Using local ip address with an unbound network – Amer Networks E5Web GUI User Manual
Page 256
through ARP queries. ARP works because the clients and the cOS Core interface are part of the
same network.
A second network might then be added to the same physical interface via a switch, but with a
new network range that does not include the physical interface's IP address. This network is said
to be not bound to the physical interface. Clients on this second network won't then be able to
communicate with the Clavister Security Gateway because ARP won't function between the
clients and the interface.
To solve this problem, a new route is added to cOS Core with the following parameters:
•
Interface: The interface on which the second network is found.
•
Network: The IP address range of the second network.
•
Local IP Address: An address within the second network's IP range.
When the Default Gateway of the second network's clients is now set to the same value as the
Local IP Address of the above route, the clients will be able to communicate successfully with the
interface. The IP address chosen in the second network is not significant, as long as it is the same
value for the Default Gateway of the clients and the Local IP Address.
The effect of adding the route with the Local IP Address is that the security gateway will act as a
gateway with the Local IP Address and respond to, as well as send out, ARP queries as though the
interface had that IP address.
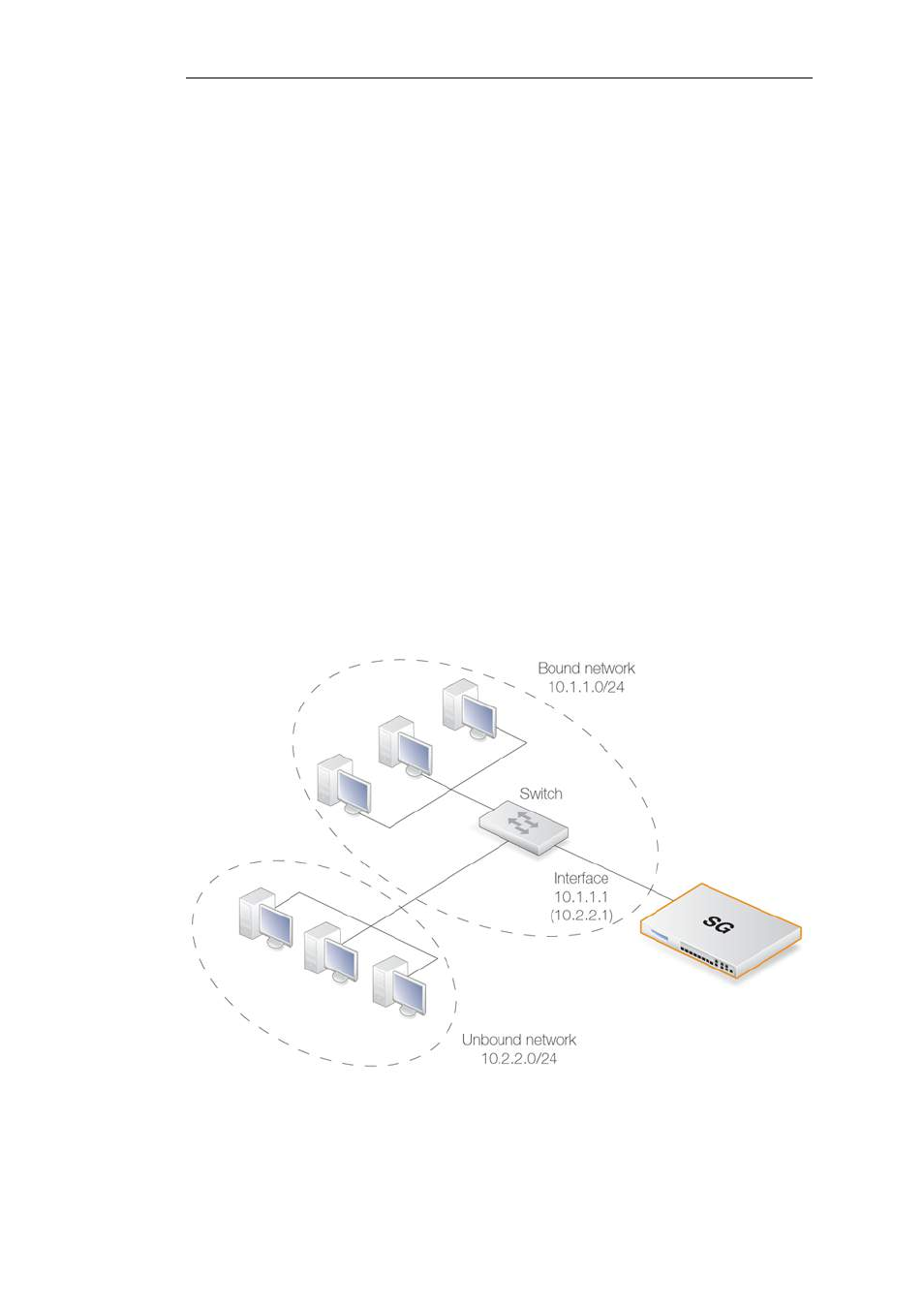
The diagram below illustrates a scenario where this feature could be used. The network
10.1.1.0/24 is bound to a physical interface that has an IP address within the network of 10.1.1.1. If
we now attach a second network 10.2.2.0/24 to the interface via the switch, it is unbound since
the interface's IP address does not belong to it.
Figure 4.2. Using Local IP Address with an Unbound Network
By adding a cOS Core route for this second network with the Local IP Address specified as 10.2.2.1,
the interface will then respond to ARP requests from the 10.2.2.0/24 network. The clients in this
Chapter 4: Routing
256
