Obtain qos measurement tools, Measure end-to-end network delay, Figure 30 qos level with g.723 codec – Nortel Networks NN43001-563 User Manual
Page 144: Figure 30 "qos level
144
ITG engineering guidelines
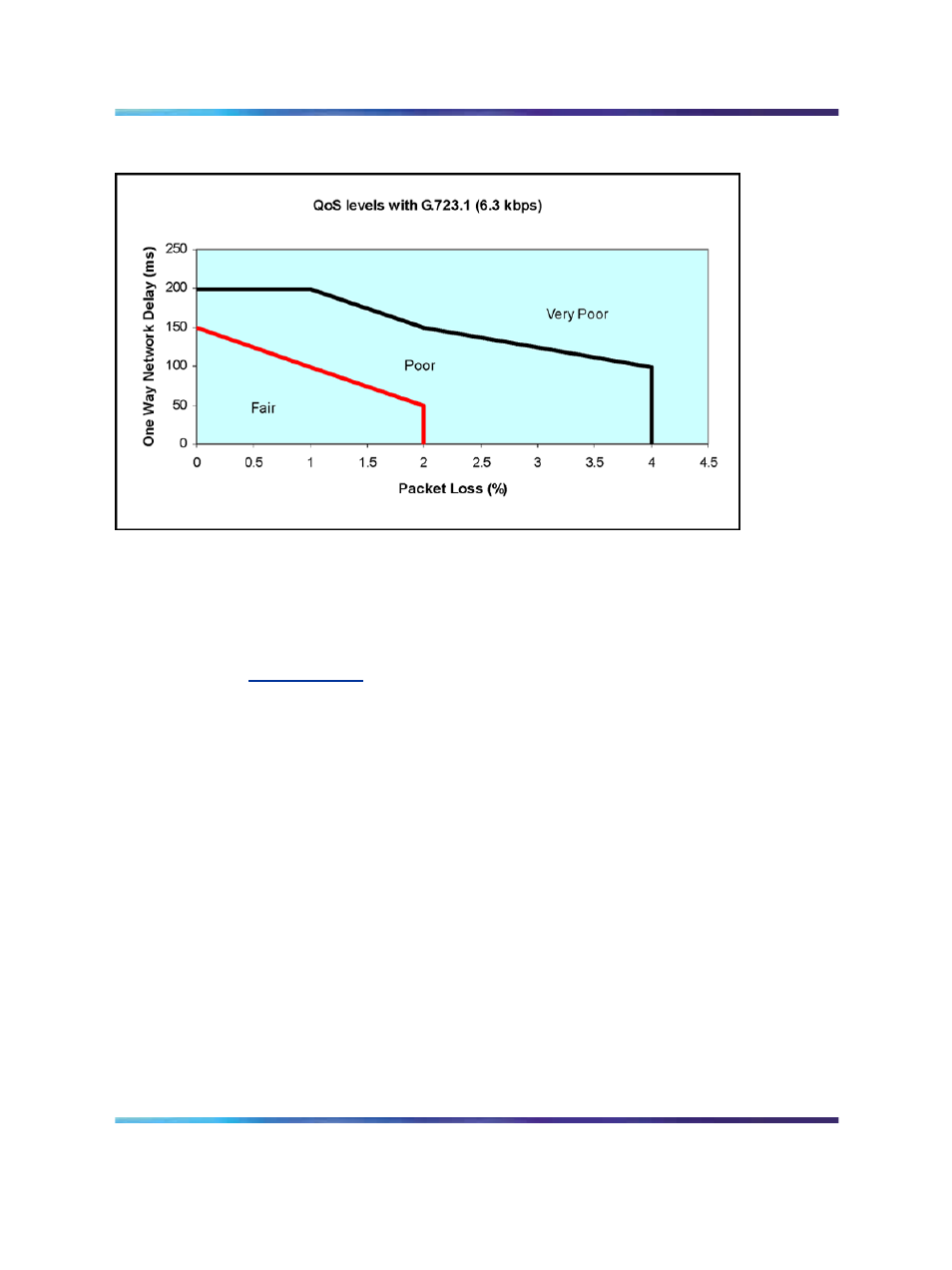
Figure 30
QoS level with G.723 codec
Obtain QoS measurement tools
PING and Traceroute are standard IP tools that are usually included with
a network host’s TCP/IP stack. A survey of QoS measurement tools and
packages, including commercial ones, can be found in the home page
of the Cooperative Association for Internet Data Analysis (CAIDA) at
These include delay monitoring tools that include features
like timestamping, plotting, and computation of standard deviation.
Measure end-to-end network delay
The basic tool used in IP networks to measure end-to-end network delay is
the
PING
program.
PING
takes a delay sample by sending an ICMP packet
from the host of the
PING
program to a destination server. PING then waits
for the packet to make a round trip. A sample of PING is as follows:
Richardson3% PING -s santa_clara_itg4 60
PING santa_clara4 (10.3.2.7):
60 data bytes
68 bytes from (10.3.2.7):
icmp_seq=0 ttl=225
time=97ms
68 bytes from (10.3.2.7):
icmp_seq=0 ttl=225
time=100ms
68 bytes from (10.3.2.7):
icmp_seq=0 ttl=225
time=102ms
68 bytes from (10.3.2.7):
icmp_seq=0 ttl=225
time=97ms
68 bytes from (10.3.2.7):
icmp_seq=0 ttl=225
time=95ms
68 bytes from (10.3.2.7):
icmp_seq=0 ttl=225
time=94ms
Nortel Communication Server 1000
IP Trunk Fundamentals
NN43001-563
01.01
Standard
Release 5.0
30 May 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks
.
