Partial bursts, Partial bursts –8 – Altera DDR SDRAM High-Performance Controllers and ALTMEMPHY IP User Manual
Page 102
6–8
Chapter 6: Functional Description—High-Performance Controller II
Controller Features Descriptions
External Memory Interface Handbook Volume 3
June 2011
Altera Corporation
Section I. DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controllers with ALTMEMPHY IP User Guide
2. Upon receiving a return data from the memory for the particular address, the ECC
logic decodes the data, checks for errors, and then merges the corrected or correct
dataword with the incoming information.
3. The ECC logic issues a write to write back the updated data and the new ECC
code.
The following corner cases can occur:
■
A single-bit error during the read phase of the read-modify-write process. In this
case, the IP core corrects the single-bit error first, increments the single-bit error
counter and then performs a partial write to this corrected decoded data word.
■
A double-bit error during the read phase of the read-modify-write process. In this
case, the IP core increments the double-bit error counter and issues an interrupt.
The IP core writes a new write word to the location of the error. The ECC status
register keeps track of the error information.
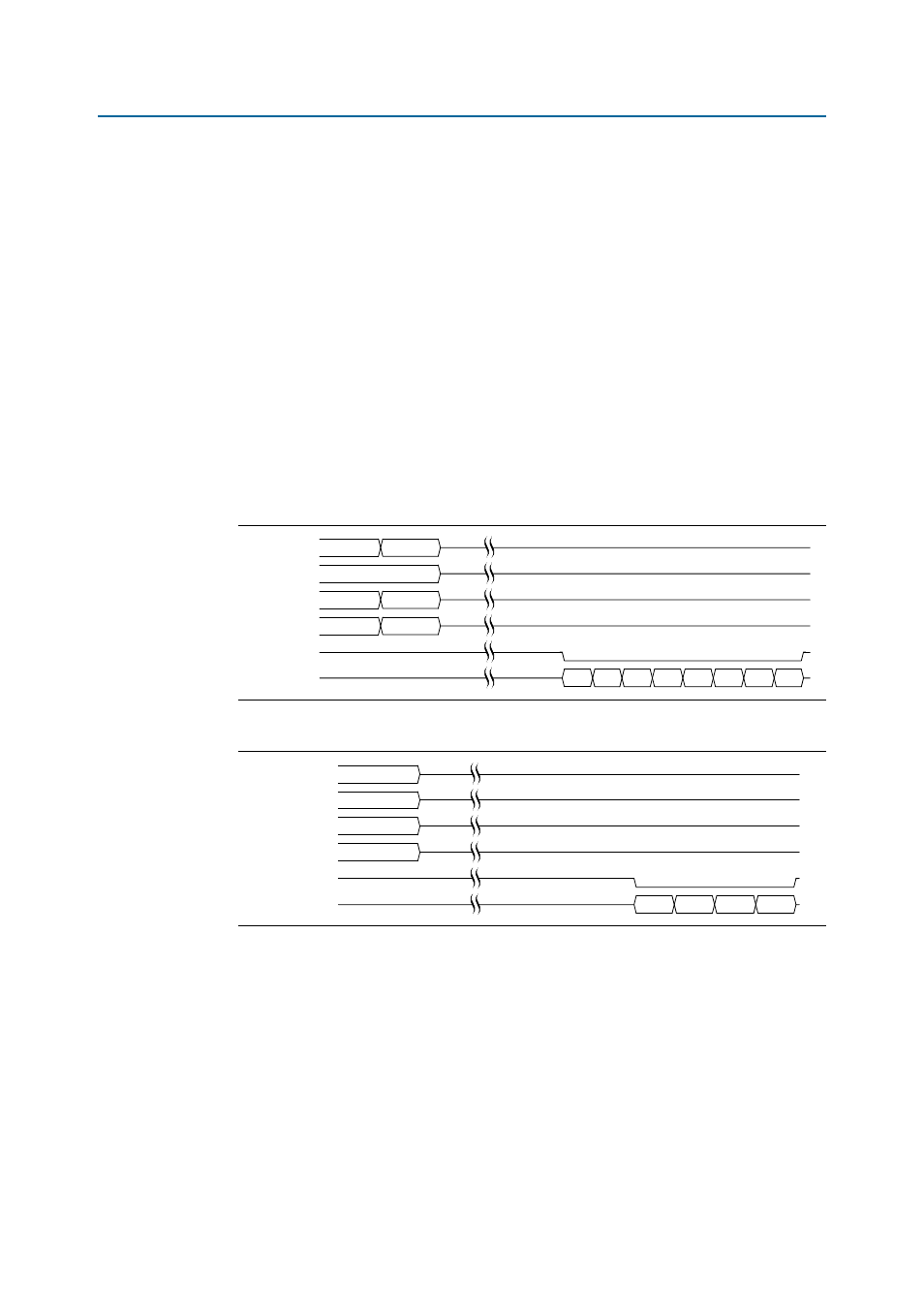
Figure 6–3
and
Figure 6–4
show partial write operations for the controller, for full and
half rate configurations, respectively.
Partial Bursts
DIMMs that do not have the DM pins do not support partial bursts. You must write a
minimum (or multiples) of memory-burst-length-equivalent words to the memory at
the same time.
Figure 6–3. Partial Write for the Controller—Full Rate
Figure 6–4. Partial Write for the Controller—Half Rate
local_address
local_size
local_be
local_wdata
mem_dm
mem_dq
0
1
2
X1
XF
01234567
89ABCDEF
67
R
R
R
EF
CD
AB
89
local_address
local_size
local_be
local_wdata
mem_dm
mem_dq
0
1
X1
01234567
67
R
R
R
