Passing traffic through the asa – Cisco ASA 5505 User Manual
Page 1861
82-5
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Configuration Guide using the CLI
Chapter 82 Troubleshooting
Testing Your Configuration
Figure 82-3
Ping Failure Because of IP Addressing Problems
Step 3
Ping each ASA interface from a remote host. For transparent mode, ping the management IP address.
This test checks whether the directly connected router can route the packet between the host and the
ASA, and whether the ASA can correctly route the packet back to the host.
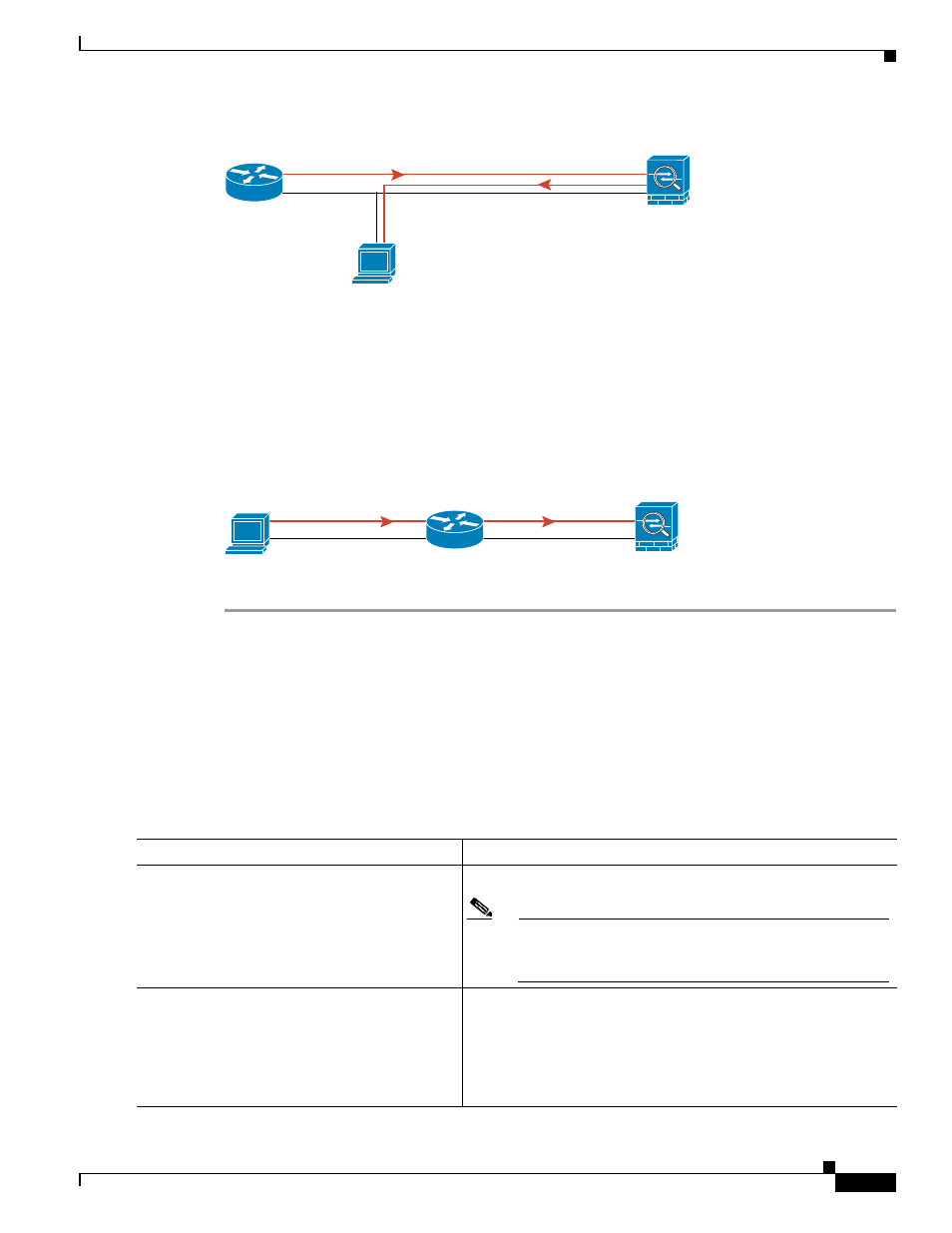
A ping might fail if the ASA does not have a return route to the host through the intermediate router (see
). In this case, the debugging messages show that the ping was successful, but syslog
message 110001 appears, indicating a routing failure.
Figure 82-4
Ping Failure Because the Security Appliance has No Return Route
Passing Traffic Through the ASA
After you successfully ping the ASA interfaces, make sure that traffic can pass successfully through the
ASA. For routed mode, this test shows that NAT is operating correctly, if configured. For transparent
mode, which does not use NAT, this test confirms that the ASA is operating correctly. If the ping fails in
transparent mode, contact the Cisco TAC.
To ping between hosts on different interfaces, perform the following steps:
192.168.1.1
192.168.1.2
192.168.1.2
Ping
Router
Security
Appliance
Host
126696
Ping
Router
Host
?
Security
Appliance
126693
Command
Purpose
Step 1
access-list ICMPACL
extended permit icmp
any any
Example:
hostname(config)# access-list ICMPACL
extended permit icmp any any
Adds an access list to allow ICMP traffic from any source host.
Note
By default, when hosts access a lower security interface,
all traffic is allowed through. However, to access a higher
security interface, you need the preceding access list.
Step 2
access-group ICMPACL
in interface
interface_name
Example:
hostname(config)# access-group ICMPACL in
interface inside
Assigns the access list to each source interface. Repeat this
command for each source interface.
