7 usage example of the modbus function, 7 usage example of the modbus function -15, App index – Yokogawa Removable Chassis DX1000N User Manual
Page 109: System configuration and actions
2-15
IM 04L41B01-17E
Using the Serial Interface
1
2
3
4
5
6
App
Index
2.7 Usage Example of the Modbus Function
Explains the setting example for both Modbus master and slave on DX1000s connected
via the serial communication. This section refers to the DX1000 set to be a Modbus
master as DX1000 master and the DX1000 set to be a Modbus slave as DX1000 slave.
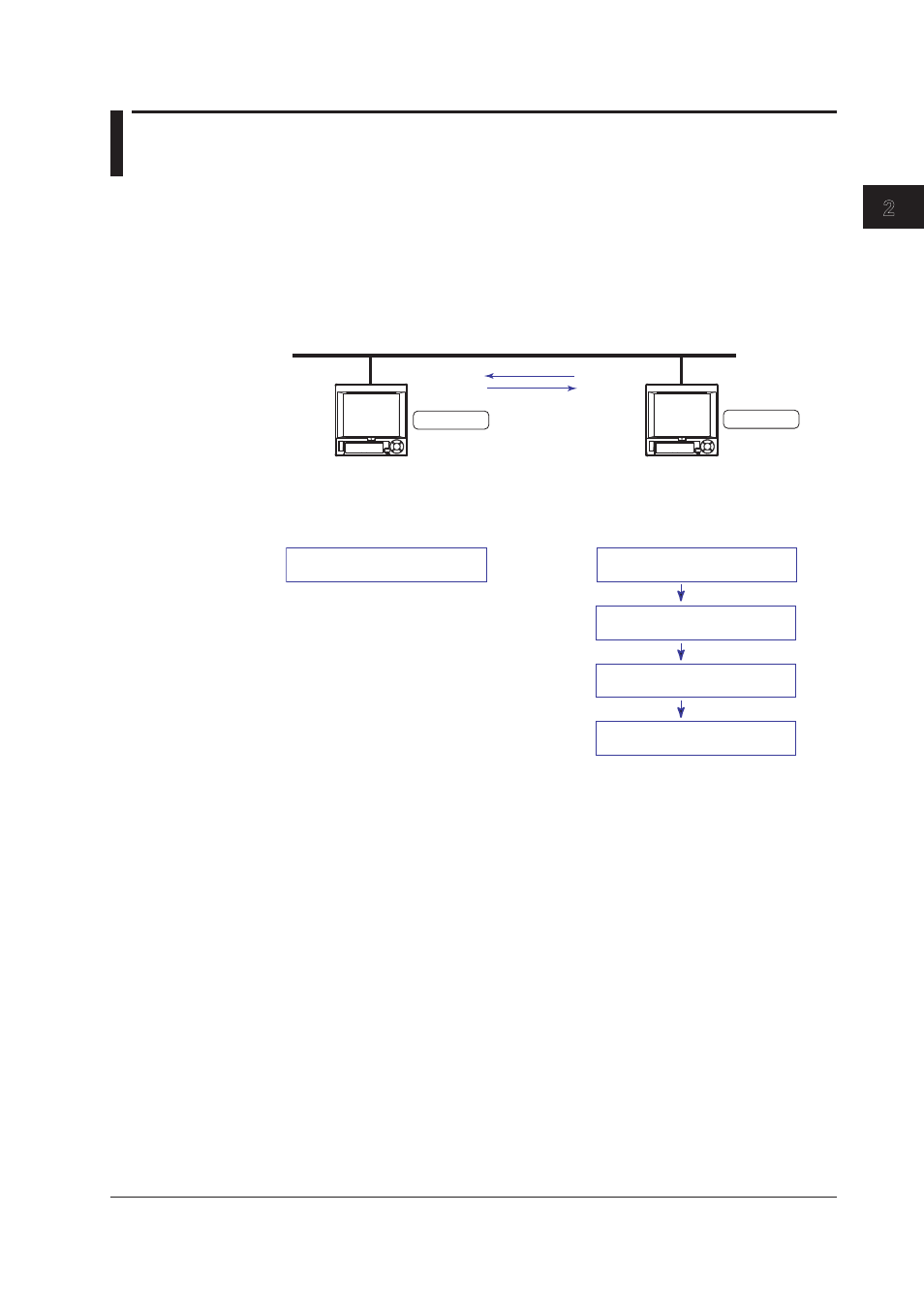
System Configuration and Actions
Uses the measurement channel, computation channel, and communication input data as
described in the figure below. Assumes other conditions are set properly.
DX1000 slave
(Modbus slave)
Serial communication
Reads a measured data from the slave.
Displays the data using the computation
channel (/M1 or /PM1 option).
DX1000 master
(
Modbus
master)
Measurement channel 1
Input range: -2.0000 to 2.0000 V
Computation channel 101
-
2.0000 to 2.0000V
Communication input data C01
Address: 1
Address: 2
Start the computation
Display the channel on Group 1
Measured data
Command
Action
• The DX1000 master reads the measured value of channel 1 on the DX1000 slave into
the communication input data C01. C01 is displayed on a computation channel 101
by including the data in the equation. The computation channel 101 is assigned to
Group1.
• The measured value of channel 1 on the DX1000 slave is transferred to the DX1000
master as an integer in the range of –20000 to 20000.
• The DX1000 master displays the read data as –2.0000 to 2.0000 V on the
computation channel 101. The following conversion is applied.
Value on the computation channel 101 of the DX master
= Communication input data C01 x 0.0001
