Lull 944E-42 Service Manual User Manual
Page 78
Boom
3.30
Model 644E-42/944E-42
Rev. 6/04
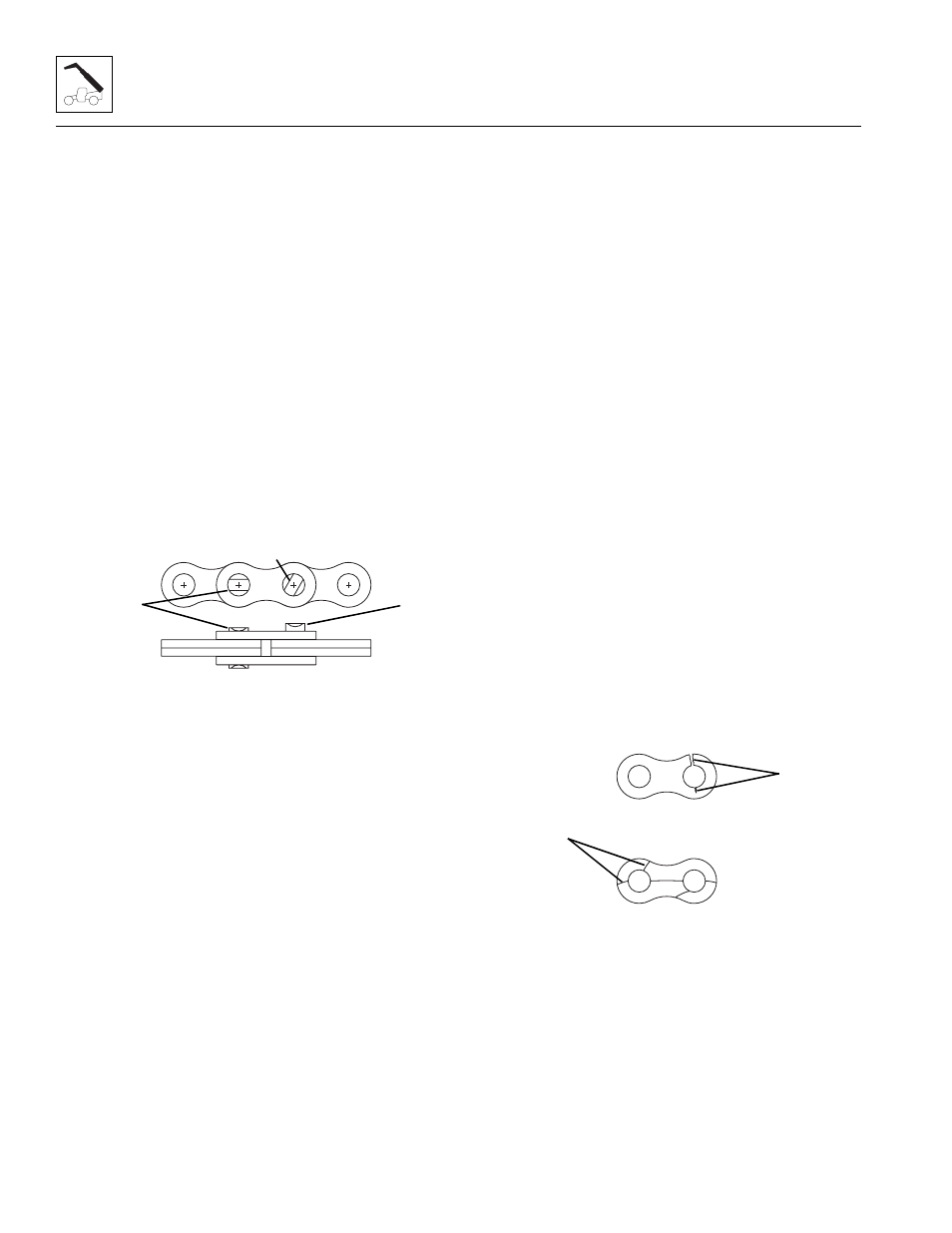
Turning or Protruding Pins
Highly loaded chain, operating with inadequate
lubrication, can generate abnormal frictional forces
between pin and link plates. When chain is allowed to
operate in this condition, a pin or series of pins, can begin
to twist out of a chain, resulting in failure.
Examine the pin head rivets to determine if the “VEE” flats
are still in correct alignment (1). Chain with rotated/
displaced heads (2) or abnormal pin protrusion (3) must
be replaced immediately. (Refer to Section 3.4.5, “Boom
Extend and Retract Chains Removal and Replacement.”)
DO NOT attempt to repair the chain by welding or driving
the pin(s) back into the chain. Once the press fit integrity
between outside plates and pins has been altered, it
cannot be restored.
Any wear pattern on the pin heads or the sides of the link
plates indicates misalignment in the system. This
condition damages the chain as well as increases
frictional loading and must be corrected.
Cracked Plates
Inspect the chains very carefully, front and back as well
as side to side, for any evidence of cracked plates. If any
one crack is discovered, the chain must be replaced in its
entirety. (Refer to Section 3.4.5, “Boom Extend and
Retract Chains Removal and Replacement.”)
• Fatigue Cracking - Fatigue cracks (4) are a result
of repeated cyclic loading beyond the chain’s
endurance limit. The size of the load and the
frequency of its occurrence are factors which
determine when fatigue failure will occur. The
loading can be continuous or intermittent
(impulse load).
• Stress Corrosion Cracking - The outside link
plates are particularly susceptible to stress
corrosion cracking (5). Like fatigue cracks, these
initiate at the point of highest stress but tend to
extend in an arc-like path between holes in the
pin plate. More than one crack can often appear
on a link plate. In addition to rusting, this
condition can be caused by exposure to an acidic
or caustic medium or atmosphere.
Stress corrosion is an environmentally assisted failure.
Two conditions must be present: corrosive agent and
static stress. In the chain, static stress is present at the
aperture due to the press fit pin. No cyclic motion is
required, and the plates can crack during idle periods.
• Corrosion Fatigue Cracking - Corrosion fatigue
cracks are very similar to fatigue cracks (4) in
appearance. They generally begin at the
aperture and grow perpendicular to the chain
pitch line. Corrosion fatigue is not the same as
stress corrosion. Corrosion fatigue is the
combined action of an aggressive environment
and cyclic stress, not a static stress alone, as in
stress corrosion.
MM2060
1
2
3
MM2080
MM2070
4
5
