The sip alg – Amer Networks E5Web GUI User Manual
Page 410
iv.
Select the ALG to be the PPTP ALG object that was defined in the first step. In this case, it
was called pptp_alg.
•
Associate this service object with the NAT IP rule that permits the traffic to flow from clients
to the remote endpoint of the PPTP tunnel. This may be the rule that NATs the traffic out to
the Internet with a destination network of all-nets.
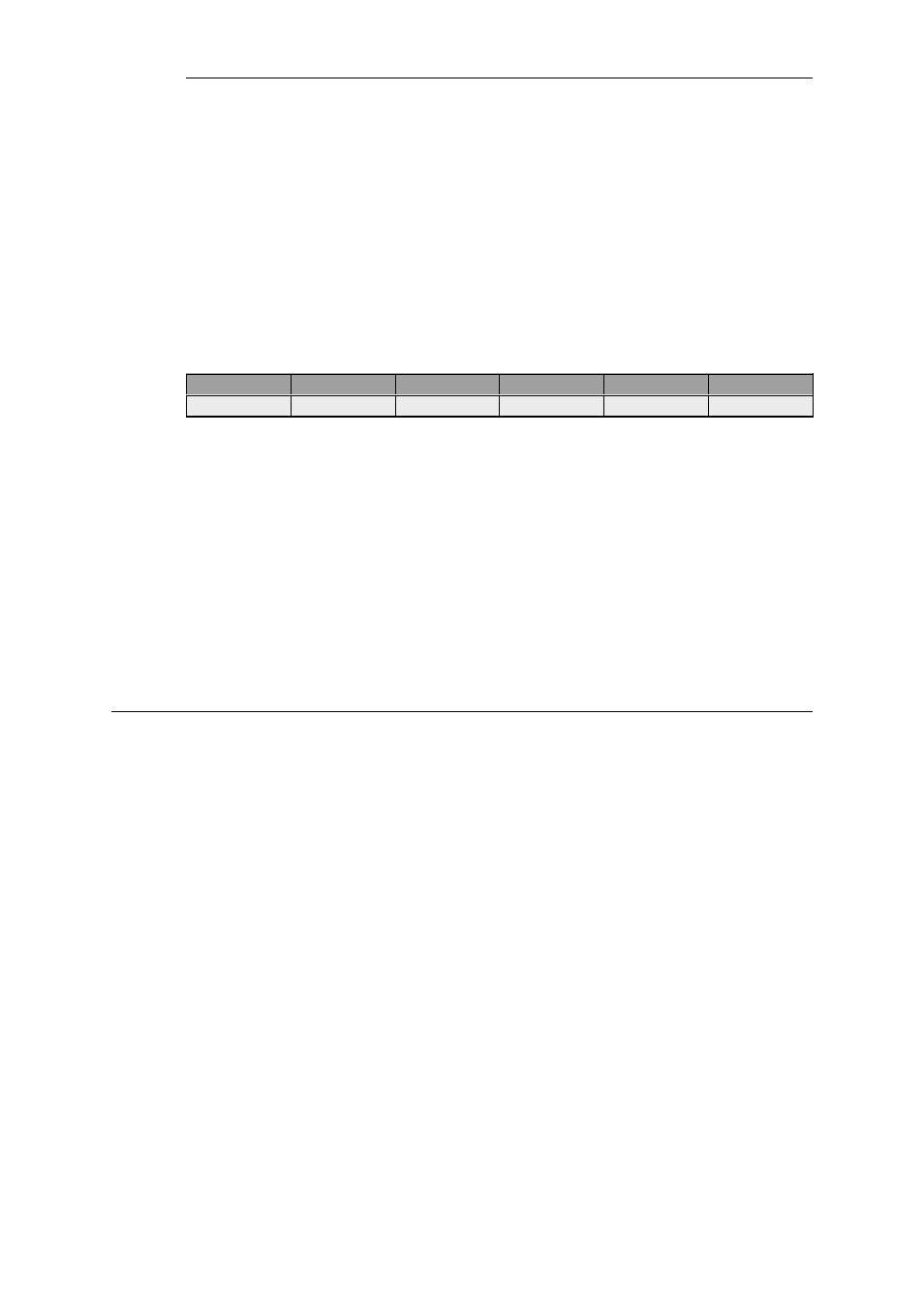
The single IP rule below shows how the custom service object called pptp_service is
associated with a typical NAT rule. The clients, which are the local end point of the PPTP
tunnels, are located behind the security gateway on the network lan_net which is connected
to the lan interface. The Internet is found on the wan interface which is the destination
interface, with all-nets as the destination network.
Action
Src Interface
Src Network
Dest Interface
Dest Network
Service
NAT
lan
lan_net
wan
all-nets
pptp_service
PPTP ALG Settings
The following settings are available for the PPTP ALG:
Name
A descriptive name for the ALG.
Echo timeout
Idle timeout for Echo messages in the PPTP tunnel.
Idle timeout
Idle timeout for user traffic messages in the PPTP tunnel.
In most cases only the name needs to be defined and the other settings can be left at their
defaults.
6.2.8. The SIP ALG
Overview
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is an ASCII (UTF-8) text based signalling protocol used to establish
sessions between clients in an IP network. It is a request-response protocol that resembles HTTP
and SMTP. The session which SIP sets up might consist of a Voice-Over-IP (VoIP) telephone call or
it could be a collaborative multi-media conference. Using SIP with VoIP means that telephony
can become another IP application which can integrate into other services.
SIP Sets Up Sessions
SIP does not know about the details of a session's content and is only responsible for initiating,
terminating and modifying sessions. Sessions set up by SIP are typically used for the streaming of
audio and video over the Internet using the RTP/RTCP protocol (which is based on UDP) but they
might also involve traffic based on the TCP protocol. An RTP/RTCP based sessions might also
involve TCP or TLS based traffic in the same session.
The SIP RFC
SIP is defined by IETF RFC 3261 and this is considered an important general standard for VoIP
communication. It is comparable to H.323, however, a design goal with SIP was to make SIP more
scalable than H.323. (For VoIP, see also Section 6.2.9, “The H.323 ALG”.)
Chapter 6: Security Mechanisms
410
