Altera DDR SDRAM High-Performance Controllers and ALTMEMPHY IP User Manual
Page 124
7–2
Chapter 7: Latency
External Memory Interface Handbook Volume 3
June 2011
Altera Corporation
Section I. DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controllers with ALTMEMPHY IP User Guide
The latency for the high-performance controller II comprises many different stages of
the memory interface.
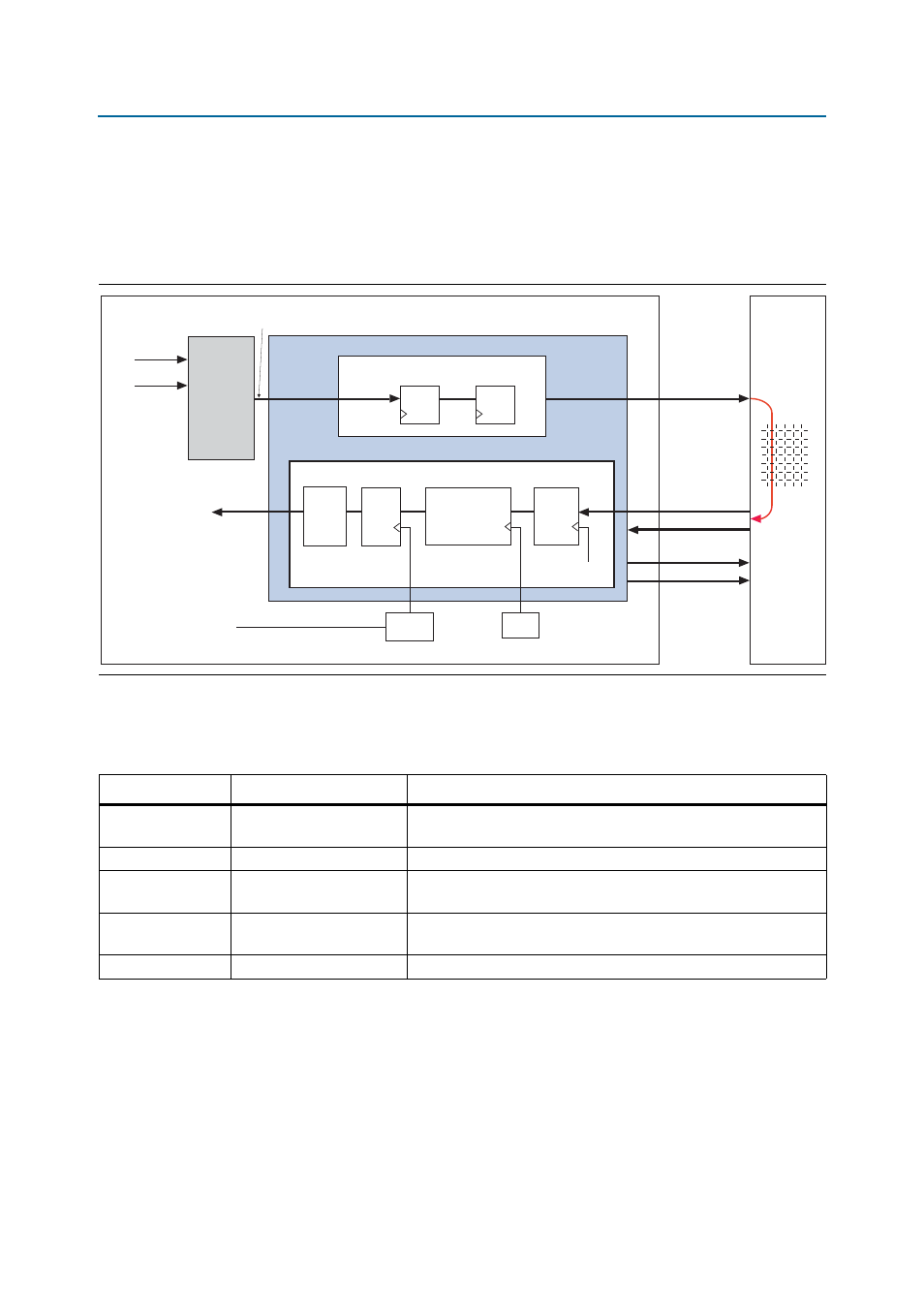
Figure 7–1 on page 7–2
shows a typical memory interface read
latency path showing read latency from the time a local_read_req signal assertion is
detected by the controller up to data available to be read from the dual-port RAM
(DPRAM) module.
Table 7–1
shows the different stages that make up the whole read and write latency
that
Figure 7–1
shows.
From
Figure 7–1
, the read latency in the high-performance controllers is made up of
four components:
read latency = controller latency (T1) + command output latency (T2) +
CAS latency (T3) + PHY read data input latency (T4)
Figure 7–1. Typical Latency Path
Shifted
DQS Clk
High-
Performance
Controller
PLL
phy_clk
local_rdata
local_read_req
control_doing_rd
PLL
0° or 180°
PHY
FPGA Device
Memory Device
Latency T3
(includes CAS
latency)
Latency T1
local_addr
mem_cs_n
mem_dq [ ]
mem_dqs [ ]
Latency T2
Address/Command Generation
Core
I/O
Alignment and
Synchronization
Capture
Shifted
DQS Clock
Resynchronization
Clock
Half-
rate
DPRAM
Read Datapath
Latency T4
mem_clk [ ]
mem_clk_n [ ]
Table 7–1. High-Performance Controller Latency Stages and Descriptions
Latency Number
Latency Stage
Description
T1
Controller
local_read_req
or local_write_req signal assertion to
ddr_cs_n
signal assertion.
T2
Command Output
ddr_cs_n
signal assertion to mem_cs_n signal assertion.
T3
CAS or WL
Read command to DQ data from the memory or write command to DQ
data to the memory.
T4
ALTMEMPHY
read data input
Read data appearing on the local interface.
T2 + T3
Write data latency
Write data appearing on the memory interface.
