1 tool movements, Path functions, Fk free contour programming – HEIDENHAIN iTNC 530 (60642x-04) User Manual
Page 222: Miscellaneous functions m, Subprograms and program section repeats, Programming with q parameters, 1 t ool mo v e ments 6.1 tool movements
222
Programming: Programming Contours
6.1 T
ool mo
v
e
ments
6.1 Tool movements
Path functions
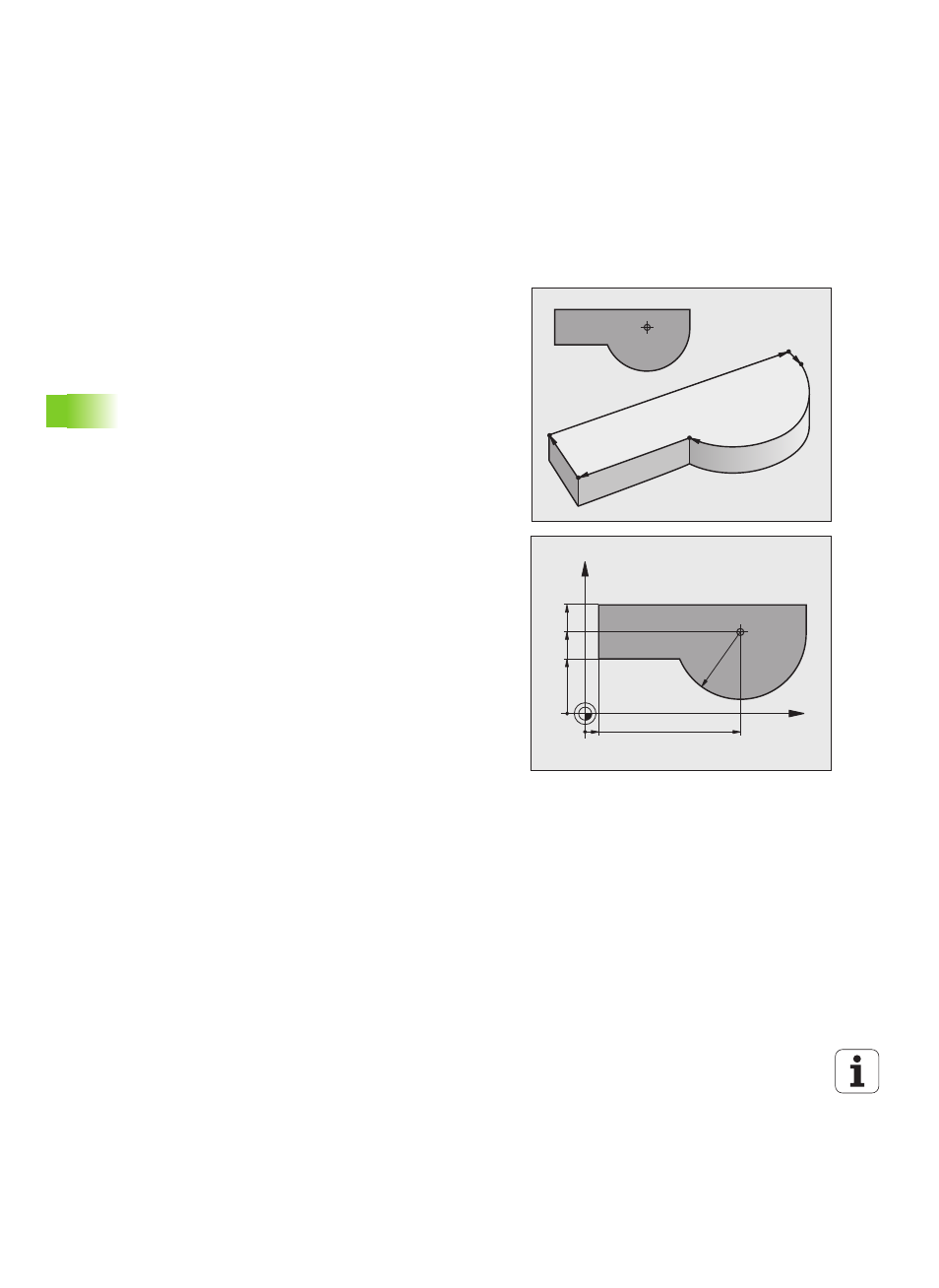
A workpiece contour is usually composed of several contour elements
such as straight lines and circular arcs. With the path functions, you
can program the tool movements for straight lines and circular arcs.
FK free contour programming
If a production drawing is not dimensioned for NC and the dimensions
given are not sufficient for creating a part program, you can program
the workpiece contour with the FK free contour programming. The
TNC calculates the missing data.
With FK programming, you also program tool movements for straight
lines
and circular arcs
Miscellaneous functions M
With the TNC’s miscellaneous functions you can affect
The program run, e.g., a program interruption
The machine functions, such as switching spindle rotation and
coolant supply on and off
The path behavior of the tool
Subprograms and program section repeats
If a machining sequence occurs several times in a program, you can
save time and reduce the chance of programming errors by entering
the sequence once and then defining it as a subprogram or program
section repeat. If you wish to execute a specific program section only
under certain conditions, you also define this machining sequence as
a subprogram. In addition, you can have a part program call a separate
program for execution.
Programming with subprograms and program section repeats is
described in Chapter 8.
Programming with Q parameters
Instead of programming numerical values in a part program, you enter
markers called Q parameters. You assign the values to the Q
parameters separately with the Q parameter functions. You can use
the Q parameters for programming mathematical functions that
control program execution or describe a contour.
In addition, programming with Q parameters enables you to measure
with the touch probe during program run.
Programming with Q parameters is described in Chapter 9.
L
L
L
CC
C
X
Y
R40
115
10
80
60
40
CC
