Managing security contexts – Cisco ASA 5505 User Manual
Page 223
5-23
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Configuration Guide using the CLI
Chapter 5 Configuring Multiple Context Mode
Changing Between Contexts and the System Execution Space
Detailed Steps
Changing Between Contexts and the System Execution Space
If you log in to the system execution space (or the admin context using Telnet or SSH), you can change
between contexts and perform configuration and monitoring tasks within each context. The running
configuration that you edit in a configuration mode, or that is used in the copy or write commands,
depends on your location. When you are in the system execution space, the running configuration
consists only of the system configuration; when you are in a context, the running configuration consists
only of that context. For example, you cannot view all running configurations (system plus all contexts)
by entering the show running-config command. Only the current configuration displays.
To change between the system execution space and a context, or between contexts, see the following
commands:
Managing Security Contexts
This section describes how to manage security contexts and includes the following topics:
•
Removing a Security Context, page 5-24
•
Changing the Admin Context, page 5-24
•
Changing the Security Context URL, page 5-25
•
Reloading a Security Context, page 5-26
Command
Purpose
mac-address auto
[prefix prefix]
Example:
hostname(config)# mac-address auto prefix
19
Automatically assign private MAC addresses to each context interface.
The prefix is a decimal value between 0 and 65535. This prefix is converted
to a 4-digit hexadecimal number, and used as part of the MAC address. The
prefix ensures that each ASA uses unique MAC addresses, so you can have
multiple ASAs on a network segment, for example. See the
section for more information about how the prefix is used.
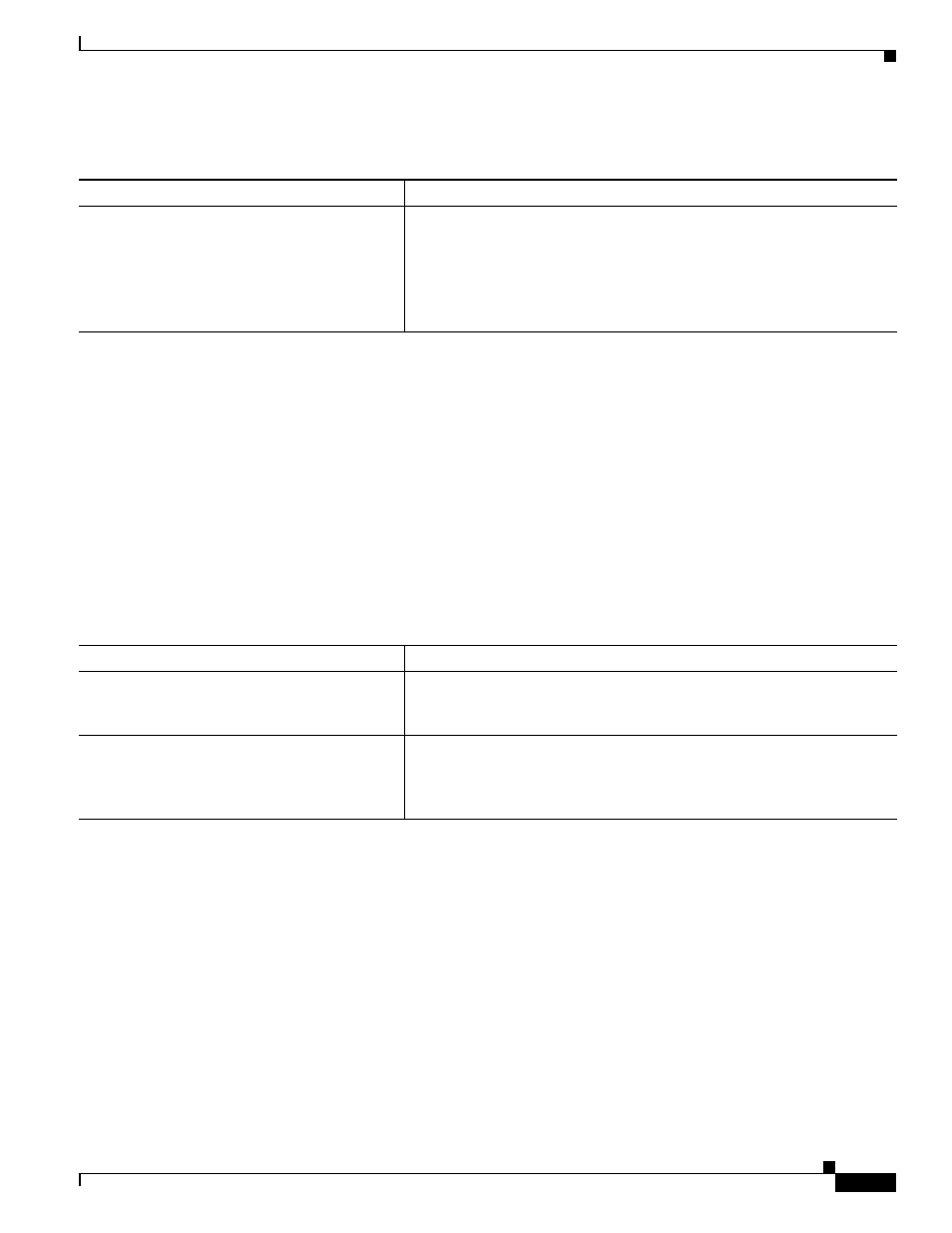
Command
Purpose
changeto context
name
Changes to a context. The prompt changes to the following:
hostname/name#
changeto system
Changes to the system execution space. The prompt changes to the
following:
hostname#
