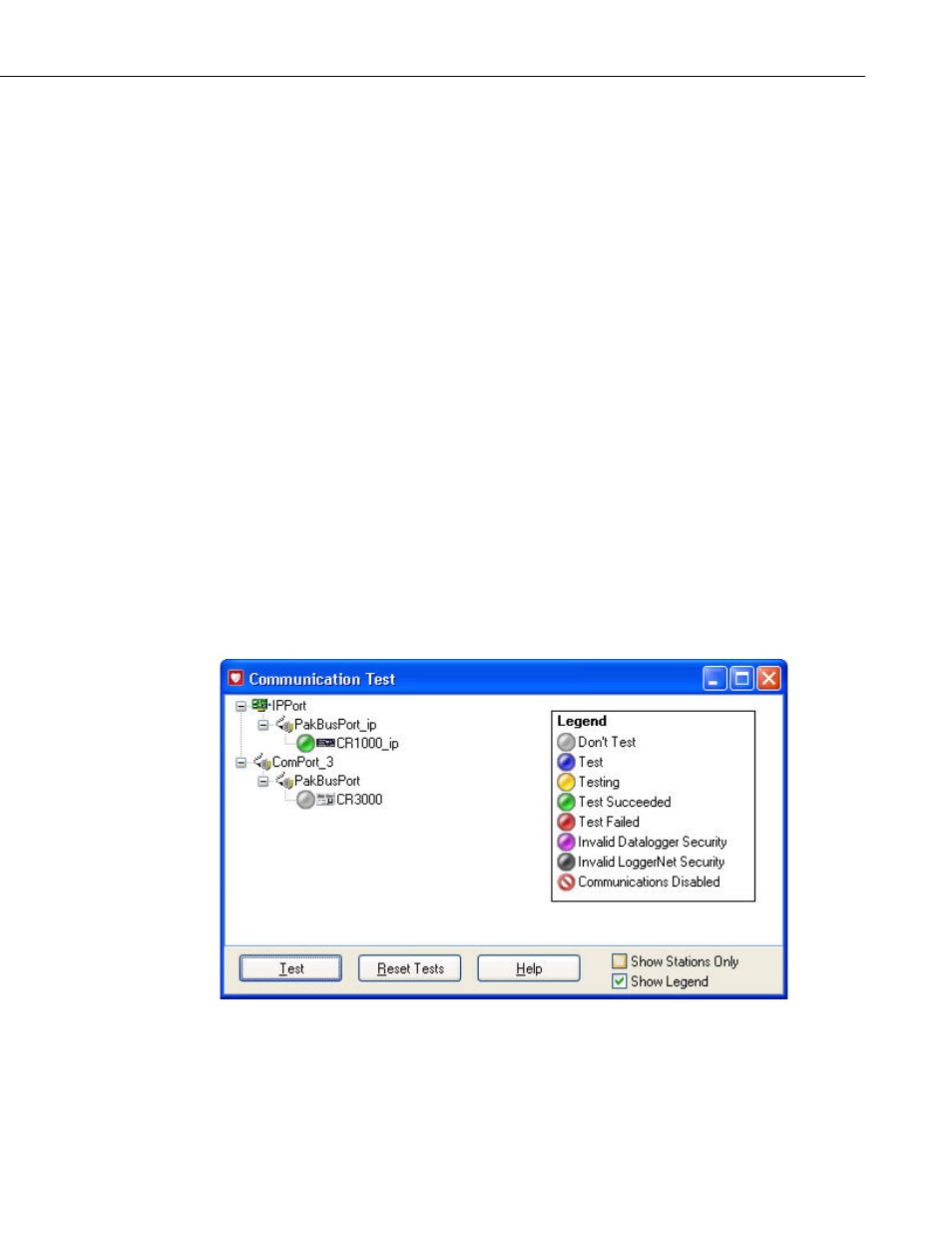
6.3 Comm Test
The Comm Test tool can be launched from the Status Monitor or the
Troubleshooter. It allows you to test the communication links to the datalogger
stations. When Comm Test is launched, you will see a window similar to the
one below with all of your devices in the network map listed.
The color of the circle to the left of each datalogger station indicates the quality
of communication. The legend displayed on the right side of the window
provides a key to the color codes. The legend can be removed from the
window by clearing the Show Legend check box.
6-15
