Comtech EF Data CDM-760 User Manual
Page 409
Appendix K
Revision 2
CDM-760 Advanced High-Speed Trunking Modem
MN-CDM760
K–9
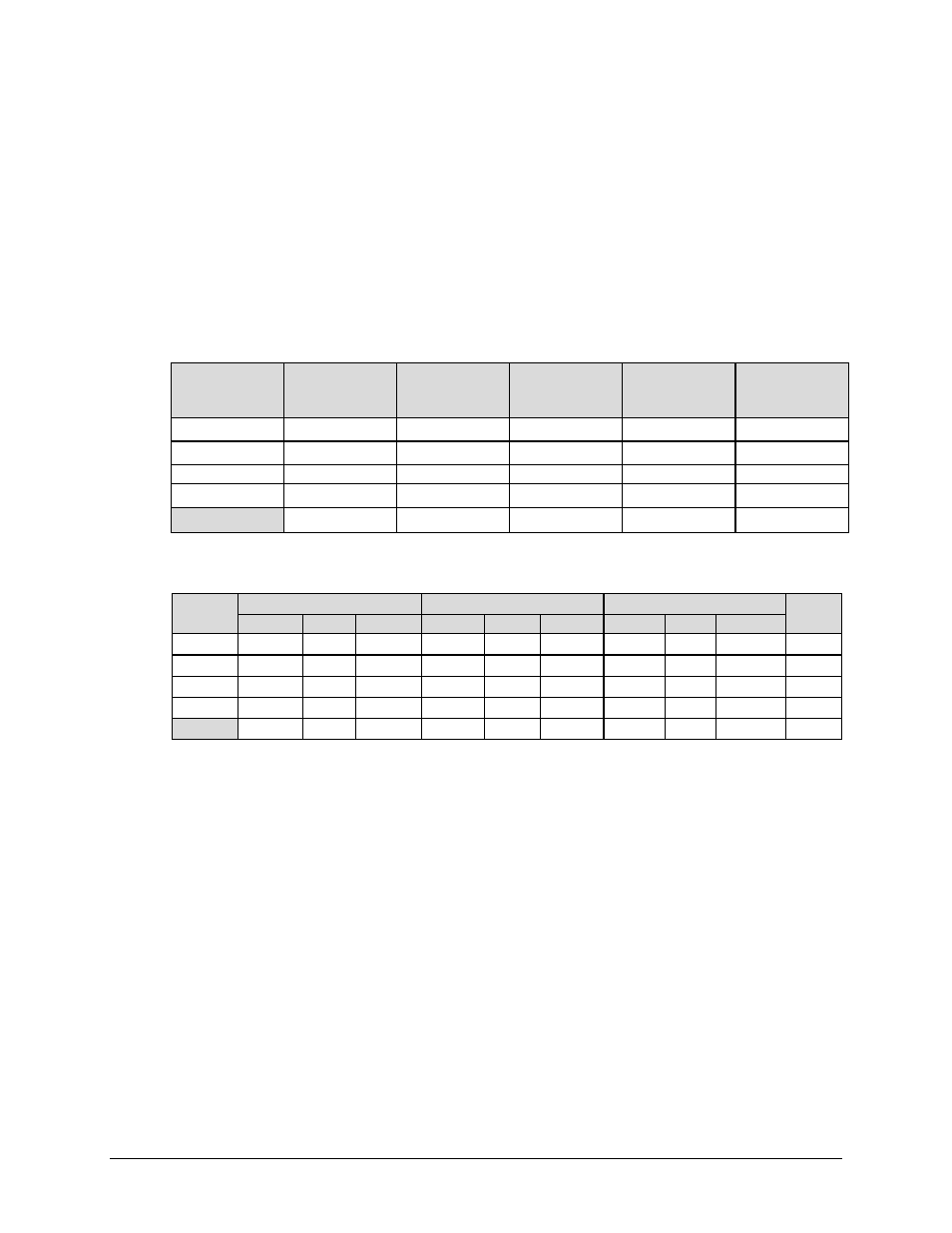
K.4.2.3.2 Example 2
•
Select Min/Max as the QoS Mode.
•
Configure each queue with minimum bandwidth (Min BW), maximum bandwidth (Max BW),
and weight as shown in Table K-6.
•
The total available bandwidth is 30000 kbps.
Calculate each individual allocated kbps.
Table K-6. Example 2 – QoS Classification
Queue
Min BW (kbps) Max BW (kbps)
Delta Max BW
(Max-Min)
(kbps)
Weight
Allowed BW
Q1
2000
4000
2000
9
– –
Q2
4000
8000
4000
8
– –
Q3
6000
16000
8000
7
– –
Q4
8000
8000
0
6
– –
Total ►
20000
40000
14000
30
30000
Table K-7. Example 2 Solution – Calculated BW Allocation
Queue
1
st
Round
2
nd
round
N
th
round
Final
kbps
Weight
Given Leftover
Weight
Given Leftover Weight Given Leftover
Q1
9
3750
1750
– –
– –
– –
– –
– –
– –
2000
Q2
8
3334
– –
8
934
268
– –
– –
– –
4000
Q3
7
2916
– –
7
816
– –
7
268
– –
4000
Q4
– –
– –
– –
– –
– –
– –
– –
– –
– –
– –
Total ►
24
10000
1750
15
268
7
0
0
10000
Table K-7 displays the solution for Example 2.
Step 1 – The sum of all queues’ minimum bandwidth (20000 kbps + total available bandwidth) =
30000 kbps. Once the sum of all minimums are met, there is a remainder of 10000 kbps overage
available for use.
The overage bandwidth is distributed to all non-served maximum bandwidth queues. In this
example, only Q1, Q2, and Q3 still have unmet maximum bandwidth.
Since Q4’s minimum and maximum bandwidths are the same, Q4 is therefore excluded from the
remaining overage distribution.
The remaining total weights are (9+8+7) = 24.
Step 2 – Calculate each bandwidth share, based on total weights (24) and bandwidth availability
(10000 kbps) after the minimum is served (20000 kbps).
