Create a spread or choke – Adobe Illustrator CS3 User Manual
Page 434
ILLUSTRATOR CS3
User Guide
428
Height/Width set to 50% (left) compared to 200% (right)
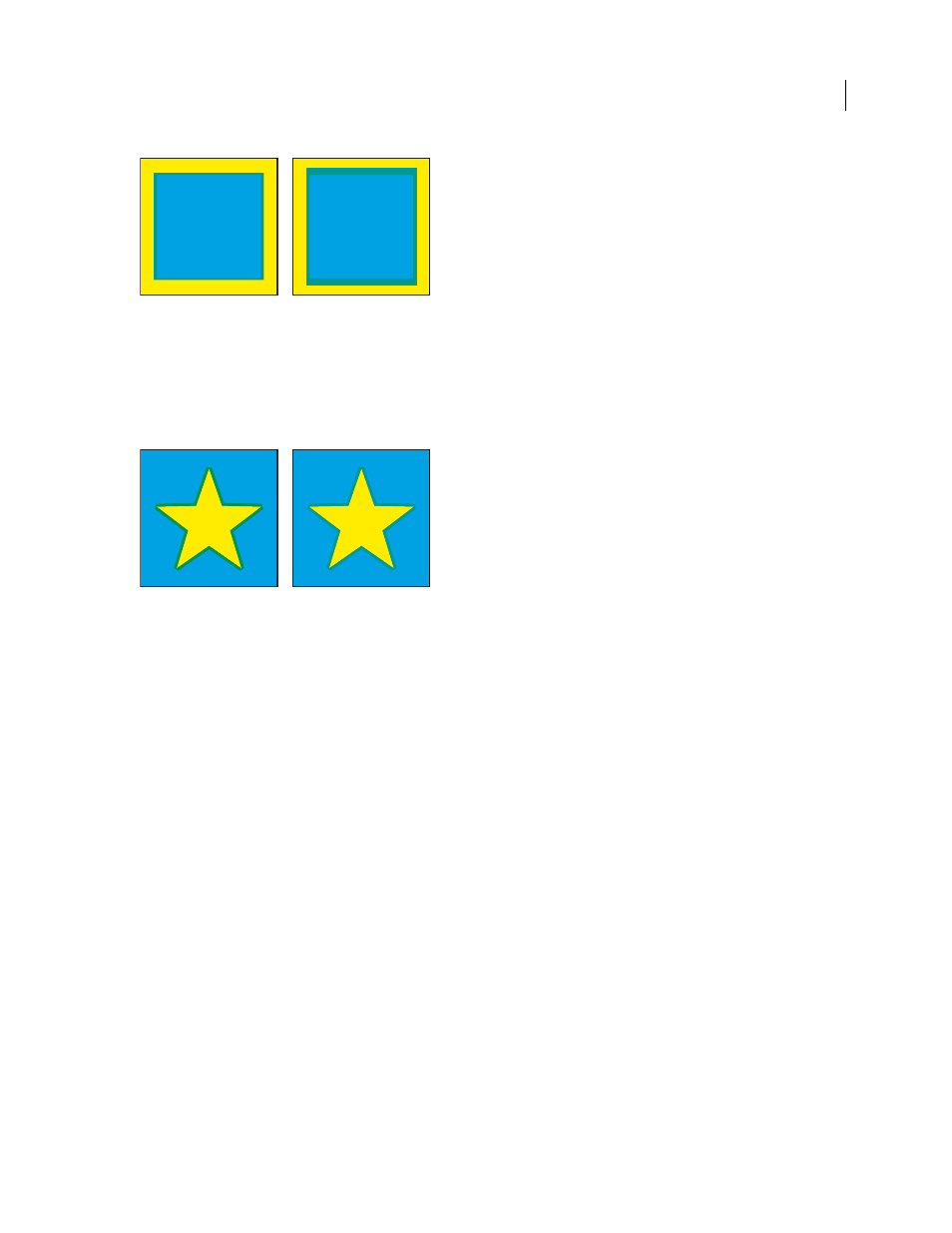
Tint Reduction
Reduces the tint of the lighter color being trapped; the darker color remains at 100%. This option is
useful when trapping two light-colored objects, where the trap line may show through the darker of the two colors,
resulting in an unsightly dark border. For example, if you trap a light yellow object into a light blue object, a bright
green border is visible where the trap is created. Check with your print shop to find out what percentage of tint is
most appropriate given the type of press, inks, paper stock, and so on being used.
Tint reduction value of 100% (trap contains 100% of lighter color) compared to tint reduction value of 50% (trap contains 50% of lighter color)
Traps With Process Color
Converts spot-color traps to equivalent process colors. This option creates an object of the
lighter of the spot colors and overprints it.
Reverse Traps
Traps darker colors into lighter colors. This option does not work with rich black—that is, black that
contains additional CMY inks.
Precision (as effect only)
Affects how precisely an object's path is calculated. The more precise the calculation, the
more accurate the drawing and the more time is required to generate the resulting path.
Remove Redundant Points (as effect only)
Removes unnecessary points.
Create a spread or choke
For more precise control of trapping and for trapping complex objects, you can create the effect of a trap by stroking
an object and setting the stroke to overprint.
1
Select the topmost object of the two objects that must trap into each other.
2
In the Stroke box in the Tools panel or the Color panel, do one of the following:
•
Create a spread by entering the same color values for the Stroke as appear in the Fill box. You can change the
stroke’s color values by selecting the stroke and then adjusting its color values in the Color panel. This method
enlarges the object by stroking its boundaries with the same color as the object’s fill.
