Application monitor mode – H3C Technologies H3C Intelligent Management Center User Manual
Page 19
5
Class Type Remarks
VMware ESX
VMware ESX 5.0
Storage device monitor HP
MSA
P2000
N/A
Applications monitored by APM include operating systems, databases, application servers, services,
and middleware. These applications provide key services for enterprises and organizations.
After an operator adds applications to APM, APM collects monitor data and evaluates the availability
and health status of the applications. Application monitor includes the following types based on the
application scope:
•
Common monitor—Monitors the availability and health status of one class of applications based
on their common characteristics. For example, you can use POP3 and SMTP application monitors
to monitor multiple email systems that provide POP3 service and SMTP service.
•
Specific monitor—Monitors the availability and health status of one type of applications based on
their specific indexes. Specific monitor gets more application index data than common monitor.
You can implement in-depth monitor on applications through specific monitor, for example,
Exchange 2003 application monitor and Exchange 2007 application monitor.
APM can monitor most mainstream network applications through common monitor and specific monitor.
Application monitor mode
Before APM monitors applications, make sure the APM server and the hosts where applications are
deployed can reach each other.
APM monitors applications in the following modes:
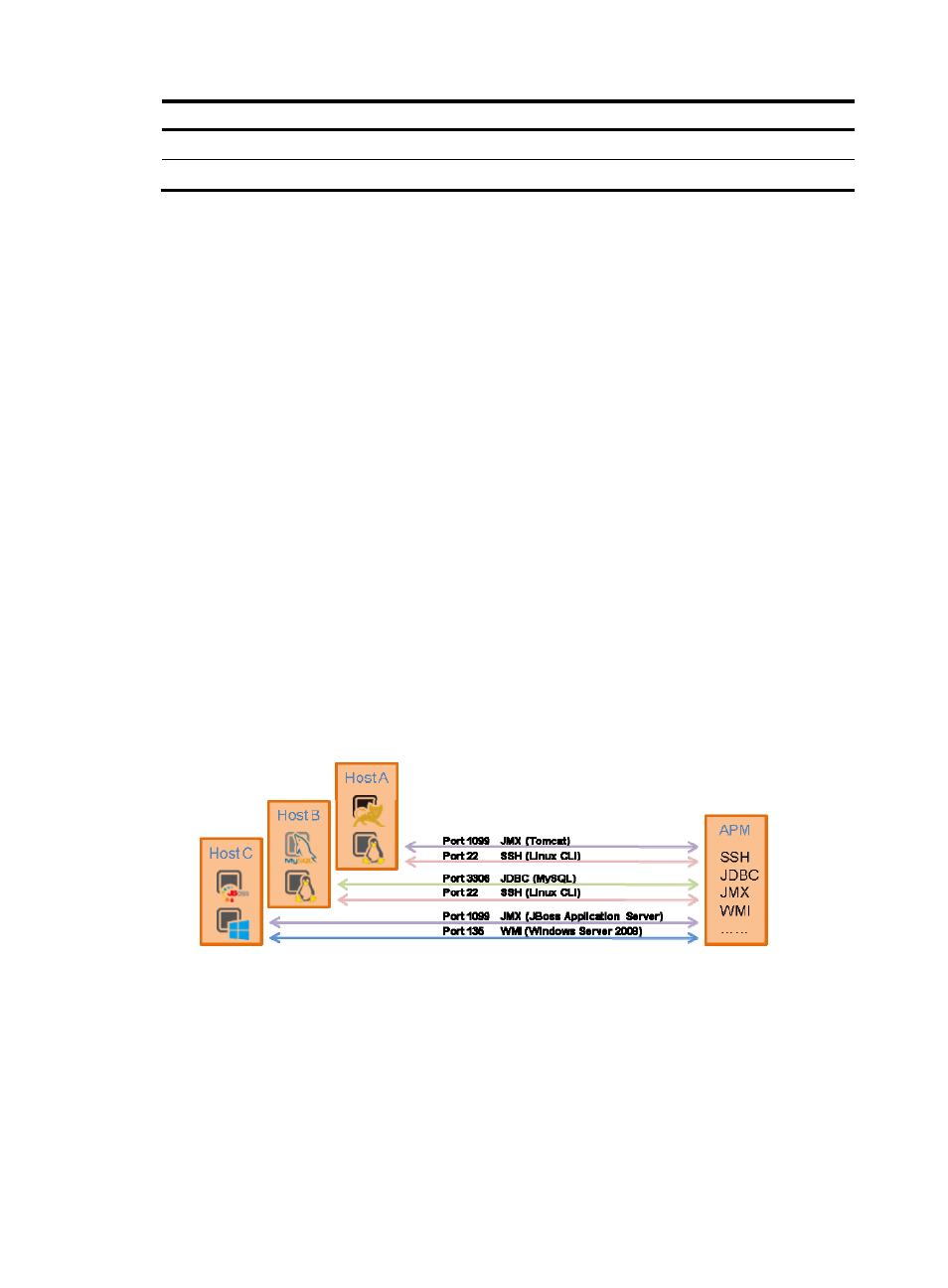
•
Remote monitor—APM accesses an application to obtain monitor index data by using SSH, Telnet,
SNMP, WMI, JMX, API, or JDBC, as shown in
Figure 2 Remote monitor
•
Local monitor—In this mode, you must deploy an APM agent on the host where the application is
deployed. The APM agent obtains monitor index data of the application by using SSH, Telnet,
SNMP, WMI, JMX, API, or JDBC. APM periodically communicates with the APM agent by using
Agent messages to obtain monitor index data.
