5 data handling overview – Guralp Systems CMG-DCM build <10,000 User Manual
Page 52
CMG-EAM (Platinum Firmware)
5 Data Handling Overview
The data handling system of the CMG-EAM is very flexible, due to its
modular software architecture. All data flowing through the CMG-
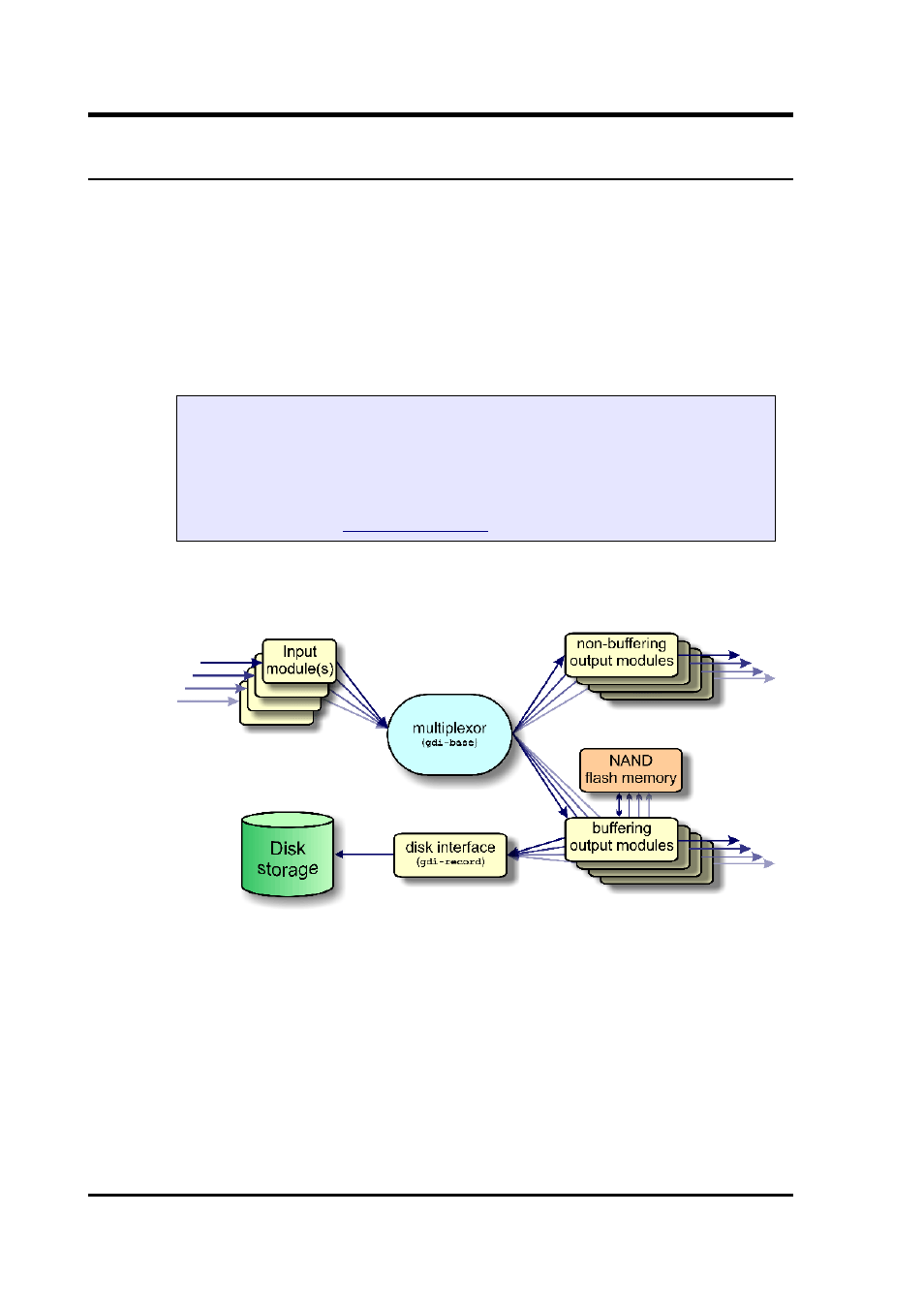
EAM is routed through a single multiplexor module called gdibase.
This communicates directly with all input modules, which handle the
various incoming data streams, and all output modules, which convert
the data into the required formats. All incoming data is stored and
accessed internally in an intermediate format, regardless of the format
in which it was originally received.
The diagram below shows the basic internal organisation of the CMG-
EAM, ignoring the CD1.1 subsystem.
The multiplexor makes incoming data available to the output modules.
These come in two flavours: simple modules (such as those for WIN,
GSMS and QSCD) simply convert the data streams and output them in
the required format; other modules maintain a ring-buffer which is
used to, for example, satisfy BRP back-fill requests. The ring-buffers
use the NAND flash memory. These output modules also send data to
gdirecord, which handles all hard disk writing requests, regardless
of format.
52
Issue C
Note: The sole exception to this is incoming CD1.1 data which,
for reasons related to frame signing (an authentication
technology), do not pass through gdibase. CD1.1 data-
handling and the associated system configuration are covered in
a separate manual, MAN-EAM-1100, which is available for
download from
