Basic concepts, Protection – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 106
95
FRR
FRR provides a quick per-link or per-node protection on an LSP.
In this approach, once a link or node fails on a path, FRR comes up to reroute the path to a new link or
node to bypass the failed link or node. This can happen in as fast as 50 milliseconds, thereby minimizing
data loss.
Once a link or node on an LSP configured with FRR fails, traffic is switched to the protection link and the
headend of the LSP starts attempting to set up a new LSP.
Basic concepts
The following are concepts that FRR involves throughout this document:
•
Primary LSP: The protected LSP.
•
Bypass LSP: An LSP used to protect the primary LSP.
•
Point of local repair (PLR): The ingress of the bypass LSP. It must be located on the primary LSP but
must not be the egress.
•
Merge point (MP): The egress of the bypass LSP. It must be located on the primary LSP but must not
be the ingress.
Protection
FRR provides link protection and node protection for an LSP.
•
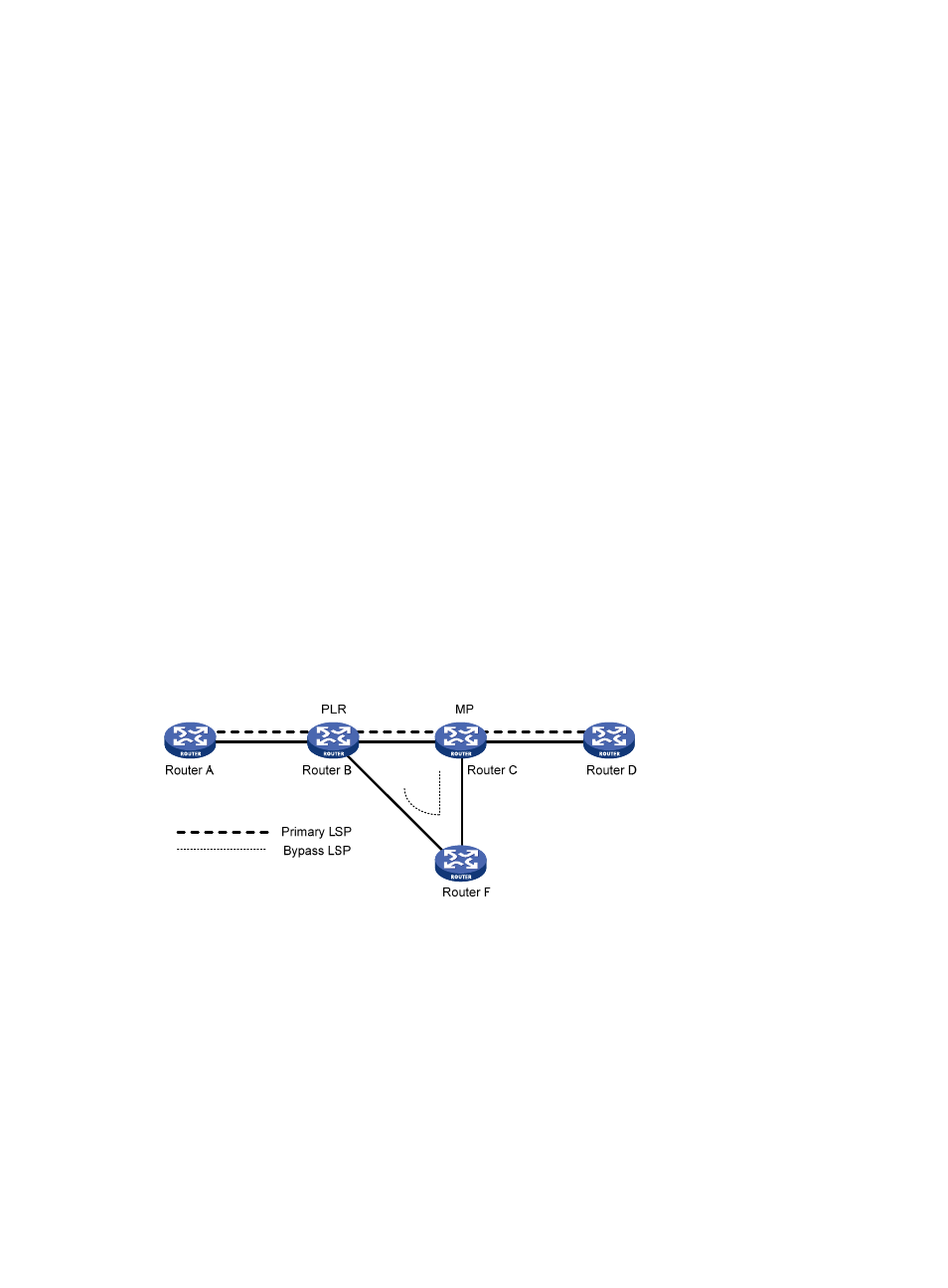
Link protection, where the PLR and the MP are connected through a direct link and the primary LSP
traverses this link. When the link fails, traffic is switched to the bypass LSP. As shown in
the primary LSP is Router A → Router B → Router C → Router D, and the bypass LSP is Router B →
Router F → Router C.
Figure 29 FRR link protection
•
Node protection, where the PLR and the MP are connected through a device and the primary LSP
traverses this device. When the device fails, traffic is switched to the bypass LSP. As shown in
, the primary LSP is Router A → Router B → Router C → Router D → Router E, and the bypass LSP
is Router B → Router F→ Router D. Router C is the protected device.
