Plc ladder logic example – Rockwell Automation 2100-GK61 DeviceNet to SCANport User Manual
Page 81
Publication 2100-UM001B-EN-P – January 2001
Ladder Logic Programming—Including Reading Inputs
5-7
PLC Ladder Logic Example
The following example uses a PLC-5, a 1771-SDN DeviceNet
scanner, and a 2100-GK61 to control a 1305, 1336 PLUS, or 1336
PLUS II drive.
The example program shows how to obtain status information from
the drive and how to control it (e.g., starting the drive, stopping the
drive, jogging the drive, sending reference, and clearing faults). When
you understand this example, you should be able to customize the
program to fit your application needs.
The example assumes that there is an operator’s station wired to an
I/O module in slot zero of module group zero of rack zero.
Important: You may want to verify a device has not failed using
word 0 of block transfer 62 before sending control data. If a device
has failed, use block transfer 52 to find out which device failed. Refer
to the 1771-SDN DeviceNet Scanner Module Manual, Publication
1771-5.14, for more information.
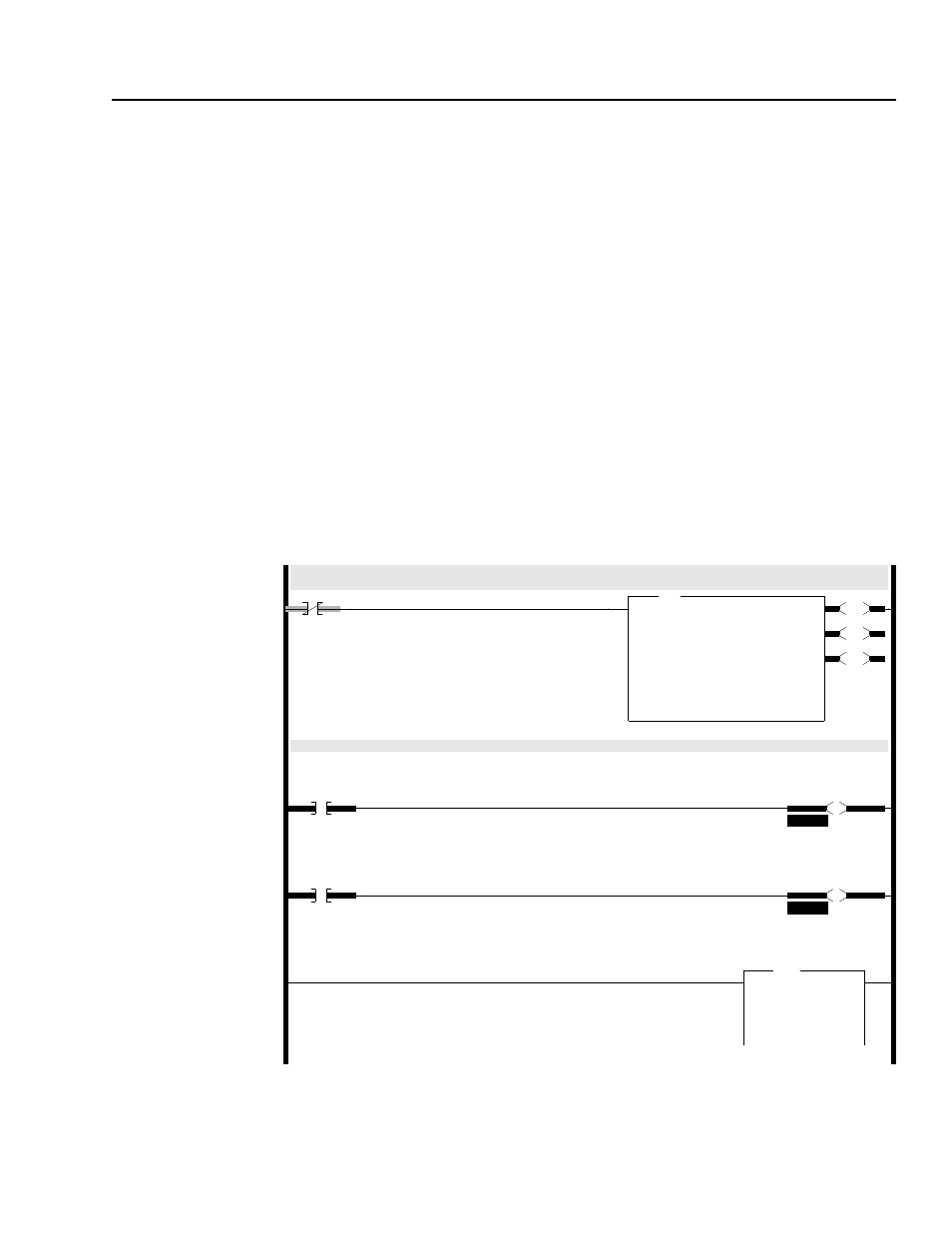
Figure 5.2
Example PLC Ladder Logic Program
The scanner gathers drive status information via DeviceNet.
The Block Transfer Read in this rung then moves the drive status data from the scanner to the PLC’s N9 data file.
0000
BT20:0
EN
EN
DN
ER
BTR
Block Transfer Read
Module Type Generic Block Transfer
Rack
000
Group
0
Module
0
Control Block
BT20:0
Data File
N9:0
Length
62
Continuous
No
BTR
Rungs 0001 through 0003 move the drive status from the Block Transfer Read data file to an operator display.
0001
N9:1
1
1305 Drive
RUNNING
Status Bit
O:000
10
Operator Display
Drive Running
Status Bit
0002
N9:1
7
1305 Drive
FAULTED
Status Bit
O:000
11
Operator Display
Drive Faulted
Status Bit
0003
MOV
Move
Source
N9:2
0<
Dest
N21:1
0<
MOV
Operator Display
Drive Feedback
Status Word
