Tracert, Introduction, Configuring tracert – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 189: Configuration prerequisites
4
Tracert
Introduction
By using the tracert command, you can trace the Layer 3 devices involved in delivering an IP packet
from source to destination to check whether a network is available. This is useful for identification of
failed node(s) in the event of network failure.
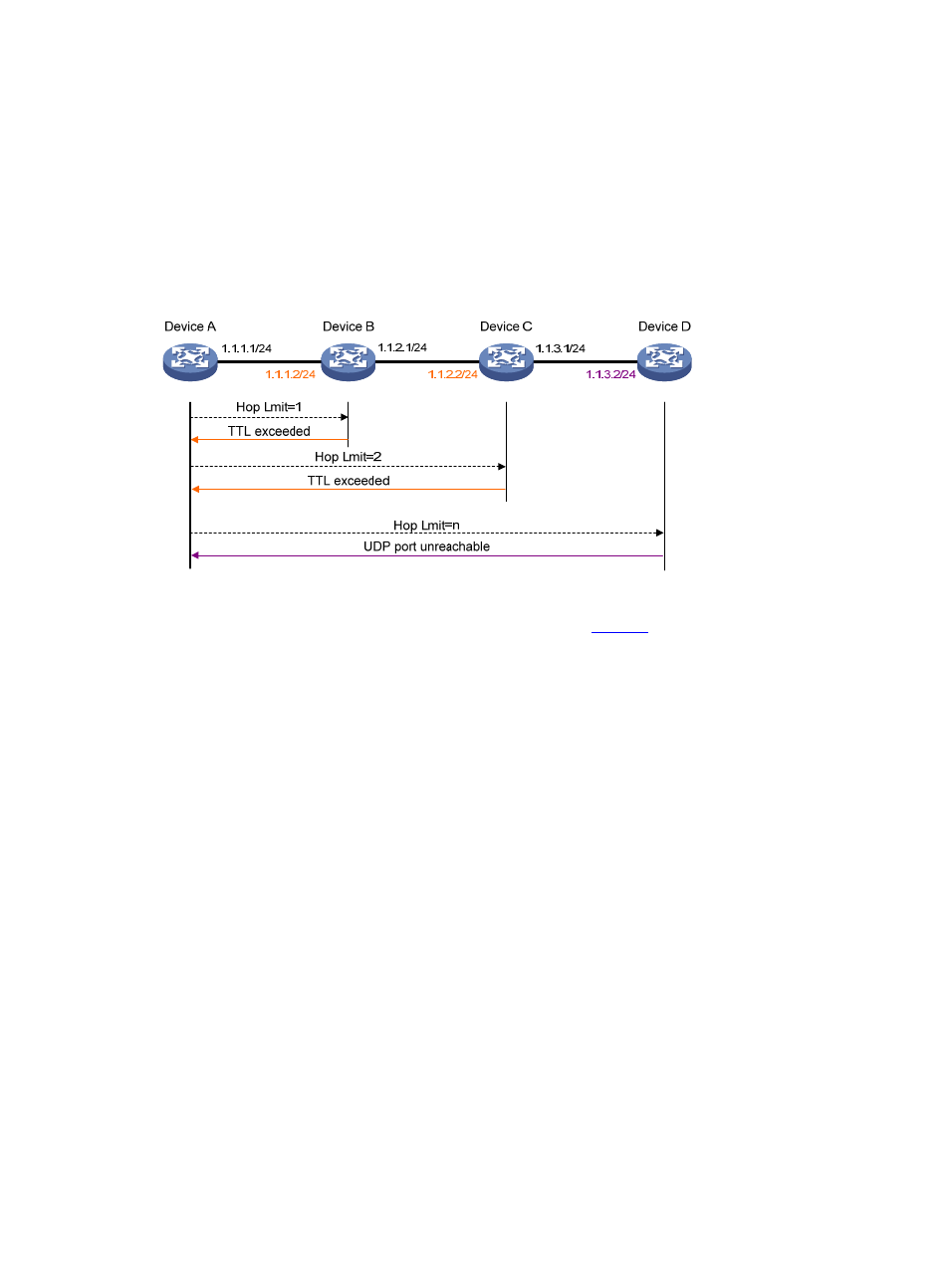
Figure 2 Tracert diagram
The tracert function is implemented through ICMP, as shown in
:
1.
The source (Device A) sends a packet with a TTL value of 1 to the destination (Device D). The UDP
port of the packet is a port number that will not be used by any application of the destination.
2.
The first hop (Device B) (the Layer 3 device that first receives the packet) responds by sending a
TTL-expired ICMP error message to the source, with its IP address 1.1.1.2 encapsulated. In this
way, the source device can get the address (1.1.1.2) of the first Layer 3 device.
3.
The source device sends a packet with a TTL value of 2 to the destination device.
4.
The second hop (Device C) responds with a TTL-expired ICMP error message, which gives the
source device the address (1.1.2.2) of the second Layer 3 device.
5.
The above process continues until the ultimate destination device is reached. No application of the
destination uses this UDP port. Therefore, the destination replies a port unreachable ICMP error
message with the destination IP address 1.1.3.2.
6.
When the source device receives the port unreachable ICMP error message, it knows that the
packet has reached the destination, and it can get the addresses of all the Layer 3 devices involved
to get to the destination device (1.1.1.2, 1.1.2.2, 1.1.3.2).
Configuring Tracert
Configuration prerequisites
•
Enable sending of ICMP timeout packets on the intermediate device (the device between the source
and destination devices). If the intermediate device is an H3C device, execute the ip ttl-expires
enable command on the device. For more information about this command, see IP Performance
Optimization Commands in the IP Services Volume.
