Sink clock tree, Sink clock tree -24 – Altera DisplayPort MegaCore Function User Manual
Page 60
Bit
Signal
Comments
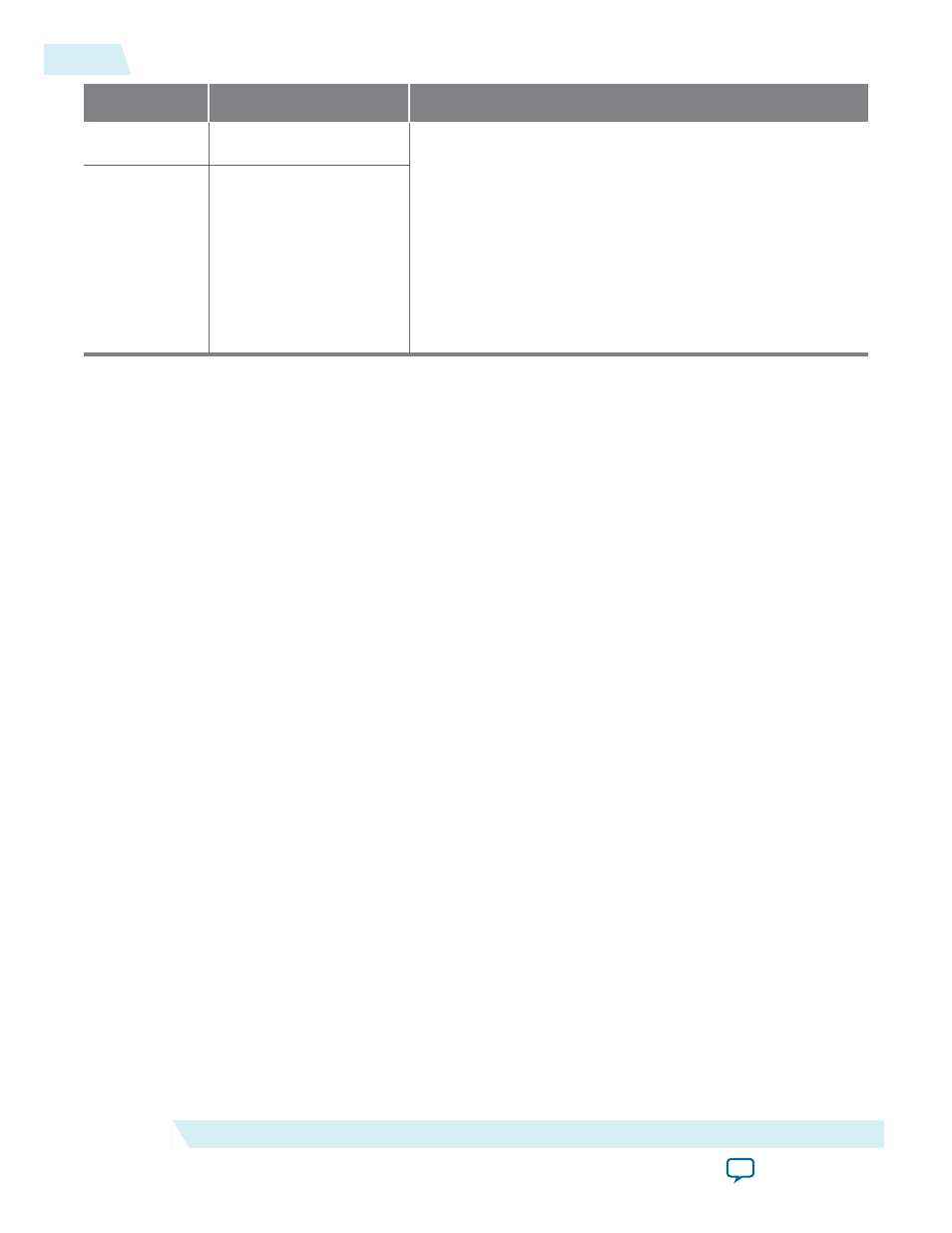
15:8
msa_MISC0[7:0]
The
MISC0[7:1]
and
MISC1[7]
fields indicate the color
encoding format. The color depth is indicated in
MISC0[7:5]
:
• 000 - 6 bpc
• 001 - 8 bpc
• 010 - 10 bpc
• 011 - 12 bpc
• 100 - 16 bpc
For details about the encoding format, refer to the Display‐
Port v1.2 specification.
7:0
msa_MISC1[7:0]
Sink Clock Tree
The IP core receives DisplayPort serial data across the high-speed serial interface (HSSI). The HSSI
requires a 135 MHz clock for correct data locking. You can supply this frequency to the HSSI using a
reference clock provided by an Altera PLL or pins. .
The IP core synchronizes HSSI 20- or 40-bit data to a single HSSI[0] clock that clocks the data into the
DisplayPort front-end decoder.
• If you select dual symbol mode, this clock is equal to the link rate divided by 20 (270, 135, or 81 MHz).
• If you turn on quad symbol mode, this clock is equal to the link rate divided by 40 (135, 67.5, or 40.5
MHz).
The IP core crosses the reconstructed pixel data into a local pixel clock (
rxN_vid_clk
) through an output
DCFIFO, which drives the pixel stream output. The
rxN_vid_clk
must be higher than or equal to the
pixel clock in the up-stream source. If
rxN_vid_clk
is slower than the up-stream pixel clock, the DCFIFO
overflows. If the
rxN_vid_clk
is faster than the up-stream source pixel clock, the output port experiences
a de-assertion of the valid port on cycles in which pixel data is not available. The optimum frequency is
the exact clock rate in the up-stream source. You require pixel clock recovery techniques to determine this
clock frequency.
Secondary stream data is clocked by
rx_ss_clk
. The sink IP core also requires a 16-MHz clock (
aux_clk
)
to drive the internal AUX controller and an Avalon clock for the Avalon-MM interface (
clk
).
5-24
Sink Clock Tree
UG-01131
2015.05.04
Altera Corporation
DisplayPort Sink
