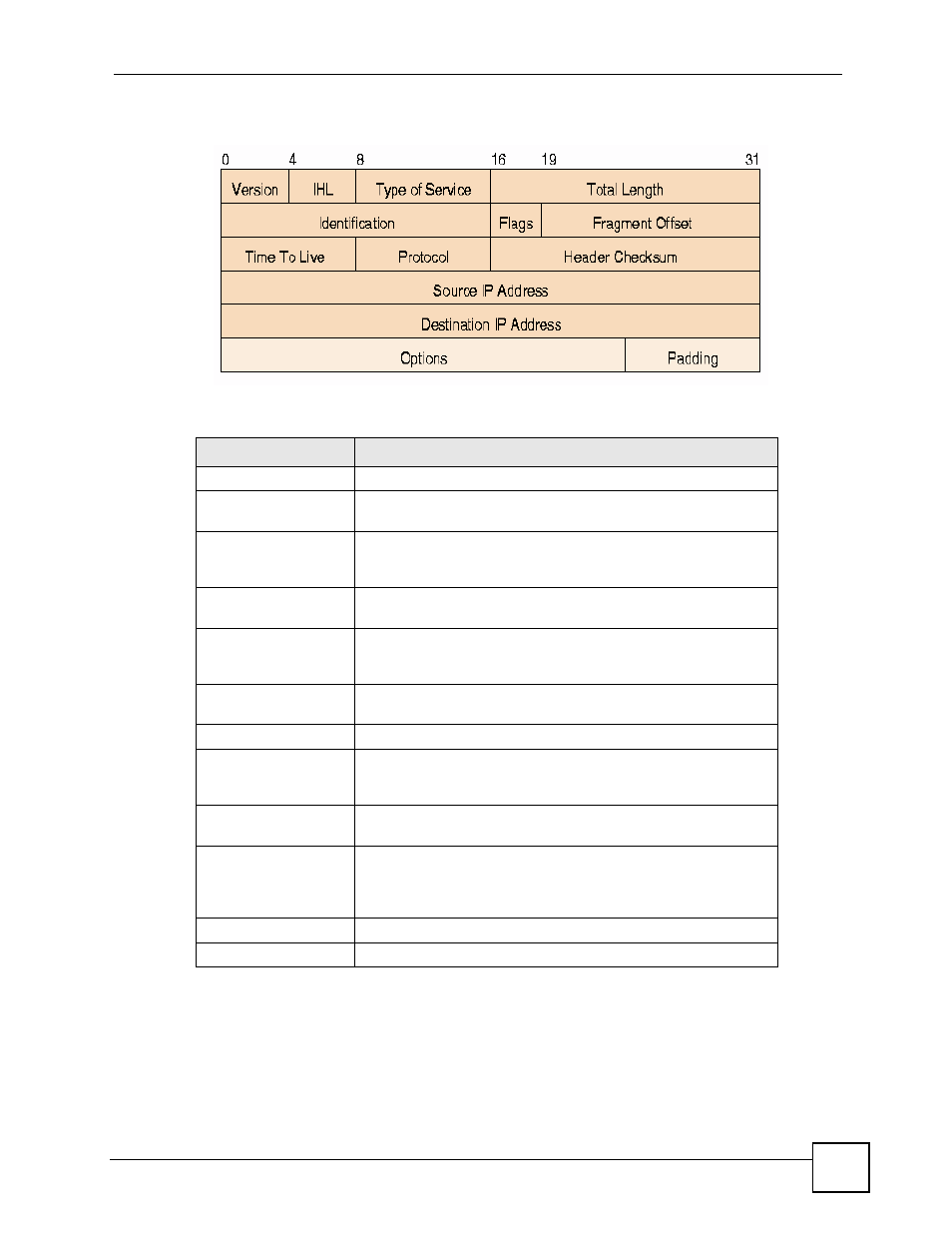
Figure 387 ip v4 packet headers, Table 160 ip v4 packet headers – ZyXEL Communications 200 Series User Manual
Page 499
Chapter 29 IDP
ZyWALL USG 100/200 Series User’s Guide
499
Figure 387 IP v4 Packet Headers
The header fields are discussed below:
Table 160 IP v4 Packet Headers
HEADER
DESCRIPTION
Version
The value 4 indicates IP version 4.
IHL
IP Header Length is the number of 32 bit words forming the total
length of the header (usually five).
Type of Service
The Type of Service, (also known as Differentiated Services Code
Point (DSCP)) is usually set to 0, but may indicate particular quality
of service needs from the network.
Total Length
This is the size of the datagram in bytes. It is the combined length
of the header and the data.
Identification
This is a 16-bit number, which together with the source address,
uniquely identifies this packet. It is used during reassembly of
fragmented datagrams.
Flags
Flags are used to control whether routers are allowed to fragment
a packet and to indicate the parts of a packet to the receiver.
Fragment Offset
This is a byte count from the start of the original sent packet.
Time To Live
This is a counter that decrements every time it passes through a
router. When it reaches zero, the datagram is discarded. It is used
to prevent accidental routing loops.
Protocol
The protocol indicates the type of transport packet being carried,
for example, 1 = ICMP; 2= IGMP; 6 = TCP; 17= UDP.
Header Checksum
This is used to detect processing errors introduced into the packet
inside a router or bridge where the packet is not protected by a link
layer cyclic redundancy check. Packets with an invalid checksum
are discarded by all nodes in an IP network.
Source IP Address
This is the IP address of the original sender of the packet.
Destination IP Address
This is the IP address of the final destination of the packet.
