Permanent magnet motor control – Rockwell Automation 20G PowerFlex 750-Series AC Drives User Manual
Page 233
Rockwell Automation Publication 750-RM002B-EN-P - September 2013
233
Motor Control
Chapter 4
Permanent Magnet Motor Control
Permanent magnet motor control is selected by setting P35 [Motor Ctrl Mode]
to the appropriate choices of motor type. Refer to Appendix D of the PowerFlex
750-Series Programming Manual, publication
for compatible list of
Allen-Bradley Servo motors and resolution criteria.
Surface Permanent Magnet (SPM) motor or Permanent Magnet Synchronous
Motor (PMSM) is a rotating electrical machine that has the stator phase
windings and rotor permanent magnets. The air gap magnetic field is provided by
these permanent magnets and hence it remains constant. The conventional DC
motor commutates itself with the use of a mechanical commutator whereas
SPM/PMSM needs electronic commutation for the direction control of current
through the windings. Because the SPM/PMSM motors in effect have their
armature coils at the stator, they need to be commutated externally with the help
of an external switching circuit. A three phase PWM inverter topology is used for
this purpose.
The torque is produced because the interaction of the magnetic fields causes the
rotor to rotate. In permanent magnet motors, one of the magnetic fields is created
by permanent magnets and the other is created by the stator coils. The maximum
torque is produced when the magnetic vector of the rotor is at 90 degrees to the
magnetic vector of the stator.
Motor data and an autotune are required for correct operation in this mode.
Refer to
for details.
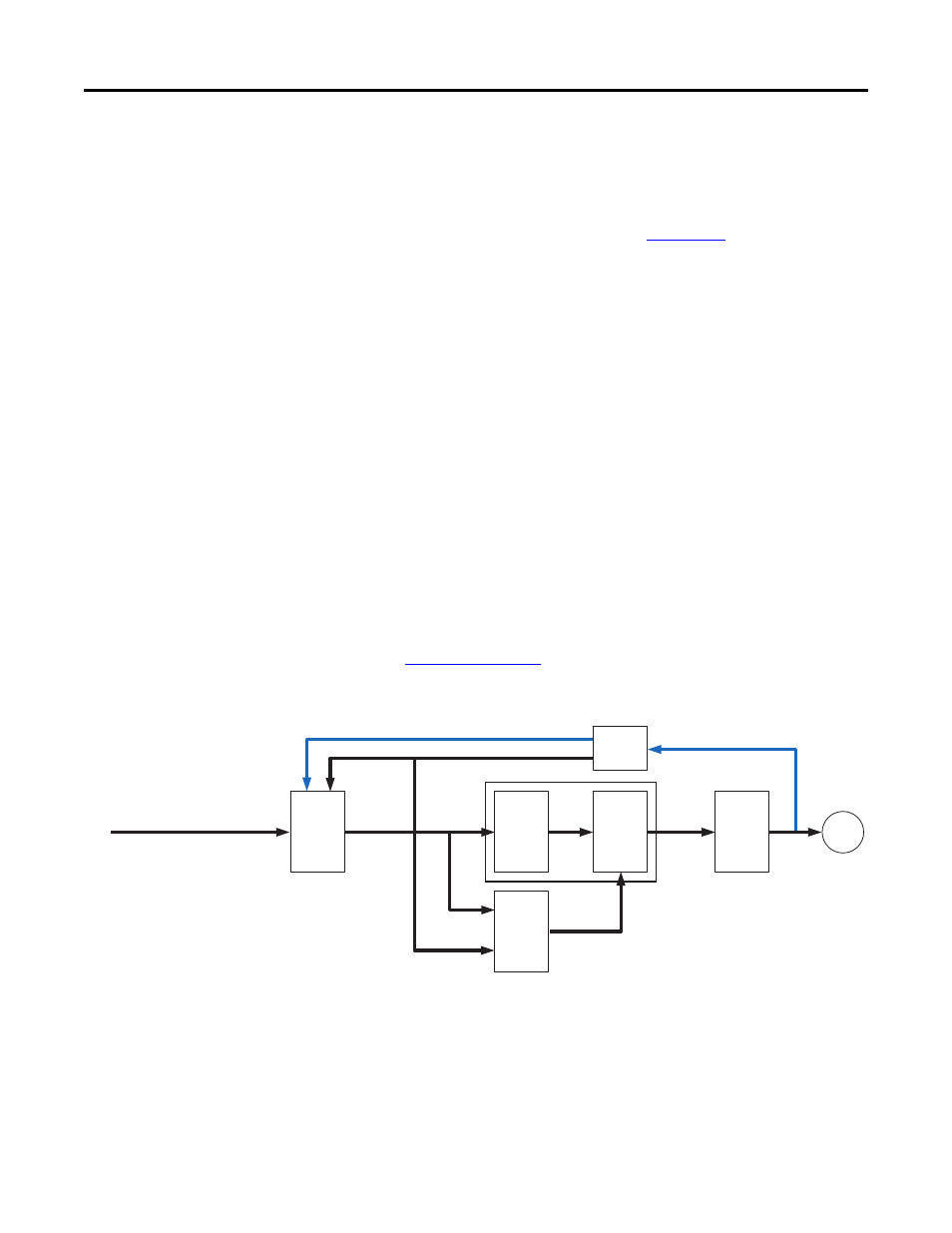
PM Sensorless Vector
Elec. Freq.
V Ref.
Gate
Signals
V/Hz
Voltage
Control
Inverter
Motor
Current
Limit
Freq. Ref.
Speed Freq.
Current
Resolver
Current Feedback
Current Feedback - Total
Torque 1 Est.
Vector
Control
V Vector
Torque 1 Est.
V/Hz Control
