Command authorization configuration example, Network requirements, Configuration procedure – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 267
15
[Device-radius-rad] primary authentication 192.168.2.20 1812
[Device-radius-rad] key authentication expert
[Device-radius-rad] server-type extended
[Device-radius-rad] user-name-format without-domain
[Device-radius-rad] quit
# Configure the default ISP domain system to use RADIUS authentication scheme rad for login users
and use local authentication as the backup.
[Device] domain system
[Device-isp-system] authentication login radius-scheme rad local
[Device-isp-system] authorization login radius-scheme rad local
[Device-isp-system] quit
# Add a local user named monitor, set the user password to 123, and specify to display the password
in cipher text. Authorize user monitor to use the telnet service and specify the level of the user as 1, that
is, the monitor level.
[Device] local-user monitor
[Device-luser-admin] password cipher 123
[Device-luser-admin] service-type telnet
[Device-luser-admin] authorization-attribute level 1
Command Authorization Configuration Example
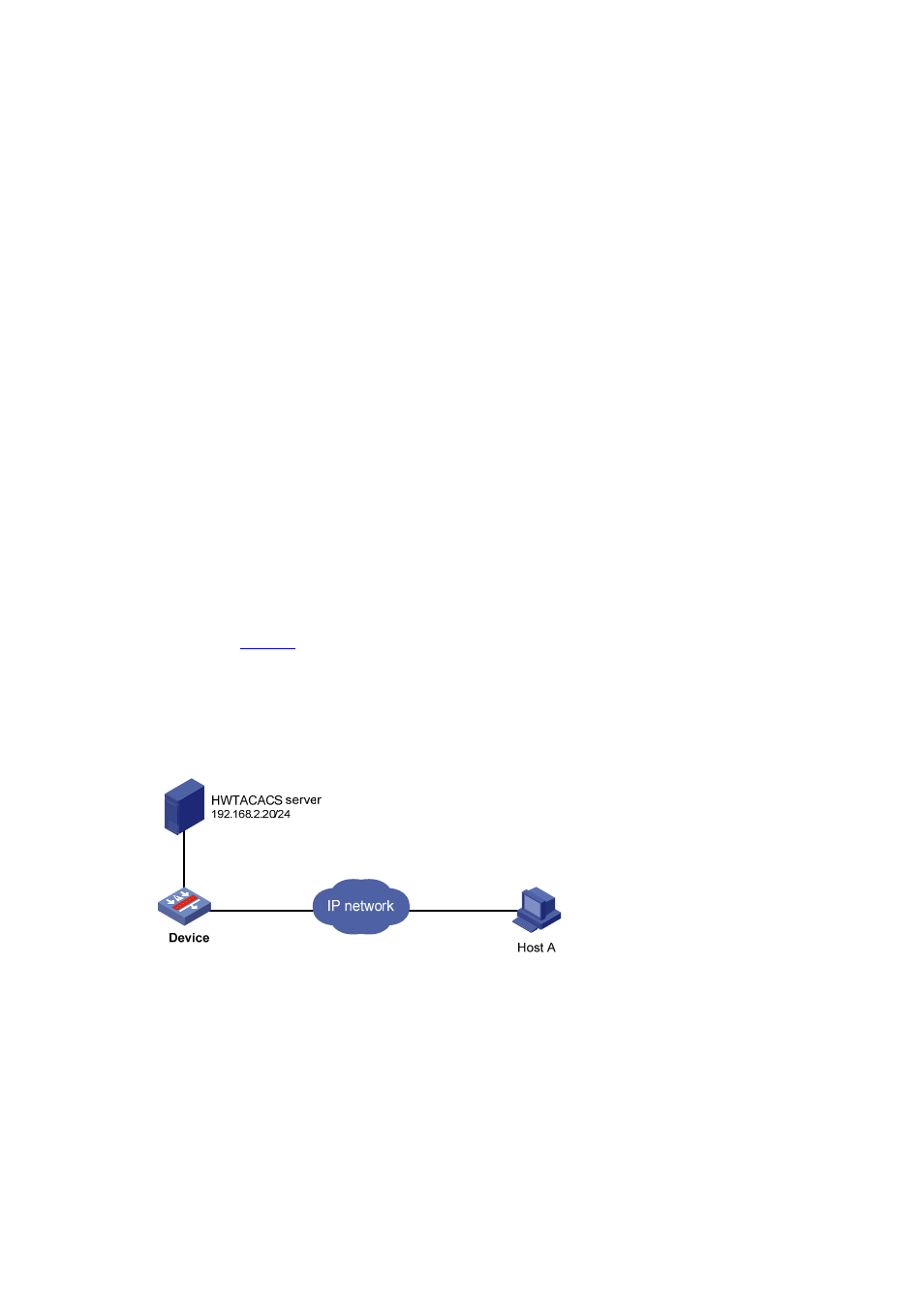
Network requirements
As shown in
, command levels should be configured for different users to secure Device: When
a user logs in to Device, the commands the user enter must be authorized by the HWTACACS server
before being executed. If the HWTACACS server fails to authorize the commands, local authorization is
used.
Figure 2 Network diagram for configuring command authorization
Configuration procedure
# Assign an IP address to Device to make Device and Host A, and Device and the HWTACACS server
reach each other. The configuration is omitted.
# Enable the telnet service on Device.
[Device] telnet server enable
