Address space overlapping, Vpn instance, Vpn-ipv4 address – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 14
3
Address space overlapping
Each VPN independently manages the addresses it uses. The assembly of such addresses for a VPN is
called an address space.
The address spaces of VPNs may overlap. For example, if both VPN 1 and VPN 2 use the addresses on
network segment 10.110.10.0/24, address space overlapping occurs.
VPN instance
In MPLS VPN, routes of different VPNs are identified by VPN instance.
A PE creates and maintains a separate VPN instance for each VPN at a directly connected site. Each
VPN instance contains the VPN membership and routing rules of the corresponding site. If a user at a site
belongs to multiple VPNs at the same time, the VPN instance of the site contains information about all of
the VPNs.
For independence and security of VPN data, each VPN instance on a PE maintains a relatively
independent routing table and a separate label forwarding information base (LFIB). VPN instance
information contains the following items: the LFIB, IP routing table, interfaces bound to the VPN instance,
and administration information of the VPN instance. The administration information of the VPN instance
includes the route distinguisher (RD), route filtering policy, and member interface list.
VPN-IPv4 address
Traditional BGP cannot process overlapping VPN routes. If, for example, both VPN 1 and VPN 2 use
addresses on the segment 10.110.10.0/24 and each advertise a route to the segment, BGP selects only
one of them, which results in the loss of the other route.
PEs use MP-BGP to advertise VPN routes and use VPN-IPv4 address family to solve the problem with
traditional BGP.
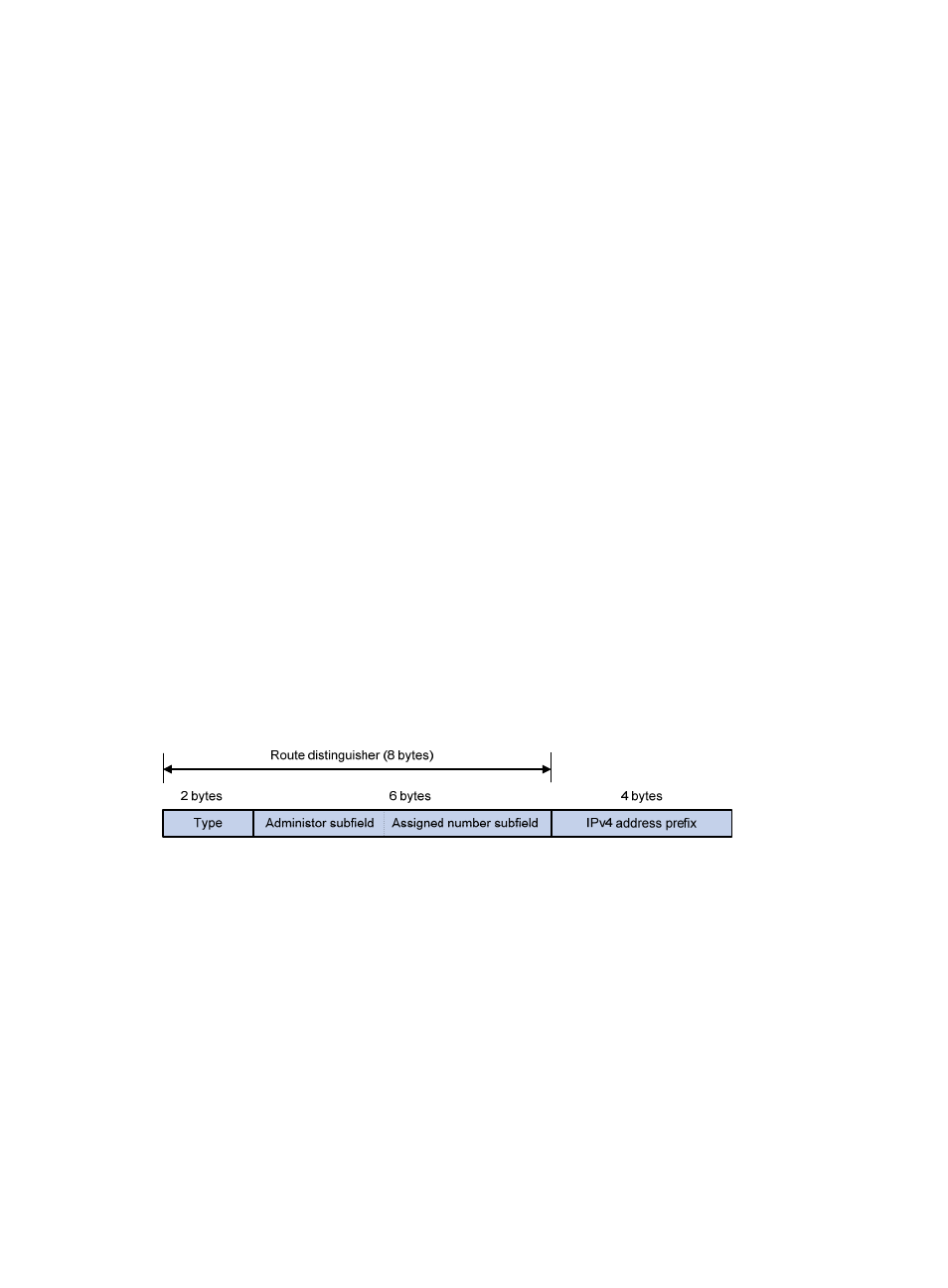
A VPN-IPv4 address consists of 12 bytes. The first eight bytes represent the RD, followed by a four-byte
IPv4 address prefix.
Figure 2 VPN-IPv4 address structure
When a PE receives an ordinary IPv4 route from a CE, it must advertise the VPN route to the peer PE. The
uniqueness of a VPN route is implemented by adding an RD to the route.
A service provider can independently assign RDs if the assigned RDs are unique. A PE can advertise
different routes to VPNs even if the VPNs are from different service providers and are using the same IPv4
address space.
Configure a distinct RD for each VPN instance on a PE, so that routes to the same CE use the same RD.
The VPN-IPv4 address with an RD of 0 is a globally unique IPv4 address.
By prefixing a distinct RD to a specific IPv4 address prefix, you get a globally unique VPN IPv4 address
prefix.
An RD can be related to an autonomous system (AS) number, in which case it is the combination of the
AS number and a discretionary number; or it can be related to an IP address, in which case it is the
combination of the IP address and a discretionary number.
