Avalon streaming (avalon-st) interface, Avalon streaming (avalon-st) interface –2, Ring – Altera RapidIO MegaCore Function User Manual
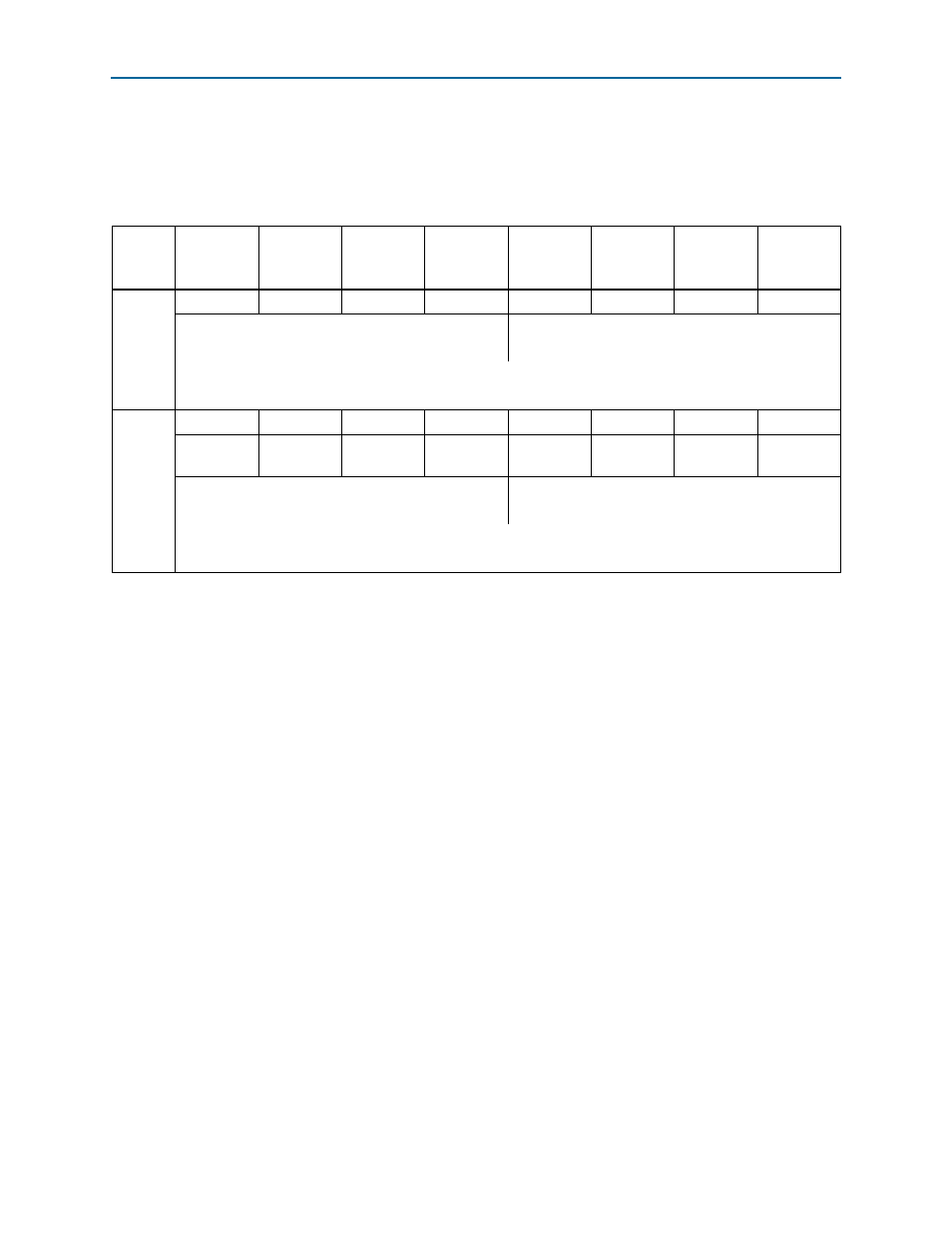
Page 48: Table 4–1, Shows the
4–2
Chapter 4: Functional Description
Interfaces
RapidIO MegaCore Function
August 2014
Altera Corporation
User Guide
No byte- or bit-order swaps occur between the Avalon-MM protocol and RapidIO
protocol, only byte- and bit-number changes. For example, RapidIO Byte0 is
Avalon-MM Byte7, and for all values of i from 0 to 63, bit i of the RapidIO 64-bit
double word[0:63] of payload is bit (63-i) of the Avalon-MM 64-bit double word[63:0].
In variations of the RapidIO IP core that have 32-bit wide Avalon-MM interfaces, the
order in which the two 32-bit words in a double word appear on the Avalon-MM
interface in a burst transaction, is inverted from the order in which they appear inside
a RapidIO packet. The RapidIO 32-bit word with wdptr=0 is the most significant half
of the double word at RapidIO address N, and the 32-bit word with wdptr=1 is the
least significant 32-bit word at RapidIO address N. Therefore, in a burst transaction on
the Avalon-MM interface, the 32-bit word with wdptr=0 corresponds to the
Avalon-MM 32-bit word at address N+4 in the Avalon-MM address space, and must
follow the 32-bit word with wdptr=1 which corresponds to the Avalon-MM 32-bit
word at address N in the Avalon-MM address space. Thus, when a burst of two or
more 32-bit Avalon-MM words is transported in RapidIO packets, the order of the
pair of 32-bit words is inverted so that the most significant word of each pair is
transmitted or received first in the RapidIO packet.
Avalon Streaming (Avalon-ST) Interface
The Avalon-ST interface provides a standard, flexible, and modular protocol for data
transfers from a source interface to a sink interface. The Avalon-ST interface protocol
allows you to easily connect components together by supporting a direct connection
to the Transport layer. The Avalon-ST interface is either 32 or 64 bits wide depending
on the RapidIO lane width. This interface is available to create custom Logical layer
functions like message passing.
For more information about how this interface functions with the RapidIO IP core,
refer to the
“Avalon-ST Pass-Through Interface” on page 4–56
.
Table 4–1. Byte Ordering
Byte
Lane
(Binary)
1000_0000
0100_0000
0010_0000
0001_0000
0000_1000
0000_0100
0000_0010
0000_0001
RapidIO
Protocol
(Big
Endian)
Byte0[0:7]
Byte1[0:7]
Byte2[0:7]
Byte3[0:7]
Byte4[0:7]
Byte5[0:7]
Byte6[0:7]
Byte7[0:7]
32-Bit Word[0:31]
32-Bit Word[0:31]
wdptr=0
wdptr=1
Double Word[0:63]
RapidIO Address N = {29'hn, 3'b000}
Avalon-
MM
Protocol
(Little
Endian)
Byte7[7:0]
Byte6[7:0]
Byte5[7:0]
Byte4[7:0]
Byte3[7:0]
Byte2[7:0]
Byte1[7:0]
Byte0[7:0]
Address=
N+7
Address=
N+6
Address=
N+5
Address=
N+4
Address=
N+3
Address=
N+2
Address=
N+1
Address=
N
32-Bit Word[31:0]
32-Bit Word[31:0]
Avalon-MM Address = N+4
Avalon-MM Address = N
64-bit Double Word0[63:0]
Avalon-MM Address = N
