Rainbow Electronics W90P710CDG User Manual
Page 337
W90P710CD/W90P710CDG
Publication Release Date: September 19, 2006
- 337 -
Revision B2
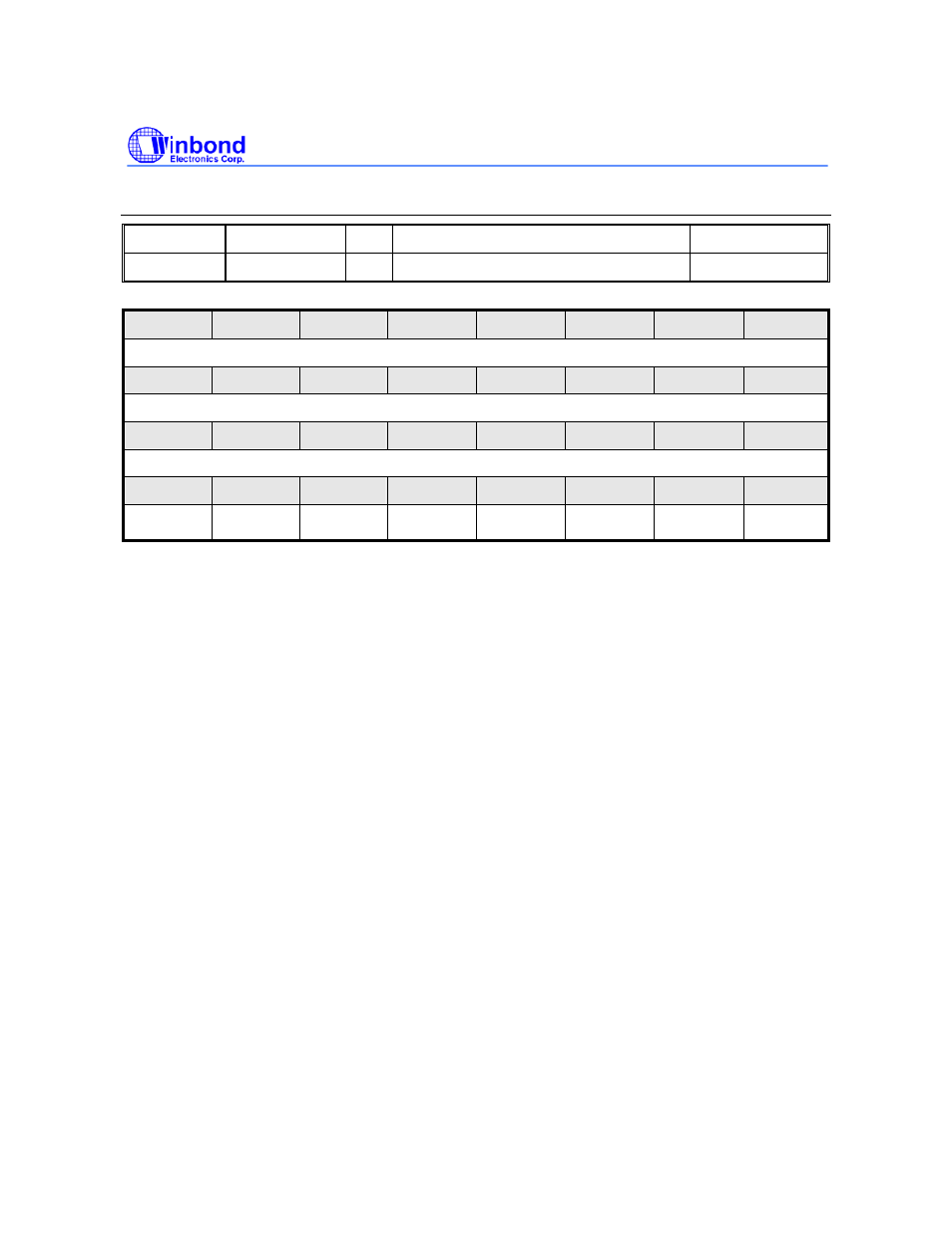
UART3 Modem Status Register (UART3_MSR)
REGISTER ADDRESS R/W
DESCRIPTION
RESET
VALUE
UART3_MSR
0xFFF8_0318
R
UART 3 Modem Status Register
0x0000_0000
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
Reserved
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
Reserved
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
Reserved
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Reserved Reserved
DSR#
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
DDSR
Reserved
6.12.5 General UART Controller
The Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART) performs a serial-to-parallel
conversion on data characters received from the peripheral such as MODEM, and a parallel-to-serial
conversion on data characters received from the CPU. There are five types of interrupts, i.e., line
status interrupt, transmitter FIFO empty interrupt, receiver threshold level reaching interrupt,
time out interrupt, and MODEM status interrupt. One 16-byte transmitter FIFO (TX_FIFO) and one
16-byte (plus 3-bit of error data per byte) receiver FIFO (RX_FIFO) has been built in to reduce the
number of interrupts presented to the CPU. The CPU can completely read the status of the UART at
any time during the operation. The reported status information includes the type and condition of the
transfer operations being performed by the UART, as well as any error conditions (parity, overrun,
framing, or break interrupt) found. The UART includes a programmable baud rate generator that is
capable of dividing crystal clock input by divisors to produce the clock that transmitter and receiver
needed. The equation is
BaudOut = crystal clock / 16 * [Divisor + 2].
The UART includes the following features:
y
Transmitter and receiver are buffered with a 16-byte FIFO each to reduce the number of
interrupts presented to the CPU.
y
Subset of MODEM control functions (DSR, DTR, by IP selection)
y
Fully programmable serial-interface characteristics:
--
5-, 6-, 7-, or 8-bit character
--
Even, odd, or no-parity bit generation and detection
--
1-, 1&1/2, or 2-stop bit generation
--
Baud rate generation
