Anti-spam filtering – Amer Networks E5Web GUI User Manual
Page 403
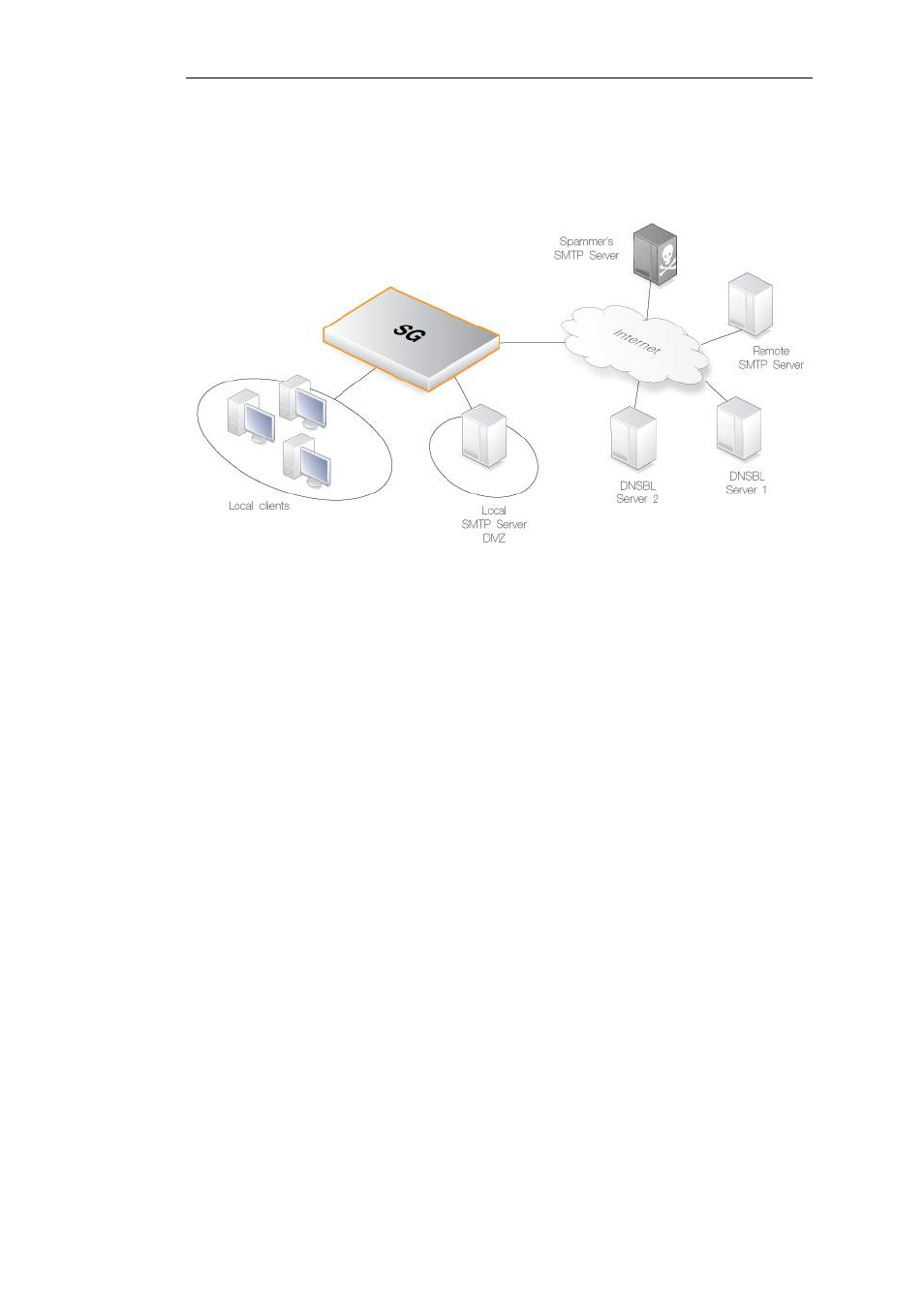
email is from a spammer or not. cOS Core examines the IP packet headers to do this.
The reply sent back by a server is either a not listed response or a listed response. In the latter case
of being listed, the DSNBL server is indicating the email might be spam and it will usually also
provide information known as a TXT record which is a textual explanation for the listing.
Figure 6.5. Anti-Spam Filtering
Creating a DNSBL Consensus
The administrator can configure the cOS Core SMTP ALG to consult multiple DNSBL servers in
order to form a consensus opinion on an email's origin address. For each new email, configured
servers are queried to assess the likelihood that the email is spam, based on its origin address.
The cOS Core administrator assigns a weight greater than zero to each configured server so that
a weighted sum can then be calculated based on all responses. The administrator can configure
one of the following actions based on the weighted sum calculated:
1.
Dropped
If the sum is greater than or equal to a predefined Drop threshold then the email is
considered to be definitely Spam and is discarded or alternatively sent to a single, special
mailbox.
If it is discarded then the administrator has the option that an error message is sent back to
the sending SMTP server (this error message is similar to the one used with blacklisting).
2.
Flagged as Spam
If the sum is greater than or equal to a predefined Spam threshold then the email is
considered as probably being Spam but forwarded to the recipient with notifying text
inserted into it.
A Threshold Calculation Example
As an example, lets suppose that three DNSBL servers are configured: dnsbl1, dnsbl2 and dnsbl3.
Weights of 3, 2 and 2 are assigned to these respectively. The Spam threshold is then set to be 5.
Chapter 6: Security Mechanisms
403
