2 internal architecture – FUJITSU MB91F109 FR30 User Manual
Page 55
31
2.2 Internal Architecture
2.2
Internal Architecture
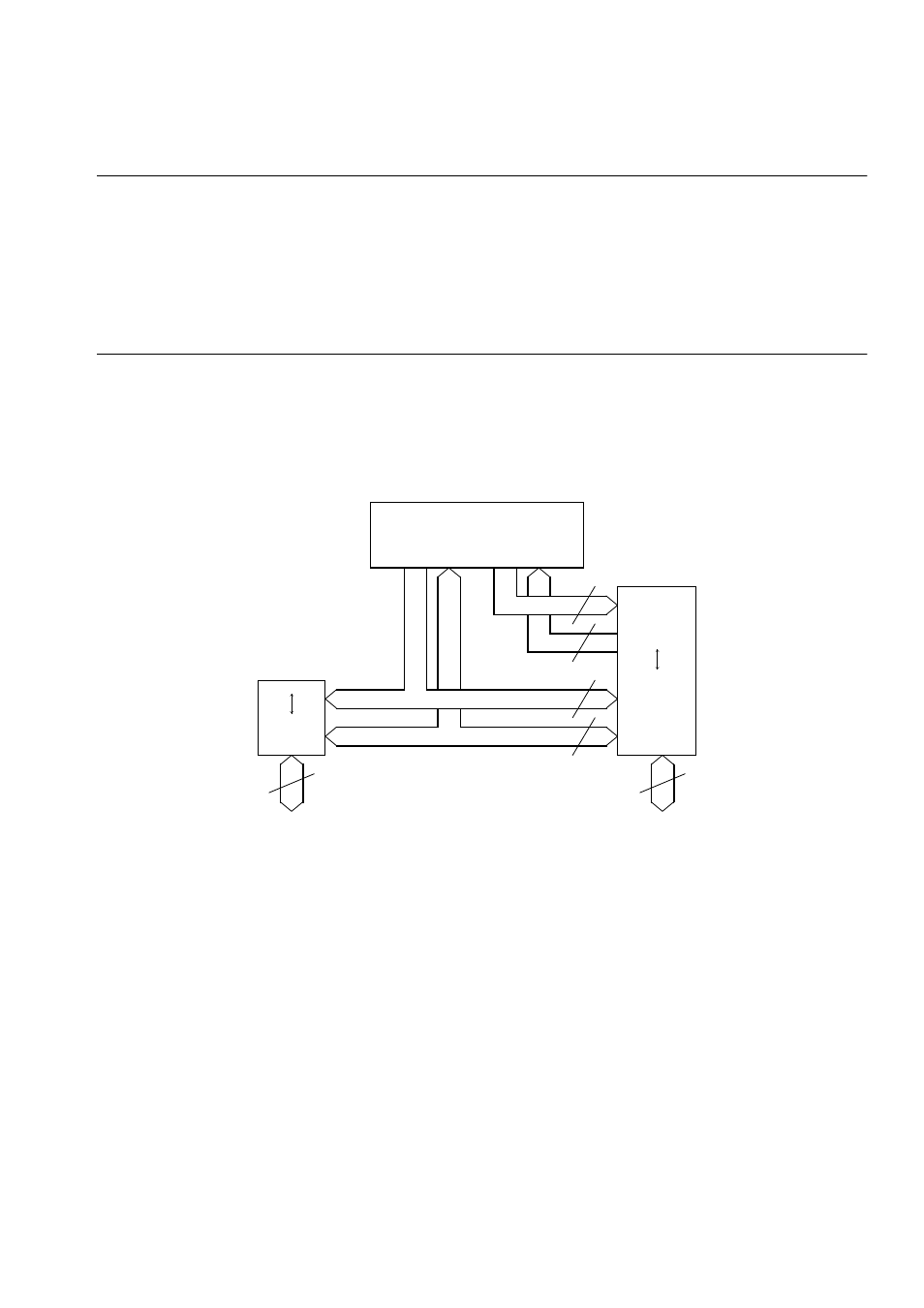
The FR CPU uses the Harvard architecture in which the instruction bus and data bus
are independent of each other.
The "32 bits <--> 16 bits" bus converter is connected to the data bus (D-BUS) to
implement the interface between the CPU and peripheral resources. The "Harvard <-->
Princeton" bus converter is connected to both I-BUS and D-BUS to implement the
interface between the CPU and bus controller.
■
Internal Architecture
Figure 2.2.1 shows the internal architecture.
Figure 2.2-1 Internal Architecture
❍
CPU
The CPU is a compact implement of the 32-bit RISC FR architecture.
It uses a five-stage instruction pipeline system to execute one instruction per cycle. The
pipeline consists of the following five stages:
•
Instruction fetch (IF): Outputs an instruction address and fetches the instruction.
•
Instruction decode (ID): Decodes the fetched instruction and also reads registers.
•
Execution (EX): Executes operation.
•
Memory access (MA): Accesses memory for loading or storing data.
•
Write back (WB): Writes the operation results (or loaded memory data) to registers.
Figure 2.2.2 shows the instruction pipeline.
32
I-ADDR
16
I-DATA
32
32bit
D-ADDR
16bit
32
D-DATA
16
32
FR CPU
D-BUS
I-BUS
R-BUS
C-BUS
Bus
converter
Bus
converter
Resources
Harvard
Princeton
Bus controller
