K.3.2 prioritization, K.3.3 drain, K.3.3.1 max/priority mode – Comtech EF Data CDM-760 User Manual
Page 403
Appendix K
Revision 2
CDM-760 Advanced High-Speed Trunking Modem
MN-CDM760
K–3
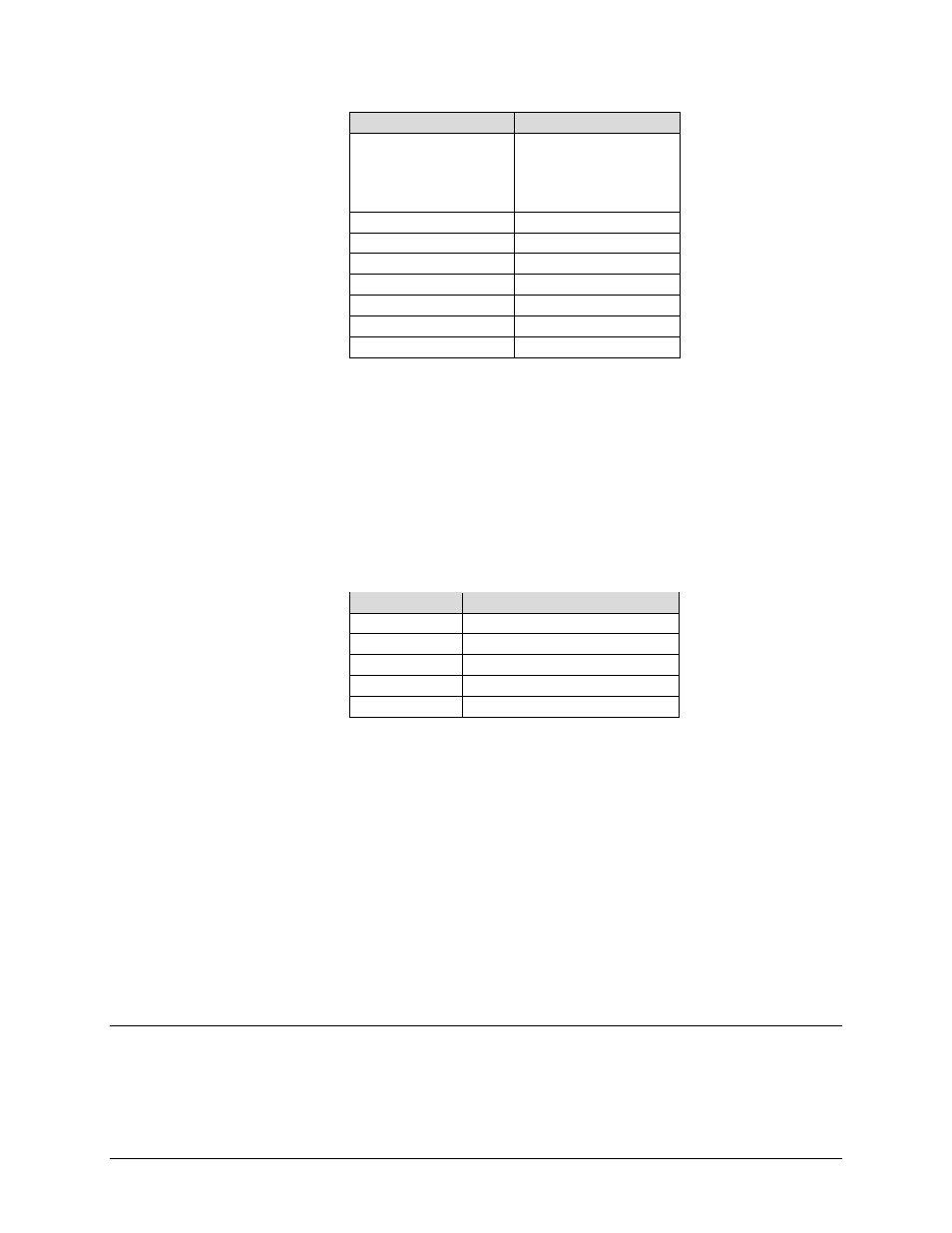
Order Precedence
Classifier
1 (cont.)
•
ICMP
•
All-IP
•
Non-IP
•
All
2
MPLS
3
VLAN
4
TOS
5
Source IP/Mask
6
Destination IP/Mask
7
Source Ports
8 (Last)
Destination Ports
K.3.2
Prioritization
Prioritization of traffic is a method of assigning various value levels to a particular classification
rule. Prioritization ensures that the packets/frames are “ordered” such that the highest level of
protection is provided to the most valuable traffic.
The CDM-760 offers eight priority levels (Table K-2), with Level 1 being the highest priority and
Level 8 the lowest priority.
Table K-2. Rule Priorities
Priority Level
Rank
1
Highest Priority
2
Second Highest Priority
3
Third Highest Priority
4 – 7
Fourth through Seventh Priorities
8
Lowest Priority
K.3.3
Drain
Once you classify and prioritize the packets or frames, you need to determine how to drain the
traffic. Does your network require you to pass all high level traffic in a strict priority manner
such that lower priority traffic could be “starved” in times of overdriving the WAN bandwidth?
Or, can determinations be made about the maximum and minimum levels of service you can
accept on a per classification rule basis?
The CDM-760 Packet Processor provides a number of choices. You may select from three top-
level QoS drain algorithms:
•
Max/Priority
•
Min/Max
•
DiffServ
K.3.3.1 Max/Priority Mode
Max/Priority QoS mode is commonly used in ACM circuits in conjunction with Weighting (see
Sect. K.4).
