Ospf providing route redundancy – Amer Networks E5Web GUI User Manual
Page 298
Under OSPF, this exchange of routing information is completely automatic.
OSPF Provides Route Redundancy
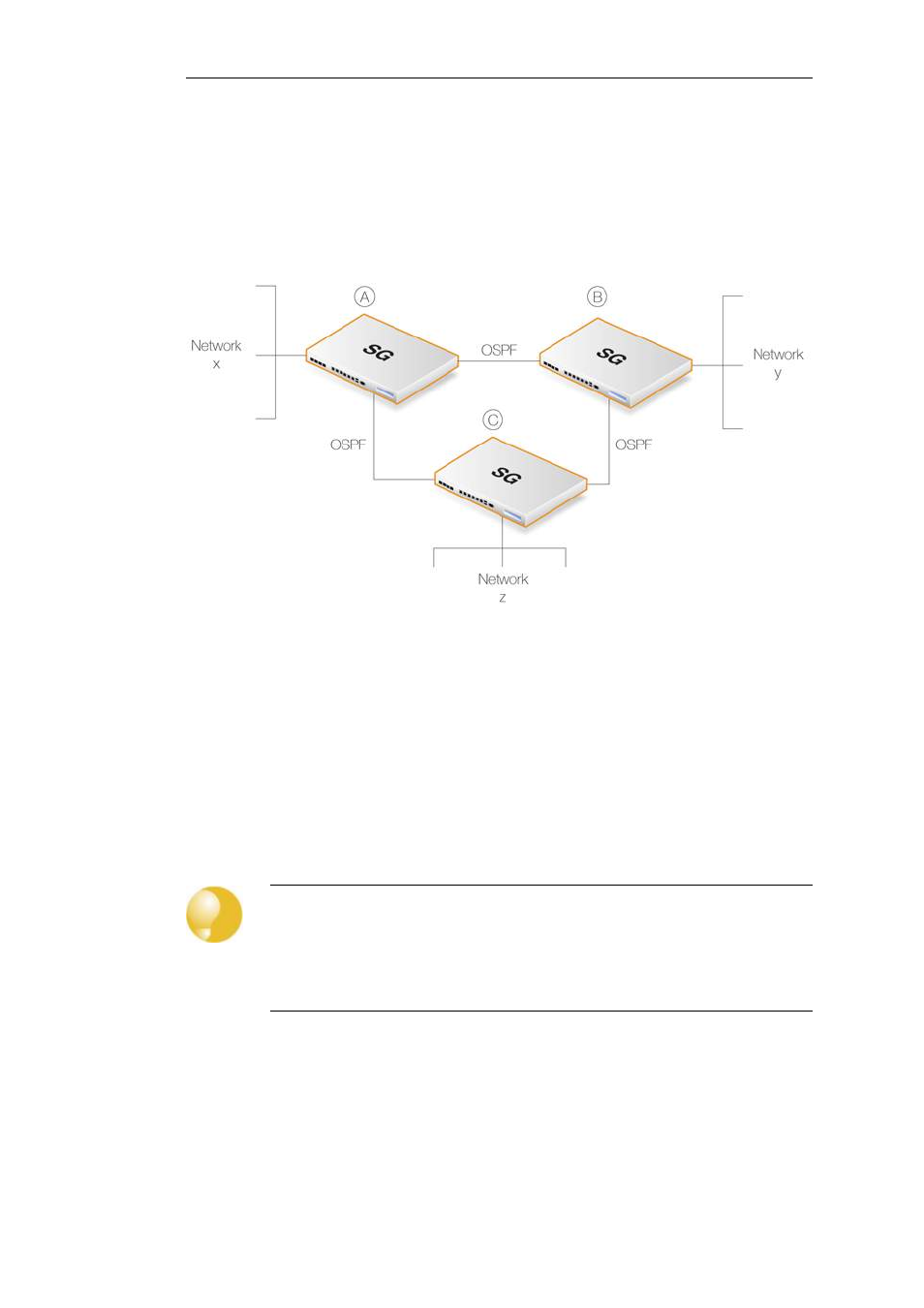
If we now take the above scenario and add a third Clavister Security Gateway called C then we
have a situation where all three security gateways are aware, through OSPF, of what networks
are attached to the other gateways. This is illustrated below.
Figure 4.12. OSPF Providing Route Redundancy
In addition, we now have route redundancy between any two of the security gateways. For
example, if the direct link between A and C fails then OSPF allows both security gateways to
know immediately that there is an alternate route between them via gateway B.
For instance, traffic from network X which is destined for network Z will be routed automatically
through security gateway B.
From the administrator's point of view, only the routes for directly connected networks need to
be configured on each security gateway. OSPF automatically provides the required routing
information to find networks connected to other security gateways, even if traffic needs to
transit several other gateways to reach its destination.
Tip: Ring topologies always provide alternate routes
When designing the topology of a network that implements OSPF, arranging Clavister
Security Gateways in a circular ring means that any security gateway always has two
possible routes to any other. Should any one inter-gateway connection fail, an
alternative path always exists.
A Look at Routing Metrics
In discussing dynamic routing and OSPF further, an understanding of Routing Metrics can be
useful and a brief explanation is given here.
Routing metrics are the criteria that a routing algorithm will use to compute the "best" route to a
destination. A routing protocol relies on one or several metrics to evaluate links across a network
Chapter 4: Routing
298
