Summary of quality assurance checks – Teledyne 9110E - Nitrogen Oxides Analyzer User Manual
Page 154
EPA Protocol Calibration
Model 9110E Instruction Manual
140
M9110E Rev B
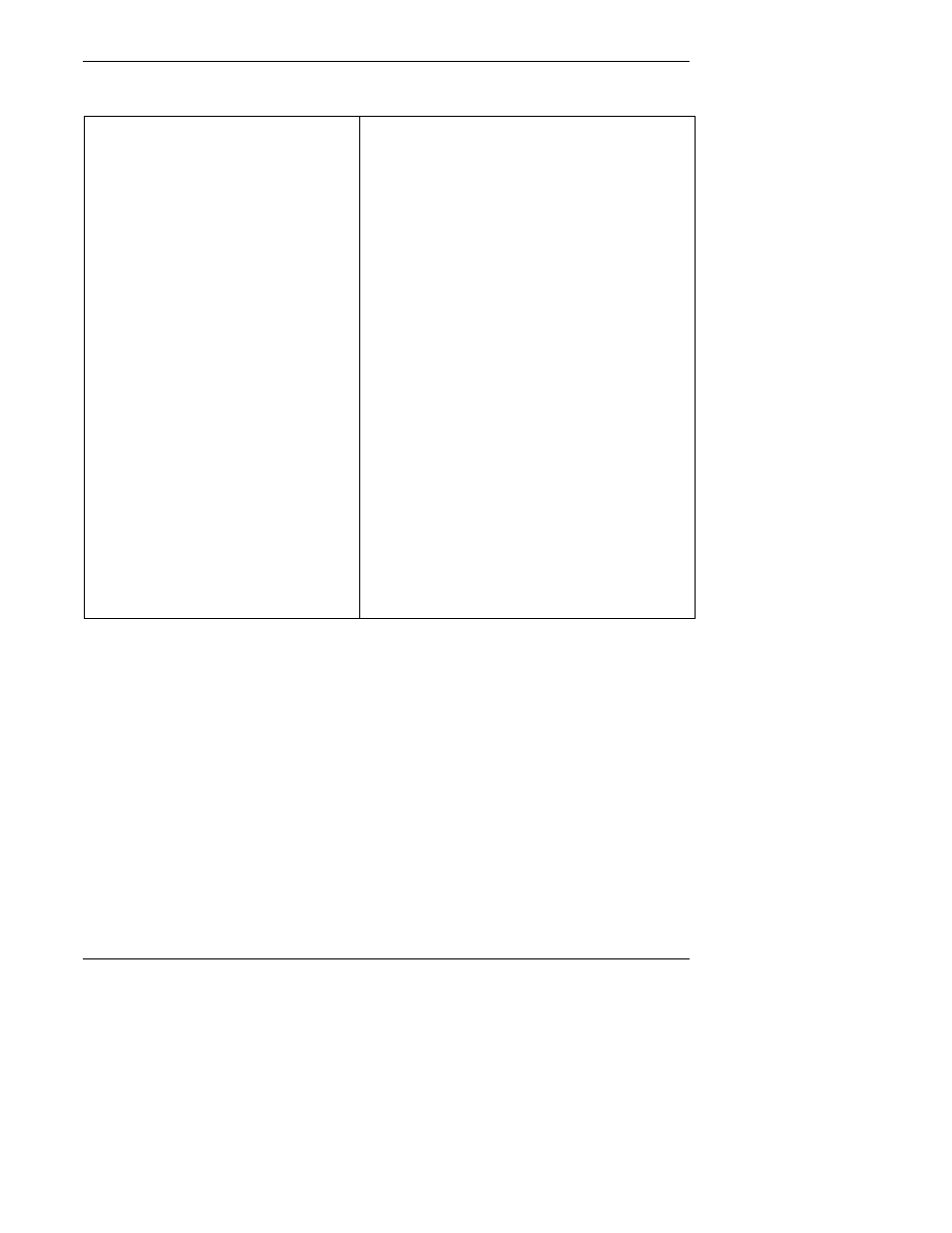
Table 8-3: Definition of Level 1 and Level 2 Zero and Span Checks
LEVEL 1 ZERO AND SPAN CALIBRATION
A Level 1 zero and span calibration is a
simplified, two-point analyzer calibration
used when analyzer linearity does not need
to be checked or verified. (Sometimes when
no adjustments are made to the analyzer,
the Level 1 calibration may be called a
zero/span check, in which case it must not
be confused with a Level 2 zero/span
check.) Since most analyzers have a
reliably linear or near-linear output
response with concentration, they can be
adequately calibrated with only two
concentration standards (two-point
concentration). Furthermore, one of the
standards may be zero concentration, which
is relatively easily obtained and need not be
certified. Hence, only one certified
concentration standard is needed for the
two-point (Level 1) zero and span
calibration. Although lacking the advan-
tages of the multipoint calibration, the two-
point zero and span calibration--because of
its simplicity--can be (and should be)
carried out much more frequently. Also,
two-point calibrations are easily automated.
Frequency checks or updating of the
calibration relationship with a two-point
zero and span calibration improves the
quality of the monitoring data by helping to
keep the calibration relationship more
closely matched to any changes (drifts) in
the analyzer response.
LEVEL 2 ZERO AND SPAN CHECK
A Level 2 zero and span check is an "unofficial" check
of an analyzer's response. It may include dynamic
checks made with uncertified test concentrations,
artificial stimulation of the analyzer's detector,
electronic or other types of checks of a portion of the
analyzer, etc.
Level 2 zero and span checks are not to be used as a
basis for analyzer zero or span adjustments,
calibration updates, or adjustment of ambient data.
They are intended as quick, convenient checks to be
used between zero and span calibrations to check for
possible analyzer malfunction or calibration drift.
Whenever a Level 2 zero or span check indicates a
possible calibration problem, a Level 1 zero and span
(or multipoint) calibration should be carried out before
any corrective action is taken.
If a Level 2 zero and span check is to be used in the
quality control program, a "reference response" for
the check should be obtained immediately following a
zero and span (or multipoint) calibration while the
analyzer's calibration is accurately known. Subsequent
Level 2 check responses should then be compared to
the most recent reference response to determine if a
change in response has occurred. For automatic Level
2 zero and span checks, the first scheduled check
following the calibration should be used for the
reference response. It should be kept in mind that any
Level 2 check that involves only part of the analyzer's
system cannot provide information about the portions
of the system not checked and therefore cannot be
used as a verification of the overall analyzer
calibration.
In addition, an independent precision check between 0.08 and 0.10 ppm must be carried
out at least once every two weeks. Table 8-4 summarizes the quality assurance activities
for routine operations. A discussion of each activity appears in the following sections.
To provide for documentation and accountability of activities, a checklist should be compiled
and then filled out by the field operator as each activity is completed.
For information on shelter and sample inlet system, an in-depth study is in Field Operations
Guide for Automatic Air Monitoring Equipment, Publication No. APTD-0736, PB 202-249 and
PB 204-650, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Air Programs, October 1972.
8.6. Summary of Quality Assurance Checks
The following items should be checked on a regularly scheduled basis to assure high quality
data from the M9110E. See Table 8-4 for a summary of activities; also the QA Handbook
should be checked for specific procedures.
