Altera DDR SDRAM High-Performance Controllers and ALTMEMPHY IP User Manual
Page 85
Chapter 5: Functional Description—ALTMEMPHY
5–39
PHY-to-Controller Interfaces
June 2011
Altera Corporation
External Memory Interface Handbook Volume 3
Section I. DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controllers with ALTMEMPHY IP User Guide
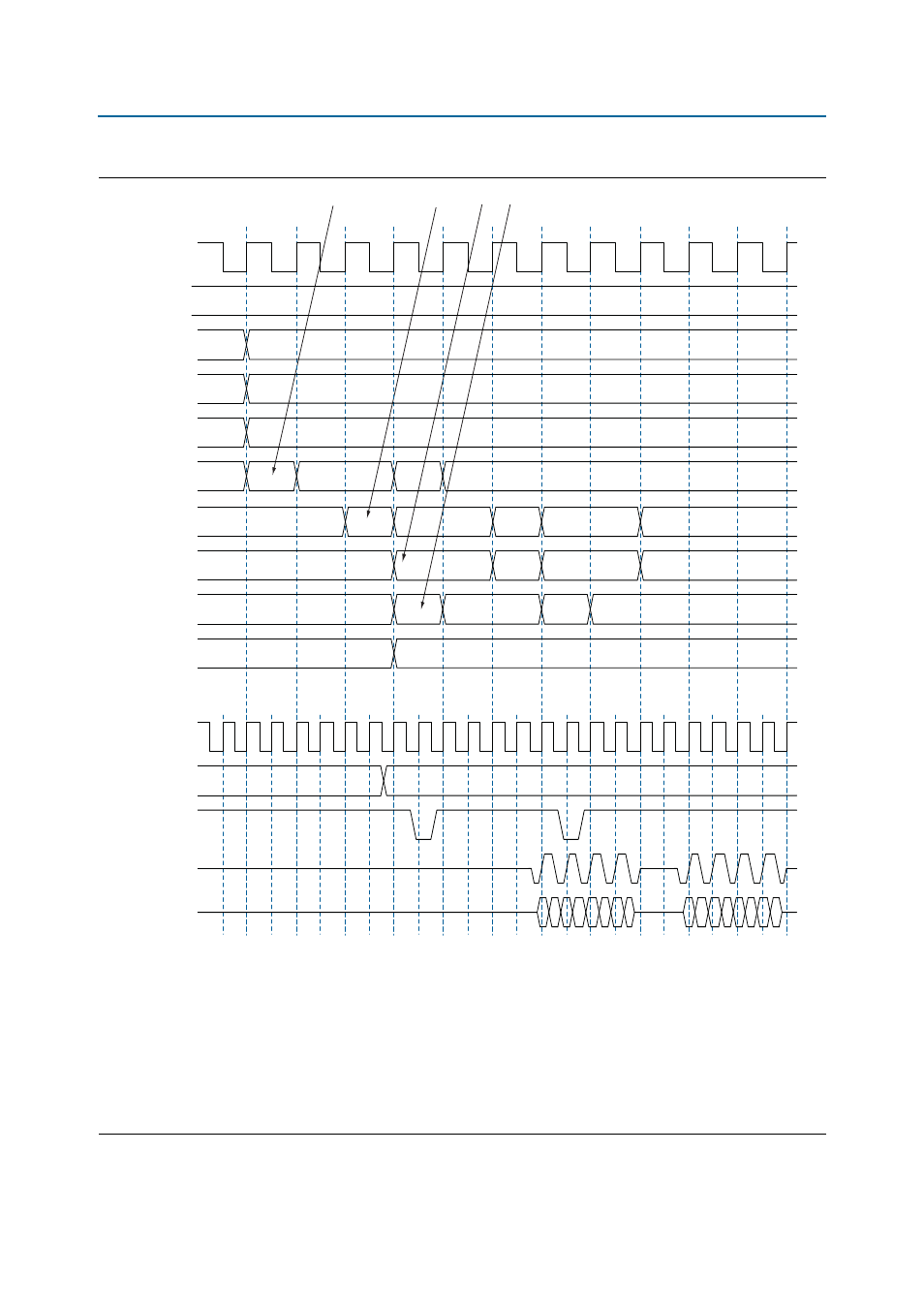
Figure 5–17. Word-Aligned Writes
Notes to
Figure 5–17
:
(1) To show the even alignment of ctl_cs_n, expand the signal (this convention applies for all other signals).
(2) The ctl_dqs_burst must go high one memory clock cycle before ctl_wdata_valid. Compare with the word-unaligned case.
(3) The ctl_wdata_valid is asserted two ctl_wlat controller clock (ctl_clk) cycles after chip select (ctl_cs_n) is asserted. The ctl_wlat
indicates the required write latency in the system. The value is determined during calibration and is dependant upon the relative delays in the
address and command path and the write datapath in both the PHY and the external DDR SDRAM subsystem. The controller must drive ctl_cs_n
and then wait ctl_wlat (two in this example) ctl_clks before driving ctl_wdata_valid.
(4) Observe the ordering of write data (ctl_wdata). Compare this to data on the mem_dq signal.
(5) In all waveforms a command record is added that combines the memory pins ras_n, cas_n and we_n into the current command that is issued.
This command is registered by the memory when chip select (mem_cs_n) is low. The important commands in the presented waveforms are WR
= write, ACT = activate.
ctl_clk
(4)
(2)
(1)
ctl_wlat
ctl_ras_n
ctl_cas_n
ctl_we_n
ctl_cs_n
ctl_dqs_burst
ctl_wdata_valid
ctl_wdata
ctl_addr
Memory
Interface
mem_clk
command
(Note 5)
mem_cs_n
mem_dqs
mem_dq
(3)
00
00
11
2
11
11
00
11
11
00
11
11
01
11
01
11
00
00
10
11
10
11
00
00
00
11
00
11
00000000
00000000
03020100
07060504
0b0a0908
0f0e0d0c
00000000
00000000
0020008
ACT
ACT
WR
