Mpls data forwarding – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 64
53
Invalid, the packet must be forwarded through MPLS. The LSR then looks for the corresponding
NHLFE entry according to the Token value to determine the label operation to be performed.
•
Incoming Label Map (ILM): ILM maps each incoming label to a set of NHLFEs. It is used to forward
labeled packets. When an LSR receives a labeled packet, it looks for the corresponding ILM entry.
If the Token value of the ILM entry is not null, the LSR looks for the corresponding NHLFE entry to
determine the label operation to be performed.
NOTE:
FTN and ILM are associated with NHLFE through Token.
MPLS data forwarding
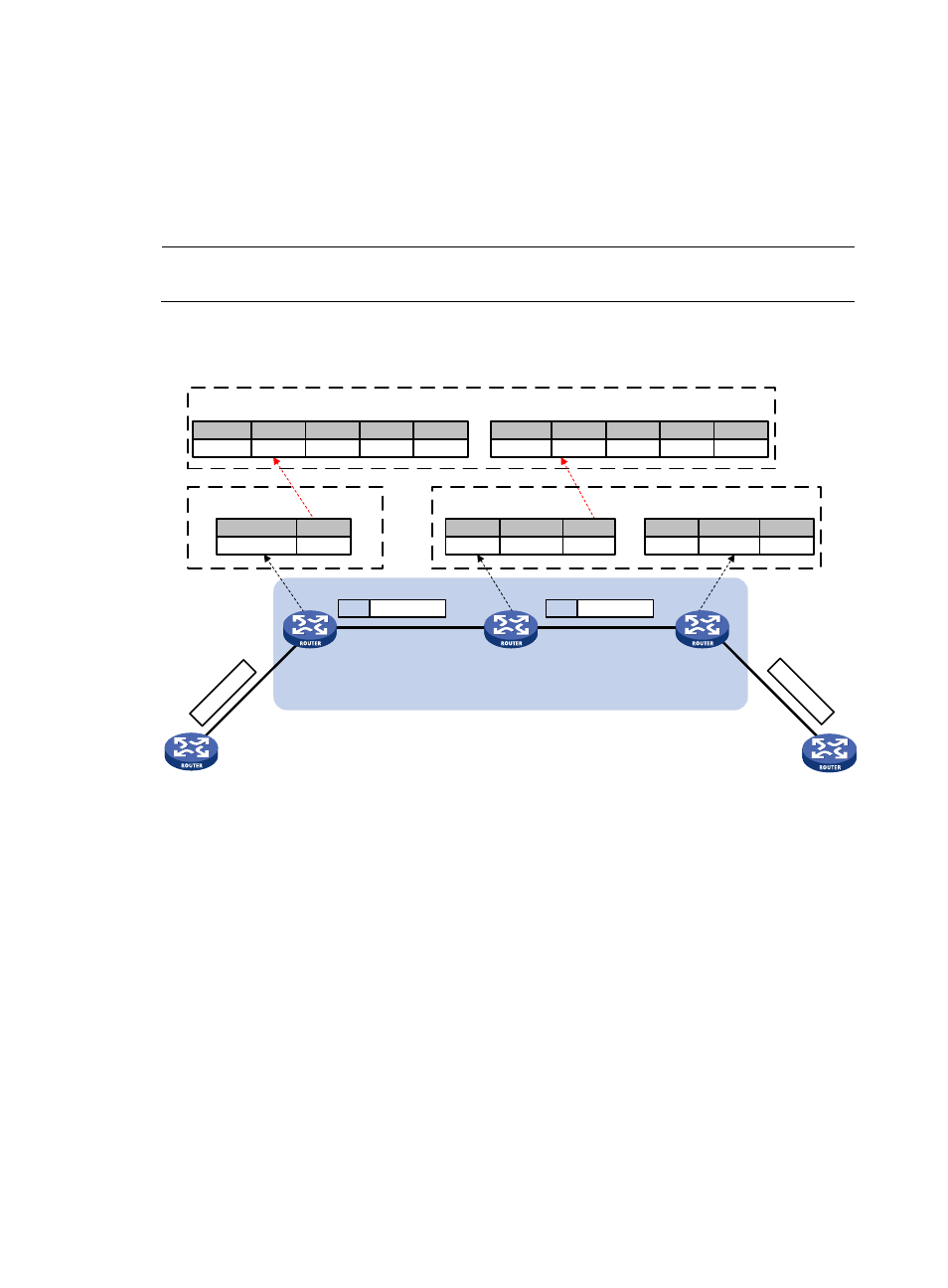
Figure 18 MPLS forwarding process diagram
Router A
Router B
Ingress
Router C
Router D
Egress
Router E
IP:4
0.1
.1.
2
MPLS domain
40
IP:40.1.1.2
50
IP:40.1.1.2
IP:40
.1.1
.2
NHLFE
ILM
FIB
GE1/0/2
Out int
Oper
Out label
Swap
50
Token
0
Next hop
30.1.1.2
GE1/0/2
Out int
Oper
Out label
Push
40
Token
0
Next hop
20.1.1.2
50
In label
Token
In int
GE1/0/1
40
In label
Token
0
In int
GE1/0/1
GE1/0/2
20.1.1.1/24
GE1/0/1
20.1.1.2/24
GE1/0/1
30.1.1.2/24
GE1/0/2
30.1.1.1/24
GE1/0/1
40.1.1.2/24
GE1/0/2
40.1.1.1/24
GE1/0/1
10.1.1.2/24
GE1/0/1
10.1.1.1/24
Dest
Token
40.1.1.0/24
0
In an MPLS domain, a packet is forwarded in the following procedure:
1.
Router B (the ingress LSR) receives a packet carrying no label. It determines the FEC of the packet
according to the destination address, and searches the FIB table for the Token value. Because the
Token value is not Invalid, Router B looks for the corresponding NHLFE entry that contains the
Token value. According to the NHLFE entry, Router B pushes label 40 to the packet, and forwards
the labeled packet to the next hop LSR (Router C) through the outgoing interface (Ethernet 1/2).
2.
Upon receiving the labeled packet, Router C looks for the ILM entry that contains the label 40 to
get the Token value. Because the Token value is not empty, Router C looks for the corresponding
NHLFE entry containing the Token value. According to the NHLFE entry, Router C swaps the
original label with label 50, and then forwards the labeled packet to the next hop LSR (Router D)
through the outgoing interface (Ethernet 1/2).
3.
Upon receiving the labeled packet, Router D (the egress) looks for the ILM entry according to the
label (50) to get the Token value. Because the Token is empty, Router D removes the label from the
packet. If the ILM entry records the outgoing interface, Router D forwards the packet through the
outgoing interface; if no outgoing interface is recorded, router D forwards the packet according to
the IP header of the packet.
