Nortel Networks NN43001-563 User Manual
Page 121
Factors that effect the real-time capacity
121
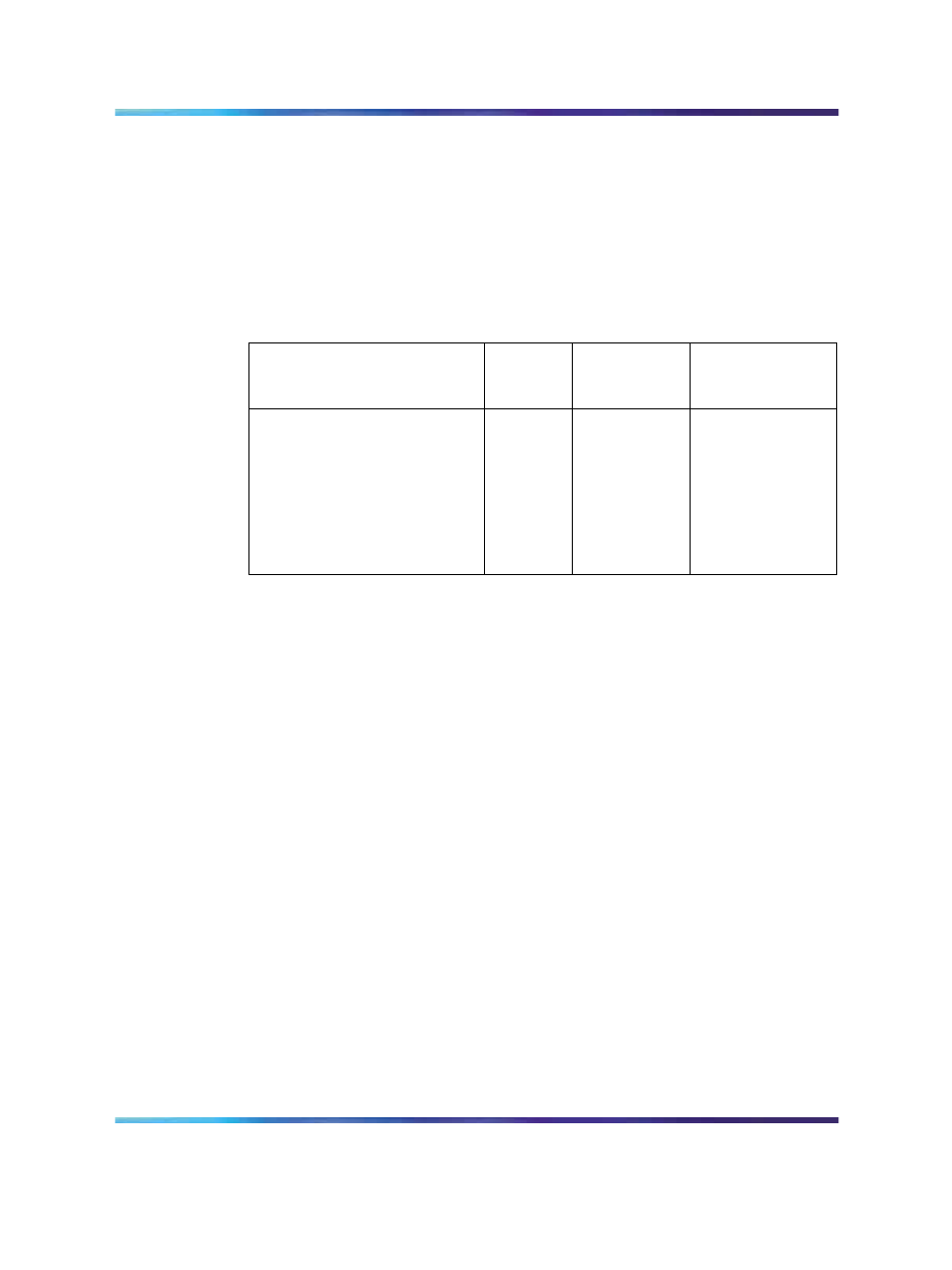
Table 20 "Example: Incremental WAN bandwidth requirement" (page 121)
summarizes the WAN traffic in kbit/s for each route. The recommended
incremental bandwidth requirement is included in the column adjusted
for 30% traffic peaking in busy hour. This assumes no correlation and
no synchronization of voice bursts in different simultaneous calls. This
assumes some statistical model of granularity and distribution of voice
message bursts due to Silence Suppression.
Table 20
Example: Incremental WAN bandwidth requirement
Destination Pair
CCS on
WAN
WAN
traffic in
kbit/s
Peaked WAN
traffic (x1.3) in
kbit/s
Santa Clara/Richardson
60
18.7
24.3
Santa Clara/Ottawa
45
14.0
18.2
Santa Clara/Tokyo
15
4.7
6.1
Richardson/Ottawa
35
10.9
14.2
Richardson/Tokyo
20
6.2
8.1
Ottawa/Tokyo
18
5.6
7.3
The following example illustrates the calculation procedure for Santa Clara
and Richardson. The total traffic on this route is 60 CCS. To use the
preferred codec of G.729AB with a 30 ms payload, the bandwidth on the
WAN is 11.2 kbit/s. WAN traffic is calculated using the following formula:
(60/36)*11.2 = 18.7 kbit/s
Augmenting this number by 30% gives a peak traffic rate of 24.3 kbit/s. This
is the incremental bandwidth required between Santa Clara and Richardson
to carry the 60 CCS voice traffic during the busy hour.
Assume that 20 CCS of the 60 CCS between Santa Clara and Richardson
is fax traffic. Of the 20 CCS, 14 CCS is from Santa Clara to Richardson,
and 6 CCS is from Richardson to Santa Clara. What is the WAN data rate
required between those two locations?
Traffic between the two sites can be broken down to 54 CCS from Santa
Clara to Richardson, and 46 CCS from Richardson to Santa Clara, with the
voice traffic 40 CCS (60 – 20) being the two-way traffic.
The bandwidth requirement calculation would be:
(40/36)*11.2 + (14/36)*33.6 = 25.51 kbit/s
Nortel Communication Server 1000
IP Trunk Fundamentals
NN43001-563
01.01
Standard
Release 5.0
30 May 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks
.
