Ident, Figure 46-1 – Cisco ASA 5505 User Manual
Page 950
46-4
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Configuration Guide using the CLI
Chapter 46 Configuring Inspection for Management Application Protocols
GTP Inspection
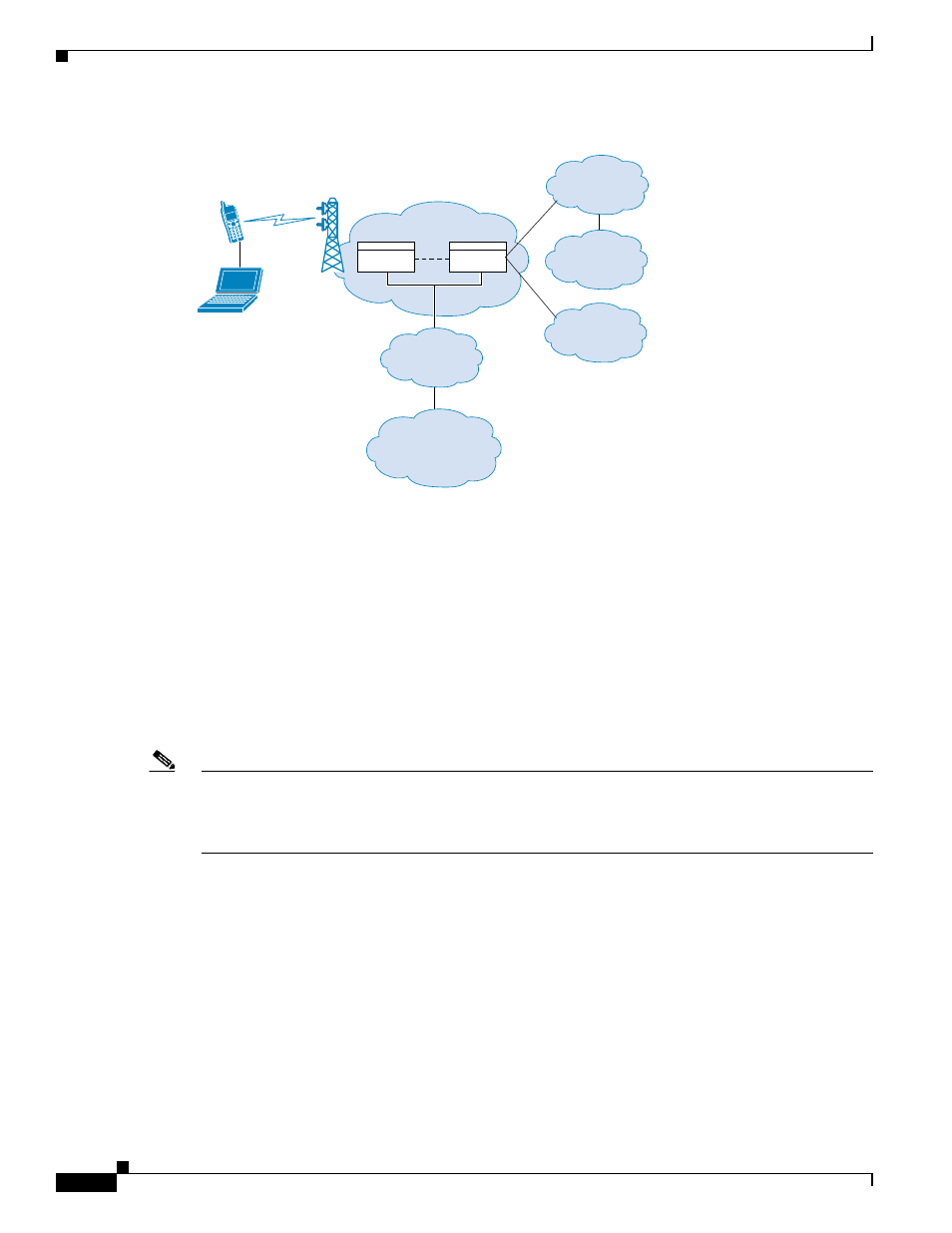
Figure 46-1
GPRS Tunneling Protocol
The UMTS is the commercial convergence of fixed-line telephony, mobile, Internet and computer
technology. UTRAN is the networking protocol used for implementing wireless networks in this system.
GTP allows multi-protocol packets to be tunneled through a UMTS/GPRS backbone between a GGSN,
an SGSN and the UTRAN.
GTP does not include any inherent security or encryption of user data, but using GTP with the ASA helps
protect your network against these risks.
The SGSN is logically connected to a GGSN using GTP. GTP allows multiprotocol packets to be
tunneled through the GPRS backbone between GSNs. GTP provides a tunnel control and management
protocol that allows the SGSN to provide GPRS network access for a mobile station by creating,
modifying, and deleting tunnels. GTP uses a tunneling mechanism to provide a service for carrying user
data packets.
Note
When using GTP with failover, if a GTP connection is established and the active unit fails before data
is transmitted over the tunnel, the GTP data connection (with a “j” flag set) is not replicated to the
standby unit. This occurs because the active unit does not replicate embryonic connections to the standby
unit.
Configuring a GTP Inspection Policy Map for Additional Inspection Control
If you want to enforce additional parameters on GTP traffic, create and configure a GTP map. If you do
not specify a map with the inspect gtp command, the ASA uses the default GTP map, which is
preconfigured with the following default values:
•
request-queue 200
•
timeout gsn 0:30:00
•
timeout pdp-context 0:30:00
•
timeout request 0:01:00
119935
Internet
Corporate
network 2
Corporate
network 1
Home PLMN
Gn
Gp
GRX
Roaming partner
(visited PLMN)
MS
SGSN
GGSN Gi
