Ip encryption example, Authentication headers, Ip encryption – Enterasys Networks CSX6000 User Manual
Page 237
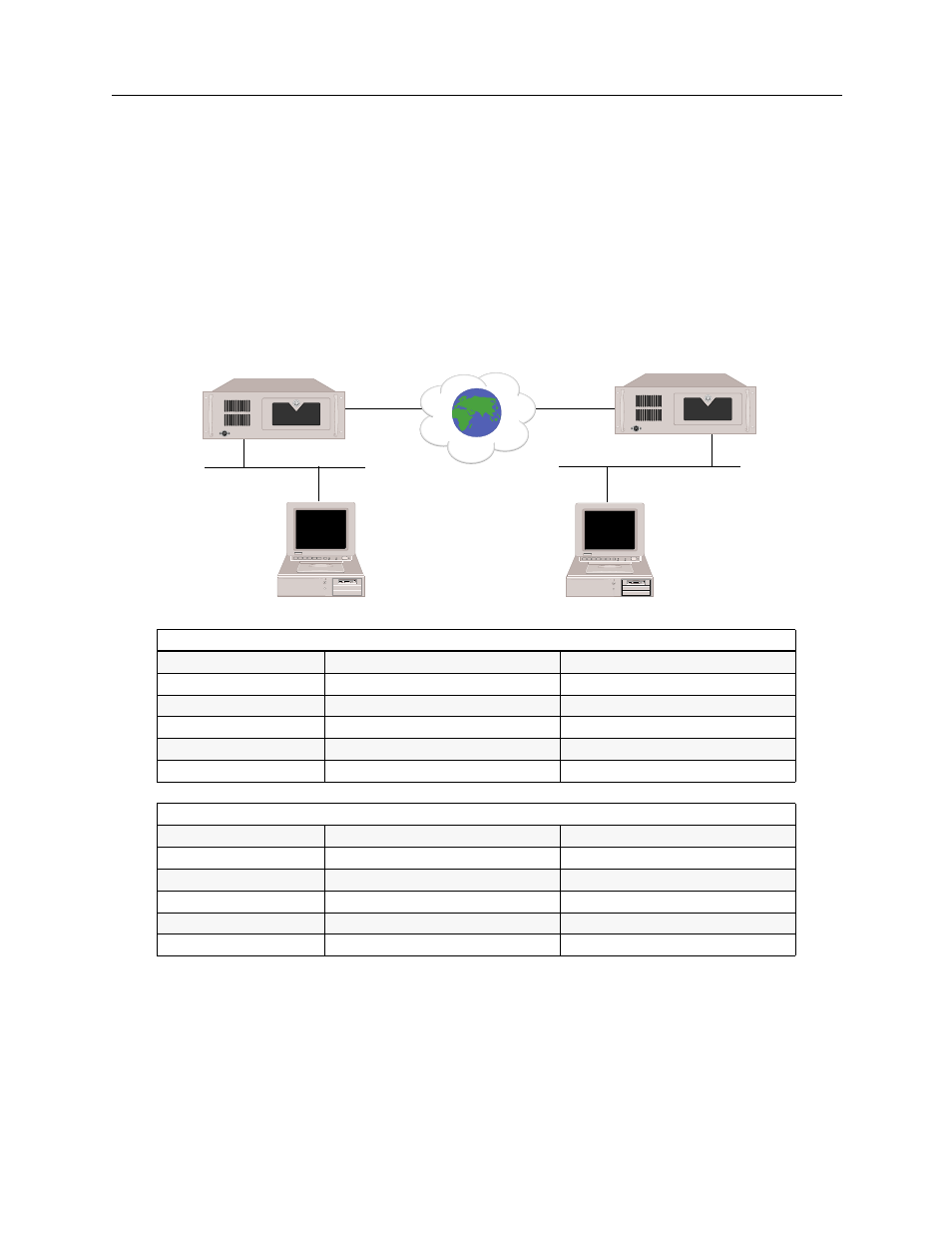
Central Site Remote Access Switch 237
C
ONFIGURING
E
NCRYPTION
Encryption Background Information
The peer must also have corresponding Security Associations. (Note that the gateway address and
the source/destination subnet addresses are switched to reflect the peer subnet.)
Security Associations between peer CyberSWITCH nodes are identified by a Security Parameter
Index (SPI). The SPI is transmitted in the ESP header and is used by the peer node to identify the
necessary information to decrypt the ESP payload.
IP E
NCRYPTION
E
XAMPLE
A
UTHENTICATION
H
EADERS
Authentication Header (AH) protocol provides integrity and authentication for IP datagrams by
assuring that a received packet originated from the destination it claims. Packets originating from
the CyberSWITCH may be authenticated with AH protocol, as long as AH is enabled and properly
configured.
Site “A”
Security Associations
Outgoing:
Incoming:
Final Destination:
197.1.2.2
197.4.2.2
Mask:
16 bits
16 bits
Destination gateway:
197.1.1.1
197.1.1.1
Shared Secret Key:
AAABBB1234567890
9876543210ABCDEF
SPI:
12345678
8888CCCC
Site “B”
Security Associations
Outgoing:
Incoming:
Final Destination:
197.4.2.2
197.1.2.2
Mask:
16 bits
16 bits
Destination gateway:
197.4.1.1
197.4.1.1
Shared Secret Key:
9876543210ABCDEF
AAABBB1234567890
SPI:
8888CCCC
12345678
197.4.1.1
"SITE A"
197.1.1.1
CSX5500
CSX5500
"SITE B"
197.4.2.2
197.1.2.2
INTERNET
Untrusted Media
Trusted
Subnet
Trusted
Subnet
