Ospf components, Ospf router process, Cos core ospf objects – Amer Networks E5Web GUI User Manual
Page 304
having a route in its routing tables for the destination.
The key aspect of an OSPF setup is that connected Clavister Security Gateways share the
information in their routing tables so that traffic entering an interface on one of the security
gateways can be automatically routed so that it exits the interface on another gateway which is
attached to the correct destination network.
Another important aspect is that the security gateways monitor the connections between each
other and route traffic by an alternate connection if one is available. A network topology can
therefore be designed to be fault tolerant. If a connection between two security gateways fails
then any alternate route that also reaches the destination will be used.
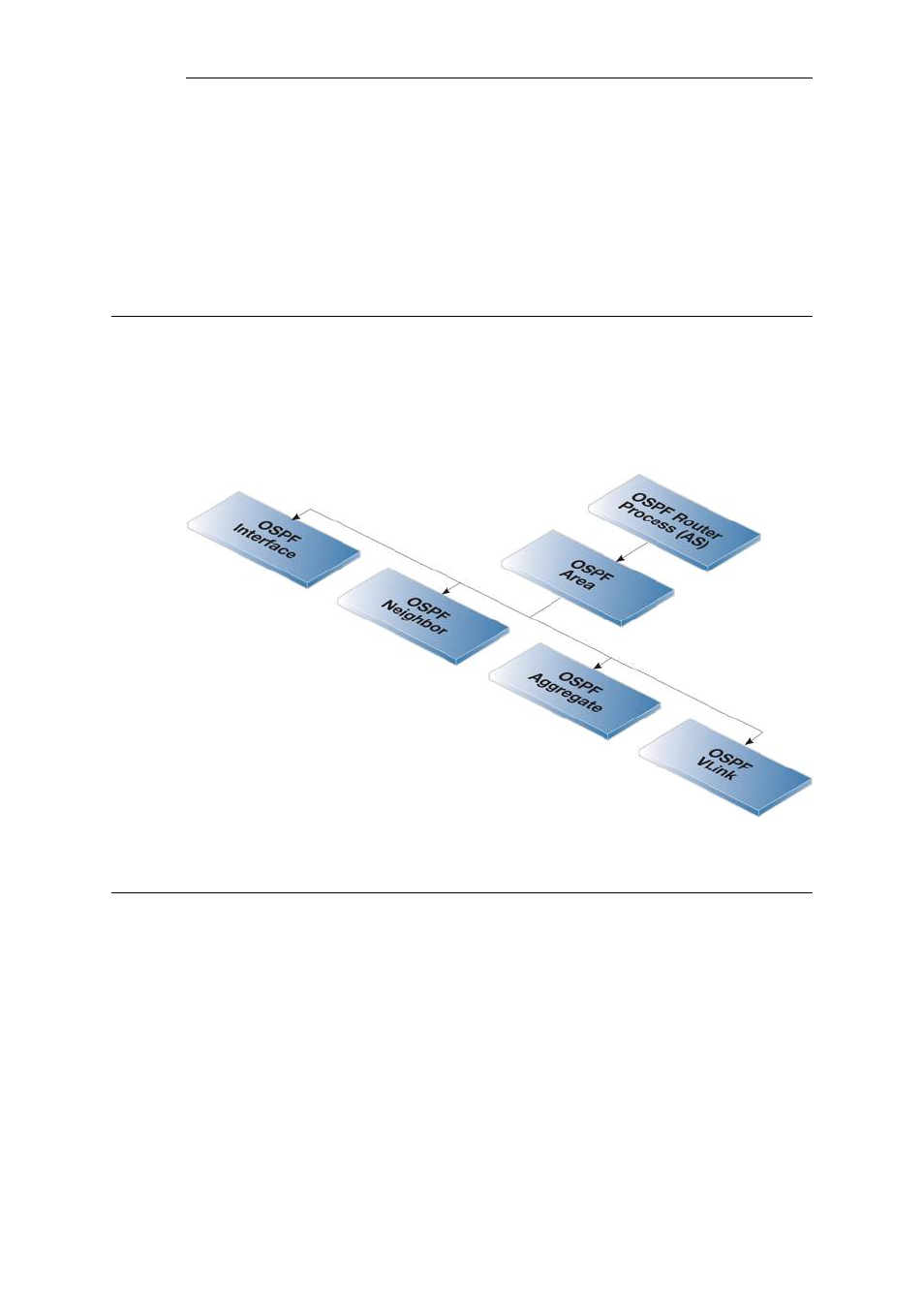
4.6.3. OSPF Components
This section looks at the cOS Core objects that need to be configured for OSPF routing. Defining
these objects creates the OSPF network. The objects should be defined on each Clavister Security
Gateway that is part of the OSPF network and should describe the same network.
An illustration of the relationship between cOS Core OSPF objects is shown below.
Figure 4.15. cOS Core OSPF Objects
4.6.3.1. OSPF Router Process
This object defines the autonomous system (AS) which is the top level of the OSPF network. A
similar Router Process object should be defined on each Clavister Security Gateway which is part
of the OSPF network.
General Parameters
Name
Specifies a symbolic name for the OSPF AS.
Router ID
Specifies the IP address that is used to identify the router in a
AS. If no Router ID is configured, the security gateway
computes the Router ID based on the highest IP address of any
Chapter 4: Routing
304
