Modulation and encoding types, Scrambling types, Interleaver (reed-solomon codec) – Comtech EF Data C5 User Manual
Page 40: 2 modulation and encoding types, 3 scrambling types, 4 interleaver (reed-solomon codec)
Specifications
C5/K1/K3 Integrated Satellite Terminal System
2–6
Rev. 0
2.1.4.2
Modulation and Encoding Types
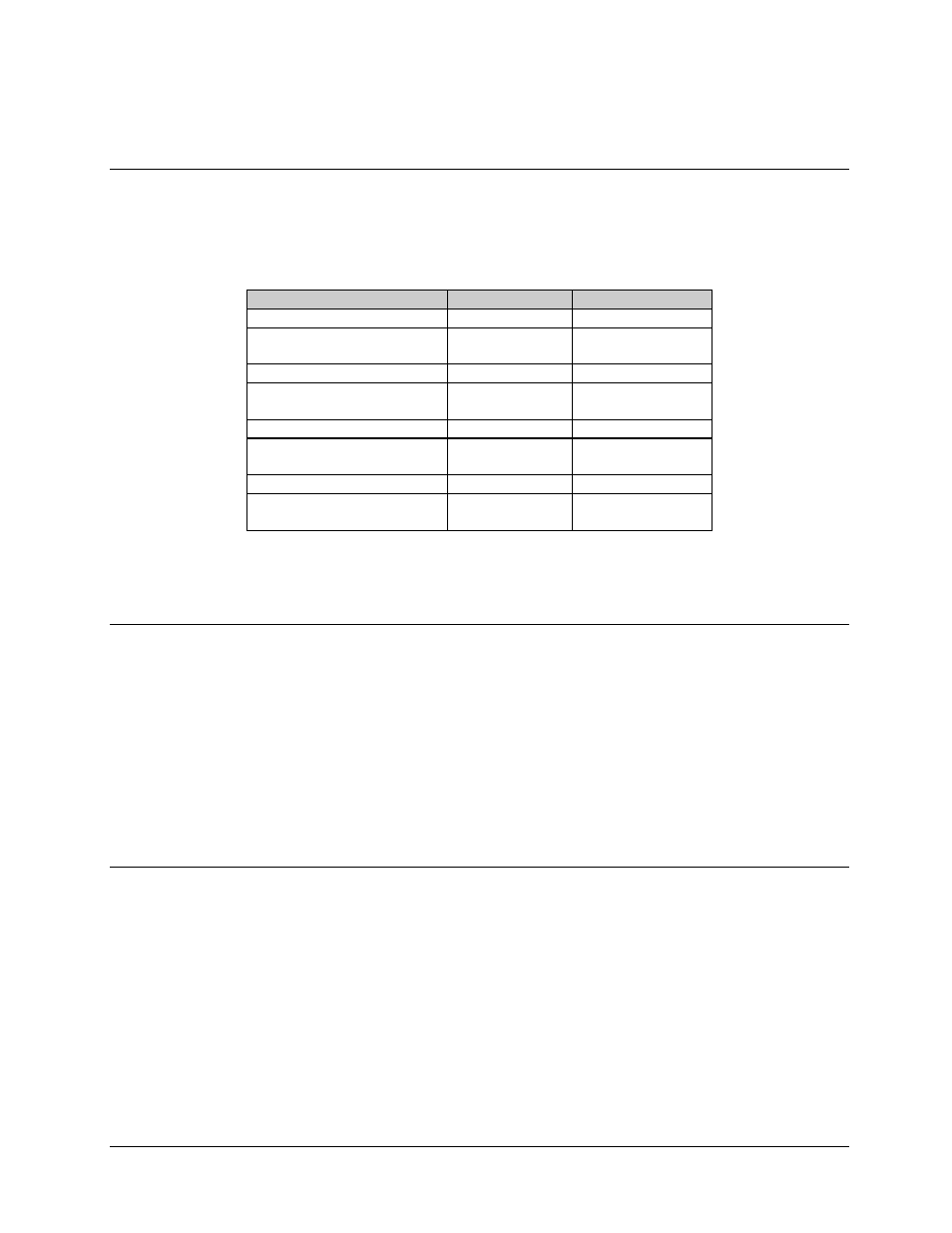
Refer to Table 2-6 for combinations of modulation and forward error correction encoding.
Table 2-6. C-Band Modulation Encoding Types
Encoder
Code Rate
Modulation
Viterbi, K7
1/2
BPSK
Viterbi, K7
Reed-Solomon
1/2
225/205 Closed
BPSK
BPSK
Viterbi, K7
1/2, 3/4, 7/8
QPSK
Viterbi, K7
Reed-Solomon
1/2, 3/4, 7/8
225/205 Closed
QPSK
QPSK
Sequential
1/2
BPSK
Sequential
Reed Solomon
1/2
225/205 Closed
BPSK
BSPK
Sequential (EFD, CSD, FDC)
1/2, 3/4, 7/8
QPSK
Sequential
Reed-Solomon
1/2, 3/4, 7/8
225/205 Closed
QPSK
QPSK
Note: Reed-Solomon concatenated coding uses INTELSAT IESS 308/309 polynomial and
is fully capable with SDM-300/SDM-300A closed network operation.
2.1.4.3 Scrambling
Types
The customer may select one of the following:
( CCITT V.35 (EFData/Comstream compatible). Sequential only.
( CCITT V.35 INTELSAT modified. Viterbi only.
( Fairchild compatible. Sequential only.
( 2
15
–1 Synchronous for use in ASYNC overhead mode.
( Modified V.35 (Closed Network Reed-Solomon).
( None.
2.1.4.4
Interleaver (Reed-Solomon Codec)
Depth 8 (Closed Network, ASYNC).
Note: The Reed-Solomon depth 8 interleaver is based on the IESS-310 specification for
8PSK and is adapted for QPSK/PRSK operation.
