Nat traversal, The esp protocol – Amer Networks E5Web GUI User Manual
Page 590
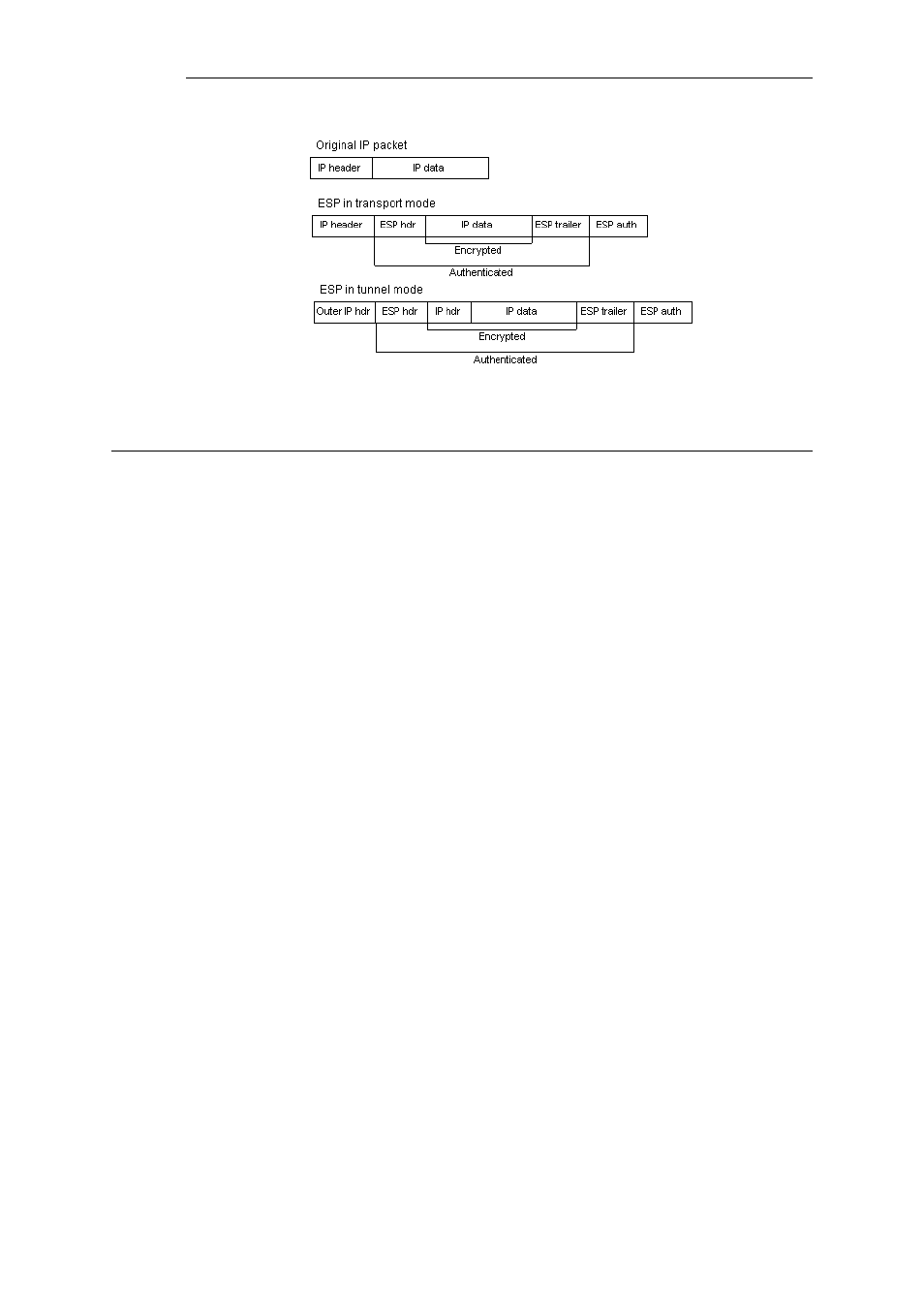
Figure 9.2. The ESP protocol
9.3.5. NAT Traversal
Both IKE and IPsec protocols present a problem in the functioning of NAT. Both protocols were
not designed to work through NATs and because of this, a technique called "NAT traversal" has
evolved. NAT traversal is an add-on to the IKE and IPsec protocols that allows them to function
when being NATed. cOS Core supports the RFC3947 standard for NAT-Traversal with IKE.
NAT traversal is divided into two parts:
•
Additions to IKE that lets IPsec peers tell each other that they support NAT traversal, and the
specific versions supported. cOS Core supports the RFC3947 standard for NAT-Traversal with
IKE.
•
Changes to the ESP encapsulation. If NAT traversal is used, ESP is encapsulated in UDP, which
allows for more flexible NATing.
Below is a more detailed description of the changes made to the IKE and IPsec protocols.
NAT traversal is only used if both ends have support for it. For this purpose, NAT traversal aware
VPNs send out a special "vendor ID" to tell the other end of the tunnel that it understands NAT
traversal, and which specific versions of the draft it supports.
Achieving NAT Detection
To achieve NAT detection both IPsec peers send hashes of their own IP addresses along with the
source UDP port used in the IKE negotiations. This information is used to see whether the IP
address and source port each peer uses is the same as what the other peer sees. If the source
address and port have not changed, then the traffic has not been NATed along the way, and NAT
traversal is not necessary. If the source address and/or port has changed, then the traffic has
been NATed, and NAT traversal is used.
Changing Ports
Once the IPsec peers have decided that NAT traversal is necessary, the IKE negotiation is moved
away from UDP port 500 to port 4500. This is necessary since certain NAT devices treat UDP
packet on port 500 differently from other UDP packets in an effort to work around the NAT
problems with IKE. The problem is that this special handling of IKE packets may in fact break the
IKE negotiations, which is why the UDP port used by IKE has changed.
Chapter 9: VPN
590
