Nat interfaces, Routing nat packets – Cisco ASA 5505 User Manual
Page 575
29-21
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Configuration Guide using the CLI
Chapter 29 Information About NAT
NAT Interfaces
The resultant ordering would be:
192.168.1.1/32 (static)
10.1.1.0/24 (static)
192.168.1.0/24 (static)
172.16.1.0/24 (dynamic) (object abc)
172.16.1.0/24 (dynamic) (object def)
192.168.1.0/24 (dynamic)
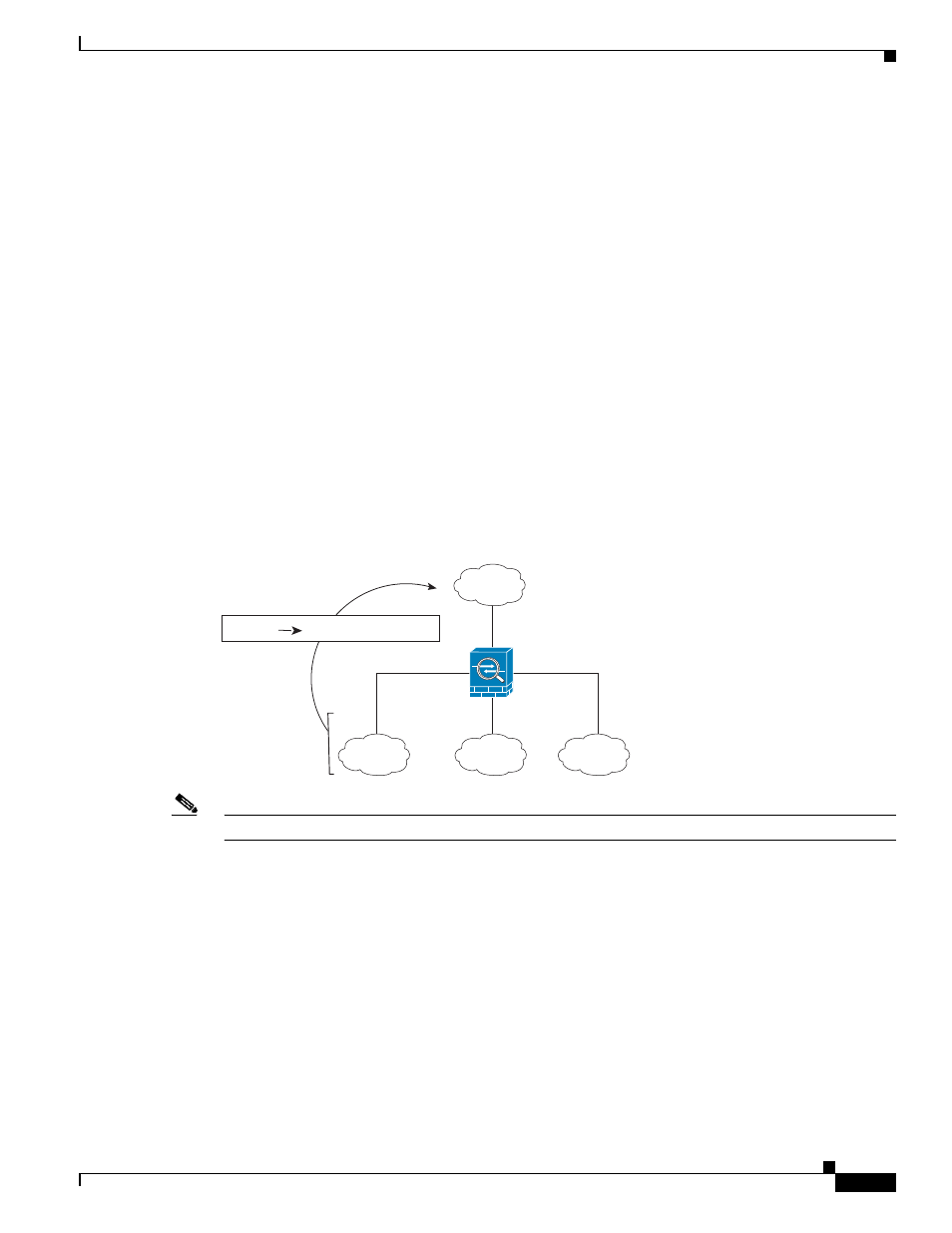
NAT Interfaces
You can configure a NAT rule to apply to any interface (in other words, all interfaces), or you can identify
specific real and mapped interfaces. You can also specify any interface for the real address, and a specific
interface for the mapped address, or vice versa.
For example, you might want to specify any interface for the real address and specify the outside
interface for the mapped address if you use the same private addresses on multiple interfaces, and you
want to translate them all to the same global pool when accessing the outside (
Figure 29-19
Specifying Any Interface
Note
For transparent mode, you must choose specific source and destination interfaces.
Routing NAT Packets
The ASA needs to be the destination for any packets sent to the mapped address. The ASA also needs to
determine the egress interface for translated packets. This section describes how the ASA handles
accepting and delivering packets with NAT, and includes the following topics:
•
Mapped Addresses and Routing, page 29-22
•
Transparent Mode Routing Requirements for Remote Networks, page 29-24
•
Determining the Egress Interface, page 29-24
Outside
Mktg
10.1.2.0
10.1.2.0
10.1.2.0
Security
Appliance
Eng
HR
10.1.2.0
209.165.201.1:xxxx
any
24
8
76
8
