Mpls forwarding, Lfib – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 63
52
Figure 17 Independent label distribution control mode
•
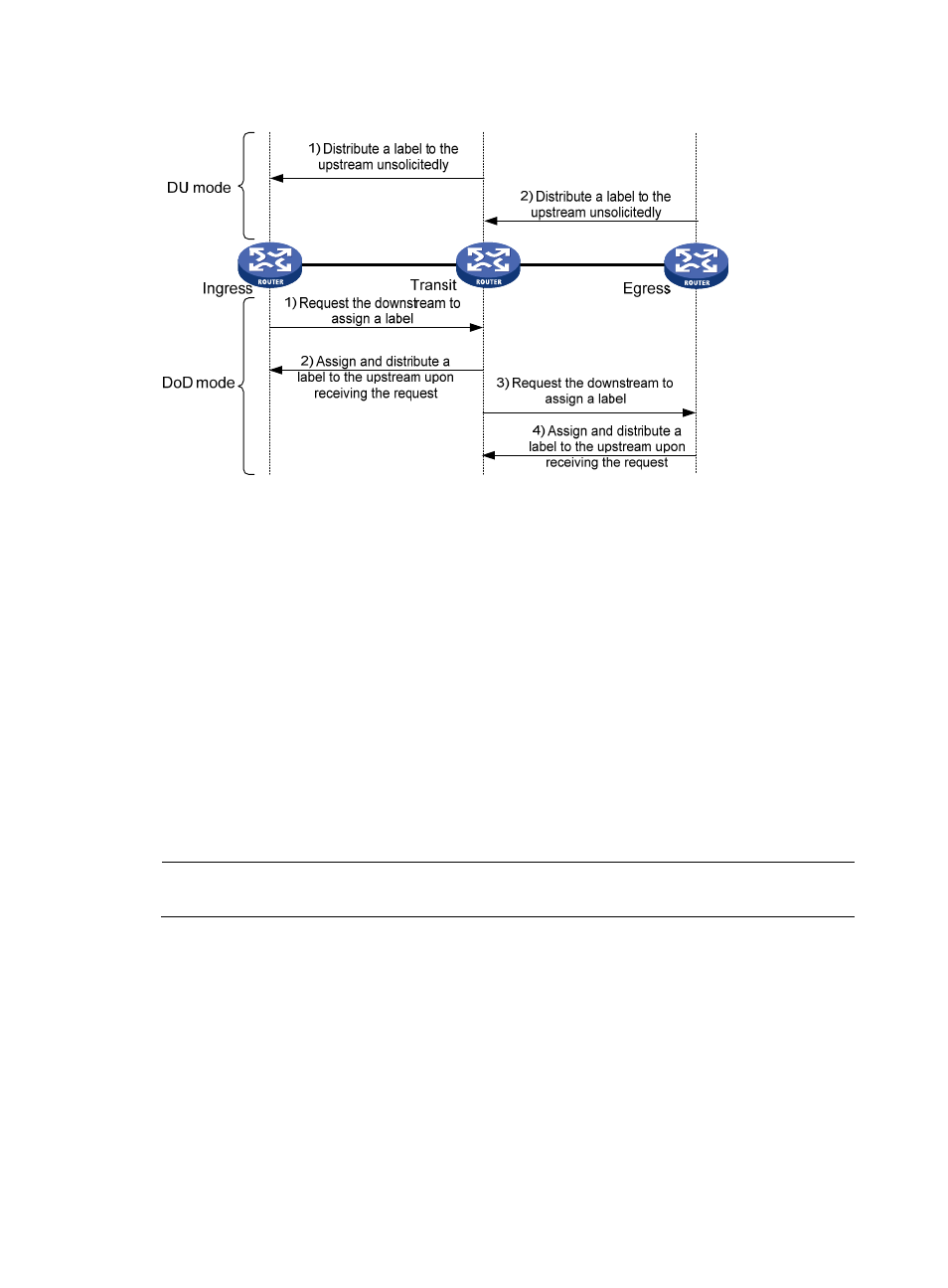
In ordered mode, an LSR distributes its label binding for a FEC upstream only when it receives a
label binding for the FEC from its downstream or it is the egress of the FEC. In
, label
distribution control is in ordered mode. In this case, if the label advertisement mode is DU, an LSR
will distribute a label upstream only when it receives a label binding for the FEC from its
downstream; if the label advertisement mode is DoD, after an LSR (Transit in this example) receives
a label request from its upstream (Ingress), the LSR (Transit) sends a label request to its downstream
(Egress). Then, after the LSR (Transit) receives the label binding from its downstream (Egress), it
distributes a label binding to the upstream (Ingress).
3.
Label retention modes
Label retention modes include liberal and conservative.
•
In liberal mode, an LSR keeps any received label binding regardless of whether the binding is from
the next hop for the FEC or not. This allows for quicker adaptation to route changes but will waste
label resources because LSRs keep extra labels.
•
In conservative mode, an LSR keeps only label bindings that are from the next hops for the FECs.
This allows LSRs to maintain fewer labels but makes LSRs slower in adapting to route changes.
NOTE:
The switch supports only the liberal mode.
MPLS forwarding
LFIB
An LFIB comprises the following table entries.
•
Next Hop Label Forwarding Entry (NHLFE): Describes the label operation to be performed. It is
used to forward MPLS packets.
•
FEC to NHLFE (FTN) map: FTN maps each FEC to a set of NHLFEs at the ingress LSR. The FTN map
is used for forwarding unlabeled packets that need MPLS forwarding. When an LSR receives an
unlabeled packet, it looks for the corresponding FIB entry. If the Token value of the FIB entry is not
