Fairbanks X SERIES PR 5410 Process Indicator User Manual
Page 77
Section 4: Commissioning
10/08 77
51207 Revision 1
Set SPAN failed
Load below deadload
The weight on the scale is less than the dead load after input of the
weight value.
The next step is calculation of the test value with [Test] (see Chapter 0), and calibration is
completed with
(see Chapter 4.5.12).
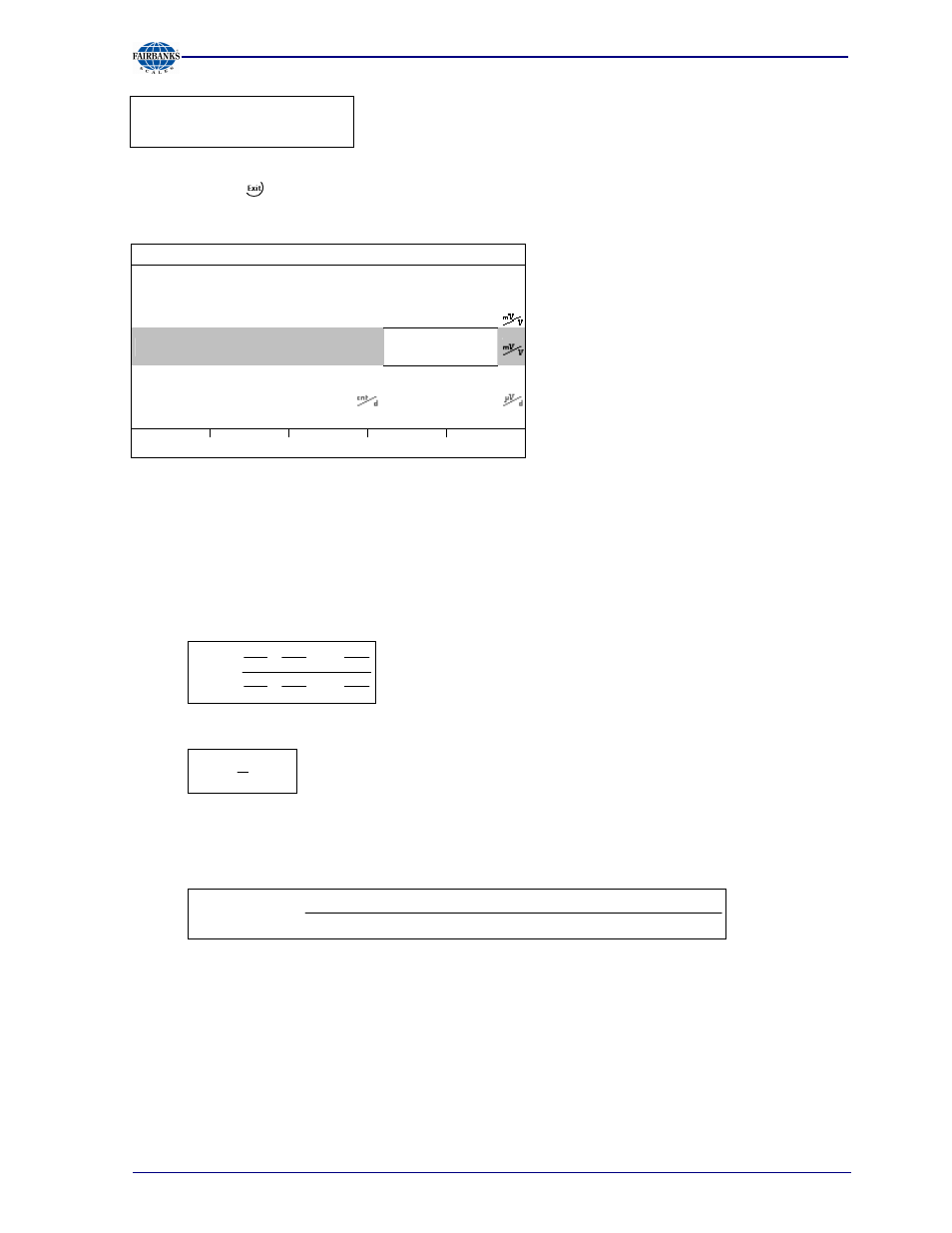
Determining span without weight
WP A/Calibration
Max
3000 d
3000 kg
Scale interval
3000 d
1 kg
Deadload at
3.00 kg
0.001000
Max at
3000.00
kg
0.000000
Not calibrated
Sensitivity
833.33
4.000000
by load
by mV/V
by data
Linear.
Test
4.5.7 Calibration with mV/V Value
The scale can be calibrated without weights. During input of the load cell mV/V value, the
acceleration of gravity at the place of installation can be taken into account. The STAR load cell
data is based on the acceleration of gravity effective at Hamburg, Germany: 9.81379 m/s².
Calculation of the average load cell sensitivity:
With D1 specification load cells, the use of sensitivity C given in the data sheet is sufficient.
The average load cell sensitivity C
Avr
is calculated as follows:
Ran
1
+
...
+
Ra2
1
+
Ra1
1
Ran
Cn
+
...
+
Ra2
C2
+
Ra1
C1
=
C
Avr
The formula is simplified when the output resistance Ra for the load cells is almost equal:
C
n
1
=
C
Avr
∑
Span: Calculation of the equivalent input voltage in mV/V
Span indicates the equivalent input voltage in mV/V related to the maximum capacity (Max) of the
scale. It is calculated as follows:
cells)
load
of
number
*
load
(nominal
capacity
cell
load
[mV/V
C
y
sensitivit
cell
load
capacity
maximum
=
[mV/V]
Span
Avr
]
*
Dead load:
Calculation of the equivalent input voltage in mV/V
The input voltage in mV/V equivalent to the dead load can be calculated by using the dead load
rather than the maximum capacity in the formula specified above.
Normally, calculation of the dead load (scale without load/empty hopper) is not necessary.
Subsequent dead load correction (as described in Chapter 0) can be used for later re-determination
of the dead load, when the scale/hopper is empty.
Example: Load cell(s) with rated output of 2mV/V at nominal load of 2000 kg, dead load 500 kg,
load cell supply voltage 12 VDC
